给定N元树和整数K ,任务是以级别顺序方式打印树的所有节点的第K个祖先。如果一个节点不存在K个祖先,则为该节点打印-1 。
例子:
Input: K = 2
Output: -1 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Explanation:
2nd ancestor does not exist for nodes 1, 2 and 3
2nd ancestor of nodes 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 is 1.
Input: K = 1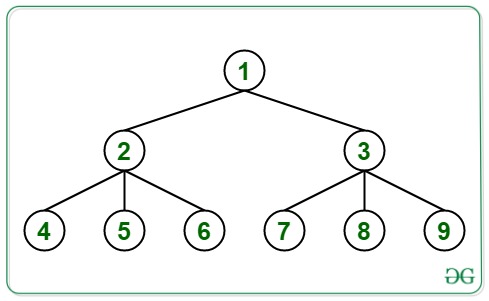
Output: -1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3
方法:方法是使用DFS查找所有节点的祖先。步骤如下:
- 可以使用DFS找到任何节点的第K个父节点,并将节点的所有父节点存储在临时向量temp []中。
- 每当在DFS中访问节点时,都会将其推入临时向量中。
- 在DFS的末尾,将从临时向量中弹出当前访问的节点。
- 对于当前访问的节点,向量包含该节点的所有祖先。
- 向量末端的第K个节点是当前访问的节点的第K个祖先,因此将其存储在ancestor []数组中。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to add an
// edge in the tree
void addEdge(vector v[],
int x, int y)
{
v[x].push_back(y);
v[y].push_back(x);
}
// DFS to find the Kth
// ancestor of every node
void dfs(vector tree[],
vector& temp,
int ancestor[], int u,
int parent, int k)
{
// Pushing current node
// in the vector
temp.push_back(u);
// Traverse its neighbors
for (auto i : tree[u]) {
if (i == parent)
continue;
dfs(tree, temp,
ancestor, i, u, k);
}
temp.pop_back();
// If K ancestors are not
// found for current node
if (temp.size() < k) {
ancestor[u] = -1;
}
else {
// Add the Kth ancestor
// for the node
ancestor[u]
= temp[temp.size() - k];
}
}
// Function to find Kth
// ancestor of each node
void KthAncestor(int N, int K, int E,
int edges[][2])
{
// Building the tree
vector tree[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
addEdge(tree, edges[i][0],
edges[i][1]);
}
// Stores all parents of a node
vector temp;
// Store Kth ancestor
// of all nodes
int ancestor[N + 1];
dfs(tree, temp, ancestor, 1, 0, K);
// Print the ancestors
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
cout << ancestor[i] << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
// Given N and K
int N = 9;
int K = 2;
// Given edges of n-ary tree
int E = 8;
int edges[8][2] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 2, 4 },
{ 2, 5 }, { 2, 6 }, { 3, 7 },
{ 3, 8 }, { 3, 9 } };
// Function Call
KthAncestor(N, K, E, edges);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to add an
// edge in the tree
static void addEdge(Vector v[],
int x, int y)
{
v[x].add(y);
v[y].add(x);
}
// DFS to find the Kth
// ancestor of every node
static void dfs(Vector tree[],
Vector temp,
int ancestor[], int u,
int parent, int k)
{
// Pushing current node
// in the vector
temp.add(u);
// Traverse its neighbors
for(int i : tree[u])
{
if (i == parent)
continue;
dfs(tree, temp,
ancestor, i, u, k);
}
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
// If K ancestors are not
// found for current node
if (temp.size() < k)
{
ancestor[u] = -1;
}
else
{
// Add the Kth ancestor
// for the node
ancestor[u] = temp.get(temp.size() - k);
}
}
// Function to find Kth
// ancestor of each node
static void KthAncestor(int N, int K, int E,
int edges[][])
{
// Building the tree
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector []tree = new Vector[N + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < tree.length; i++)
tree[i] = new Vector();
for(int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
addEdge(tree, edges[i][0],
edges[i][1]);
}
// Stores all parents of a node
Vector temp = new Vector();
// Store Kth ancestor
// of all nodes
int []ancestor = new int[N + 1];
dfs(tree, temp, ancestor, 1, 0, K);
// Print the ancestors
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
