在Java中传递和返回对象
尽管Java严格按值传递,但传递原始类型或引用类型的确切效果不同。当我们将原始类型传递给方法时,它是按值传递的。但是当我们将一个对象传递给一个方法时,情况会发生巨大的变化,因为对象是通过有效的引用调用来传递的。 Java做了一件有趣的事情,它是值传递和引用传递之间的混合体。
基本上,函数函数通过调用其中的某些方法来要求参数更改自身。
- 在创建类类型的变量时,我们只创建对对象的引用。因此,当我们将此引用传递给方法时,接收它的参数将引用与参数引用的对象相同的对象。
- 这实际上意味着对象的行为就像它们通过引用调用传递给方法一样。
- 对方法内对象的更改确实反映了用作参数的对象。
说明:让我们假设创建了三个对象“ob1”、“ob2”和“ob3”:
ObjectPassDemo ob1 = new ObjectPassDemo(100, 22);
ObjectPassDemo ob2 = new ObjectPassDemo(100, 22);
ObjectPassDemo ob3 = new ObjectPassDemo(-1, -1);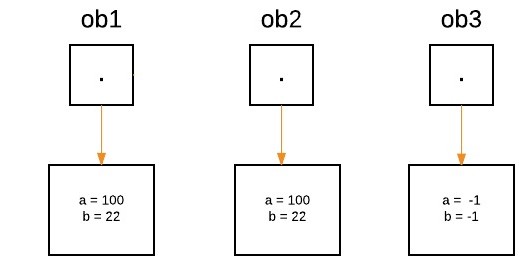
在方法方面,声明了名称为 a 的 Foo 类型的引用,并且最初将其分配为 null。
boolean equalTo(ObjectPassDemo o);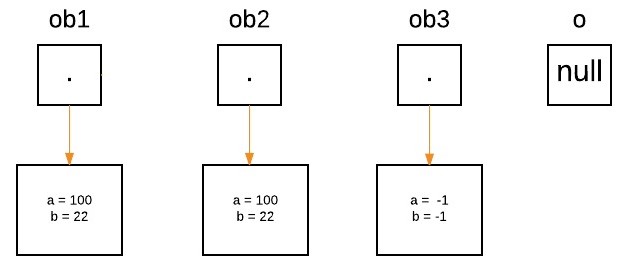
当我们调用equalTo方法时,引用'o'将被分配给作为参数传递的对象,即'o'将引用'ob2'作为以下语句执行。
System.out.println("ob1 == ob2: " + ob1.equalTo(ob2));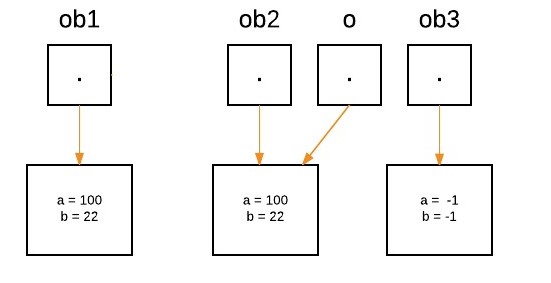
现在我们可以看到,在 'ob1' 上调用了 equalTo 方法,而 'o' 指的是 'ob2'。由于两个引用的 'a' 和 'b' 的值相同,因此 if(condition) 为真,因此将返回布尔值 true。
if(o.a == a && o.b == b)再次执行以下语句时,'o' 将重新分配给 'ob3'。
System.out.println("ob1 == ob3: " + ob1.equalTo(ob3));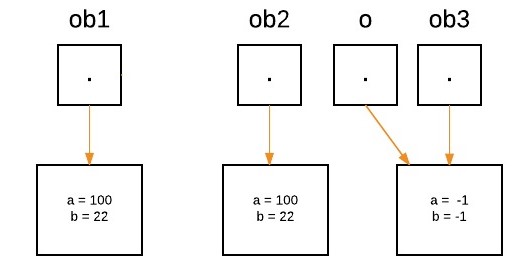
- 现在我们可以看到,equalTo 方法在 'ob1' 上被调用,而 'o' 指的是 'ob3'。由于两个引用的 'a' 和 'b' 的值不同,所以 if(condition) 为 false,所以 else 块将执行,并返回 false。
在Java中,我们可以将对象传递给方法,如下面的程序所示:
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate Objects Passing to Methods.
