求 tan 30° 的值
三角学是处理三角形边与角关系的数学分支。用三角法很容易找到大山或塔的高度,在天文学中也很容易找到恒星或行星之间的距离,广泛用于物理学、建筑学和 GPS 导航系统。
三角学的原理是“如果两个三角形的角相同,那么它们的边的比例相同”。边长可以不同,但边长比相同。
三角函数
三角函数也称为圆函数或三角比。角度和边的关系由这些三角函数表示。有六个三角函数正弦,余弦,正切,余割,正割,余切。
- Sin = 垂直/斜边
- Cos = 基数/斜边
- 棕褐色 = 垂直/底部
- 婴儿床 = 底座/垂直
- 秒 = 斜边/底
- Cosec = 斜边/垂直
垂直、底边和斜边是直角三角形的三个边。让我们详细了解这些术语,
- 垂直- 角度前面的边是垂直的。在这种情况下, 30°前面的边称为它的垂线。
- 底边——底边是与角接触的边之一,但斜边永远不能被视为底边。
- 什么是斜边-与直角(90°)相对的边称为斜边,它是最长的边。
Note: Perpendicular and base are not fixed for a triangle. In a triangle, a side is perpendicular for an angle, but the same side is a base for another angle.
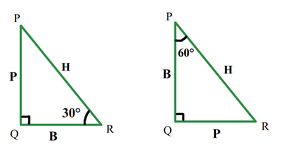
如上图所示,对于同一个三角形,如果考虑角度 30°,垂直边是边 PQ,但如果我们考虑角度 60°,我们的垂直边是边 QR。
求 tan 30° 的值。
解决方案:
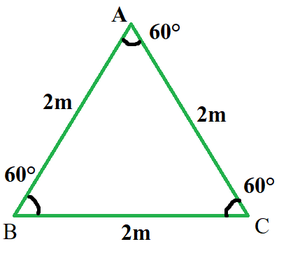
To calculate tan 30°, take ratios of its perpendicular and its base. For which calculate the length of perpendicular and base. To find lengths of sides we take the help of an equilateral triangle.
- Take an equilateral triangle of side length 2m.
- Now from any vertex draw an altitude.
- The altitude drawn divides the equilateral triangle into two right triangles.
- Now we have a length of two sides in the right triangle.
- The third side is calculated by baudhayan theorem or Pythagoras theorem.
Altitude in equilateral triangle bisect the angle and the side, So angle DAC is 30° and side DC is 1m.
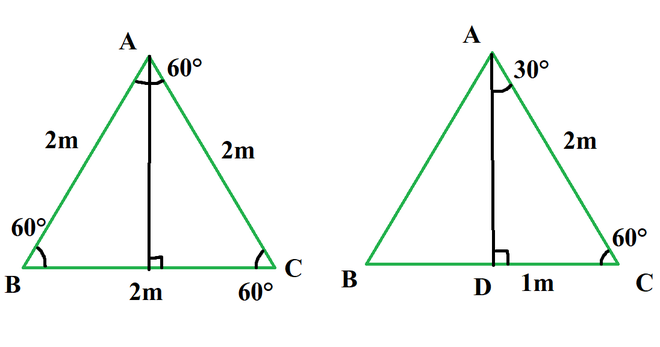
Let the length of side AD is x.
Applying Pythagoras theorem in triangle ADC.
P2 + B2 = H2
AD2 + DC2 = AC2
x2 + 12 = 22
x2 + 1 = 4
x2 = 3
x = √3
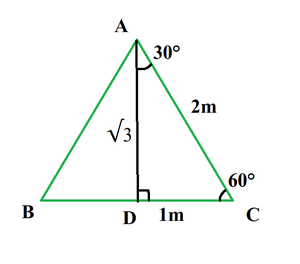
So, tan 30° = DC/AD
Tan30° = 1/√3
一旦在所有方面都进行了计算,还可以找到其他三角比,例如:
- 正弦 30° = 1/2
- 余弦 30° = √3/2
示例问题
问题1:直角三角形,一个角是30°,30°的底边是3m。求垂线的长度。
解决方案:
Given: Base = 3m
Tan 30 = 1/√3
P/B = 1/√3
P/3 = 1/√3
p = √3
问题2:直角三角形的斜边是20cm,一边是10√3cm,求三角形的角。
解决方案:
Given: H = 20, and B = 10√3
Finding third side using pythagoras theorem.
P2 + B2 = H2
P2 + (10√3)2 = 202
p2 + 300 = 400
P2 = 100
p = 10
The third side is 10cm. The ratio of the two sides 10cm and 10√3cm is 1/√3, So there must be an angle of 30° in triangle Since the triangle is a right angle, so the third angle is
90° – 30° = 60°
The Angles of a triangle are 30°, 60°, 90°.