System.out.print(ancestor[i] + " ");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given N and K
int N = 9;
int K = 2;
// Given edges of n-ary tree
int E = 8;
int edges[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 },
{ 2, 4 }, { 2, 5 },
{ 2, 6 }, { 3, 7 },
{ 3, 8 }, { 3, 9 } };
// Function call
KthAncestor(N, K, E, edges);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar Python3
# Python3 implementation of
# the above approach
# Function to add an
# edge in the tree
def addEdge(v, x, y):
v[x].append(y)
v[y].append(x)
# DFS to find the Kth
# ancestor of every node
def dfs(tree, temp, ancestor, u, parent, k):
# Pushing current node
# in the vector
temp.append(u)
# Traverse its neighbors
for i in tree[u]:
if (i == parent):
continue
dfs(tree, temp, ancestor, i, u, k)
temp.pop()
# If K ancestors are not
# found for current node
if (len(temp) < k):
ancestor[u] = -1
else:
# Add the Kth ancestor
# for the node
ancestor[u] = temp[len(temp) - k]
# Function to find Kth
# ancestor of each node
def KthAncestor(N, K, E, edges):
# Building the tree
tree = [[] for i in range(N + 1)]
for i in range(E):
addEdge(tree, edges[i][0],
edges[i][1])
# Stores all parents of a node
temp = []
# Store Kth ancestor
# of all nodes
ancestor = [0] * (N + 1)
dfs(tree, temp, ancestor, 1, 0, K)
# Print the ancestors
for i in range(1, N + 1):
print(ancestor[i], end = " ")
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Given N and K
N = 9
K = 2
# Given edges of n-ary tree
E = 8
edges = [ [ 1, 2 ], [ 1, 3 ],
[ 2, 4 ], [ 2, 5 ],
[ 2, 6 ], [ 3, 7 ],
[ 3, 8 ], [ 3, 9 ] ]
# Function call
KthAncestor(N, K, E, edges)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# implementation of
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to add an
// edge in the tree
static void addEdge(List []v,
int x, int y)
{
v[x].Add(y);
v[y].Add(x);
}
// DFS to find the Kth
// ancestor of every node
static void dfs(List []tree,
List temp,
int []ancestor, int u,
int parent, int k)
{
// Pushing current node
// in the vector
temp.Add(u);
// Traverse its neighbors
foreach(int i in tree[u])
{
if (i == parent)
continue;
dfs(tree, temp,
ancestor, i, u, k);
}
temp.RemoveAt(temp.Count - 1);
// If K ancestors are not
// found for current node
if (temp.Count < k)
{
ancestor[u] = -1;
}
else
{
// Add the Kth ancestor
// for the node
ancestor[u] = temp[temp.Count - k];
}
}
// Function to find Kth
// ancestor of each node
static void KthAncestor(int N, int K, int E,
int [,]edges)
{
// Building the tree
List []tree = new List[N + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < tree.Length; i++)
tree[i] = new List();
for(int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
addEdge(tree, edges[i, 0],
edges[i, 1]);
}
// Stores all parents of a node
List temp = new List();
// Store Kth ancestor
// of all nodes
int []ancestor = new int[N + 1];
dfs(tree, temp, ancestor, 1, 0, K);
// Print the ancestors
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
Console.Write(ancestor[i] + " ");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given N and K
int N = 9;
int K = 2;
// Given edges of n-ary tree
int E = 8;
int [,]edges = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 },
{ 2, 4 }, { 2, 5 },
{ 2, 6 }, { 3, 7 },
{ 3, 8 }, { 3, 9 } };
// Function call
KthAncestor(N, K, E, edges);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar 输出:
-1 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 1 1
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)