// Class
// Helper class
class ObjectPassDemo {
int a, b;
// Constructor
ObjectPassDemo(int i, int j)
{
a = i;
b = j;
}
// Method
boolean equalTo(ObjectPassDemo o)
{
// Returns true if o is equal to the invoking
// object notice an object is passed as an
// argument to method
return (o.a == a && o.b == b);
}
}
// Main class
public class GFG {
// MAin driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating object of above class inside main()
ObjectPassDemo ob1 = new ObjectPassDemo(100, 22);
ObjectPassDemo ob2 = new ObjectPassDemo(100, 22);
ObjectPassDemo ob3 = new ObjectPassDemo(-1, -1);
// Checking whether object are equal as custom
// values
// above passed and printing corresponding boolean
// value
System.out.println("ob1 == ob2: "
+ ob1.equalTo(ob2));
System.out.println("ob1 == ob3: "
+ ob1.equalTo(ob3));
}
}Java
// Java program to Demonstrate One Object to
// Initialize Another
// Class 1
class Box {
double width, height, depth;
// Notice this constructor. It takes an
// object of type Box. This constructor use
// one object to initialize another
Box(Box ob)
{
width = ob.width;
height = ob.height;
depth = ob.depth;
}
// constructor used when all dimensions
// specified
Box(double w, double h, double d)
{
width = w;
height = h;
depth = d;
}
// compute and return volume
double volume() { return width * height * depth; }
}
// MAin class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating a box with all dimensions specified
Box mybox = new Box(10, 20, 15);
// Creating a copy of mybox
Box myclone = new Box(mybox);
double vol;
// Get volume of mybox
vol = mybox.volume();
System.out.println("Volume of mybox is " + vol);
// Get volume of myclone
vol = myclone.volume();
System.out.println("Volume of myclone is " + vol);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate Returning of Objects
// Class 1
class ObjectReturnDemo {
int a;
// Constructor
ObjectReturnDemo(int i) { a = i; }
// Method returns an object
ObjectReturnDemo incrByTen()
{
ObjectReturnDemo temp
= new ObjectReturnDemo(a + 10);
return temp;
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating object of class1 inside main() method
ObjectReturnDemo ob1 = new ObjectReturnDemo(2);
ObjectReturnDemo ob2;
ob2 = ob1.incrByTen();
System.out.println("ob1.a: " + ob1.a);
System.out.println("ob2.a: " + ob2.a);
}
}ob1 == ob2: true
ob1 == ob3: false定义一个将其类的对象作为参数的构造函数
对象参数最常见的用途之一涉及构造函数。通常,在实践中,需要构造一个新对象,以便它最初与某个现有对象相同。为此,我们可以使用 Object.clone() 方法或定义一个构造函数,该构造函数将其类的对象作为参数。
例子
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate One Object to
// Initialize Another
// Class 1
class Box {
double width, height, depth;
// Notice this constructor. It takes an
// object of type Box. This constructor use
// one object to initialize another
Box(Box ob)
{
width = ob.width;
height = ob.height;
depth = ob.depth;
}
// constructor used when all dimensions
// specified
Box(double w, double h, double d)
{
width = w;
height = h;
depth = d;
}
// compute and return volume
double volume() { return width * height * depth; }
}
// MAin class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating a box with all dimensions specified
Box mybox = new Box(10, 20, 15);
// Creating a copy of mybox
Box myclone = new Box(mybox);
double vol;
// Get volume of mybox
vol = mybox.volume();
System.out.println("Volume of mybox is " + vol);
// Get volume of myclone
vol = myclone.volume();
System.out.println("Volume of myclone is " + vol);
}
}
Volume of mybox is 3000.0
Volume of myclone is 3000.0返回对象
在Java中,方法可以返回任何类型的数据,包括对象。例如,在下面的程序中, incrByTen()方法返回一个对象,其中一个(整数变量)的值比调用对象中的值大十。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate Returning of Objects
// Class 1
class ObjectReturnDemo {
int a;
// Constructor
ObjectReturnDemo(int i) { a = i; }
// Method returns an object
ObjectReturnDemo incrByTen()
{
ObjectReturnDemo temp
= new ObjectReturnDemo(a + 10);
return temp;
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating object of class1 inside main() method
ObjectReturnDemo ob1 = new ObjectReturnDemo(2);
ObjectReturnDemo ob2;
ob2 = ob1.incrByTen();
System.out.println("ob1.a: " + ob1.a);
System.out.println("ob2.a: " + ob2.a);
}
}
ob1.a: 2
ob2.a: 12Note: When an object reference is passed to a method, the reference itself is passed by use of call-by-value. However, since the value being passed refers to an object, the copy of that value will still refer to the same object that its corresponding argument does. That’s why we said that java is strictly pass-by-value.