Python| Pandas Series.tz_localize
Python是一种用于进行数据分析的出色语言,主要是因为以数据为中心的Python包的奇妙生态系统。 Pandas就是其中之一,它使导入和分析数据变得更加容易。
Pandas 系列是带有轴标签的一维 ndarray。标签不必是唯一的,但必须是可散列的类型。该对象支持基于整数和基于标签的索引,并提供了许多用于执行涉及索引的操作的方法。
Pandas Series.tz_localize()函数用于将 Series 或 DataFrame 的 tz-naive 索引本地化到目标时区。此操作本地化索引。为了本地化时区朴素系列中的值,我们可以使用 Series.dt.tz_localize()。
Syntax: Series.tz_localize(tz, axis=0, level=None, copy=True, ambiguous=’raise’, nonexistent=’raise’)
Parameter :
tz : string or pytz.timezone object
axis : the axis to localize
level : If axis ia a MultiIndex, localize a specific level. Otherwise must be None
copy : Also make a copy of the underlying data
ambiguous : ‘infer’, bool-ndarray, ‘NaT’, default ‘raise’
nonexistent : str, default ‘raise’
Returns : Series or DataFrame
示例 #1:使用Series.tz_localize()函数将给定系列的时区朴素索引本地化到目标时区。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', 'Lisbon', 'Rio', 'Moscow'])
# Create the Datetime Index
didx = pd.DatetimeIndex(start ='2014-08-01 10:00', freq ='W',
periods = 6)
# set the index
sr.index = didx
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 : 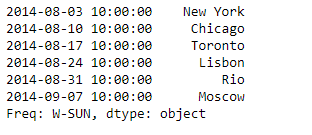
现在我们将使用Series.tz_localize()函数将给定的时区朴素索引本地化为时区感知索引。目标时区是“美国/中部”。
# Localize to 'US / Central'
sr.tz_localize('US/Central')
输出 : 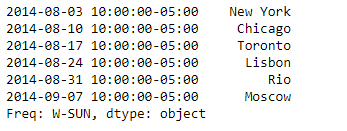
正如我们在输出中看到的, Series.tz_localize()函数已将给定的原始时区索引转换为时间感知索引。示例 #2:使用Series.tz_localize()函数将给定系列的时区朴素索引本地化到目标时区。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series([19.5, 16.8, 22.78, 20.124, 18.1002])
# Create the Datetime Index
didx = pd.DatetimeIndex(start ='2014-08-01 10:00', freq ='W',
periods = 5)
# set the index
sr.index = didx
# Print the series
print(sr)
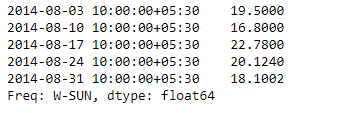
输出 : 
现在我们将使用Series.tz_localize()函数将给定的时区朴素索引本地化为时区感知索引。目标时区是“亚洲/加尔各答”。
# Localize to 'Asia/Calcutta'
sr.tz_localize('Asia/Calcutta')
输出 :