📌 相关文章
- 在C ++中传递和返回对象(1)
- 在C++中传递和返回对象
- 在C ++中传递和返回对象
- 在C++中传递和返回对象(1)
- 在Java中传递和返回对象(1)
- 在Java中传递和返回对象
- 用Java传递和返回对象
- 如何通过 JavaScript 中的函数传递原始/对象类型?
- 如何通过 JavaScript 中的函数传递原始对象类型?(1)
- 如何将数组传递给C C++中的函数(1)
- 如何将数组传递给C / C++中的函数
- 如何将数组传递给C / C++中的函数
- python中的返回对象(1)
- c# 函数返回 - C# (1)
- 如何从Python函数返回一个 json 对象?(1)
- 如何从Python函数返回一个 json 对象?
- 如何在函数c#中返回数组(1)
- 如何在javascript中返回一个对象(1)
- C#|返回对象的方法
- C#|返回对象的方法(1)
- 将数组传递给C中的函数
- C++ 将数组传递给函数
- 数组传递给C中的函数
- C++ 将数组传递给函数(1)
- 将数组传递给C中的函数(1)
- 将数组传递给 c 中的函数 (1)
- 如何使函数返回字符串 c (1)
- 在C++中通过指针传递Vs通过引用传递
- 在C++中通过指针传递Vs通过引用传递
📜 如何通过C++函数传递和返回对象?
📅 最后修改于: 2020-09-25 05:04:30 🧑 作者: Mango
在本教程中,我们将学习在C++编程中将对象传递给函数并从函数返回对象。
在C++编程中,我们可以将对象传递给函数 ,就像传递常规参数一样。
示例1:C++将对象传递给函数
// C++ program to calculate the average marks of two students
#include
using namespace std;
class Student {
public:
double marks;
// constructor to initialize marks
Student(double m) {
marks = m;
}
};
// function that has objects as parameters
void calculateAverage(Student s1, Student s2) {
// calculate the average of marks of s1 and s2
double average = (s1.marks + s2.marks) / 2;
cout << "Average Marks = " << average << endl;
}
int main() {
Student student1(88.0), student2(56.0);
// pass the objects as arguments
calculateAverage(student1, student2);
return 0;
} 输出
Average Marks = 72在这里,我们将两个Student对象student1和student2传递给了calculateAverage() 函数。

示例2:C++从函数返回对象
#include
using namespace std;
class Student {
public:
double marks1, marks2;
};
// function that returns object of Student
Student createStudent() {
Student student;
// Initialize member variables of Student
student.marks1 = 96.5;
student.marks2 = 75.0;
// print member variables of Student
cout << "Marks 1 = " << student.marks1 << endl;
cout << "Marks 2 = " << student.marks2 << endl;
return student;
}
int main() {
Student student1;
// Call function
student1 = createStudent();
return 0;
} 输出
Marks1 = 96.5
Marks2 = 75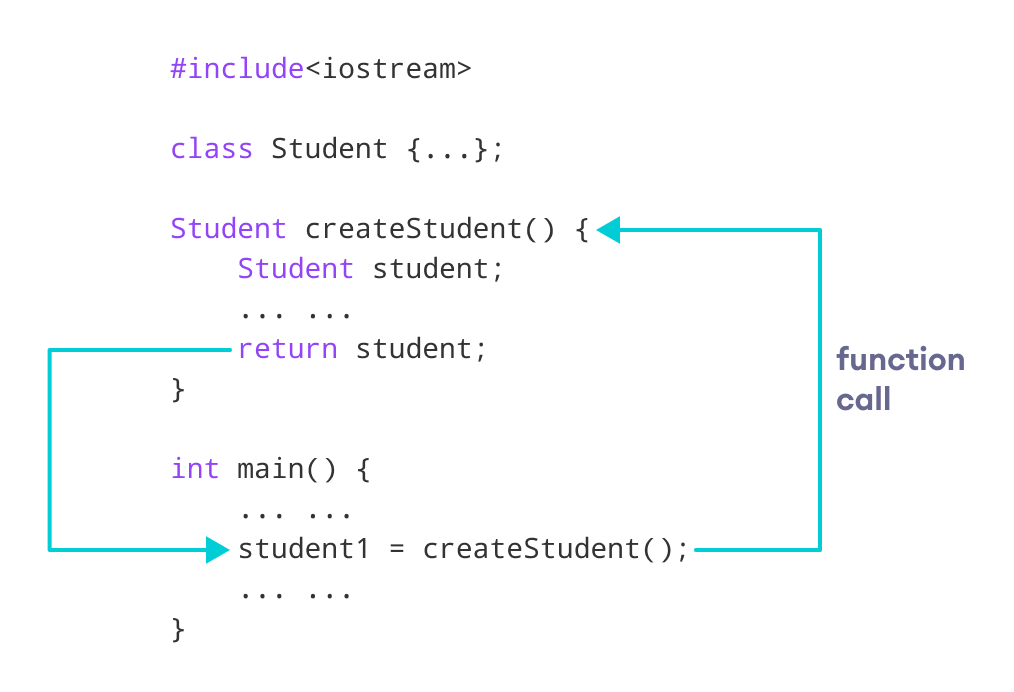
在此程序中,我们创建了一个函数 createStudent() ,该函数返回Student类的对象。
我们从main()方法调用了createStudent() 。
// Call function
student1 = createStudent();在这里,我们将createStudent()方法返回的对象存储在student1 。