二叉树中节点的第 K 个祖先 |设置 3
给定一棵二叉树,其中节点的编号从1到N 。给定一个节点和一个正整数K 。我们必须在二叉树中打印给定节点的第 K个祖先。如果不存在任何这样的祖先,则打印-1 。
例如,在下面给出的二叉树中,节点4和5的第二个祖先是1 。节点4的第三个祖先将是-1 。
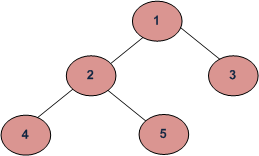
方法:首先我们从根找到给定关键数据的路径,并将其存储到一个向量中,然后我们简单地返回向量的第 k个索引。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of Tree
struct node {
node *left, *right;
int data;
};
// To create a new node
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* temp = new node;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
temp->data = data;
return temp;
}
// Function to find the path from
// root to the target node
bool RootToNode(node* root, int key, vector& v)
{
if (root == NULL)
return false;
// Add current node to the path
v.push_back(root->data);
// If current node is the target node
if (root->data == key)
return true;
// If the target node exists in
// the left or the right sub-tree
if (RootToNode(root->left, key, v)
|| RootToNode(root->right, key, v))
return true;
// Remove the last inserted node as
// it is not a part of the path
// from root to target
v.pop_back();
return false;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
// Given node
int target = 4;
// Vector to store the path from
// root to the given node
vector v;
// Find the path from root to the target node
RootToNode(root, target, v);
int k = 2;
// Print the Kth ancestor
if (k > v.size() - 1 || k <= 0)
cout << -1;
else
cout << v[v.size() - 1 - k];
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Structure of Tree
static class node
{
node left, right;
int data;
};
// To create a new node
static node newNode(int data)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.left = temp.right = null;
temp.data = data;
return temp;
}
// Function to find the path from
// root to the target node
static boolean RootToNode(node root, int key,
Vector v)
{
if (root == null)
return false;
// Add current node to the path
v.add(root.data);
// If current node is the target node
if (root.data == key)
return true;
// If the target node exists in
// the left or the right sub-tree
if (RootToNode(root.left, key, v)
|| RootToNode(root.right, key, v))
return true;
// Remove the last inserted node as
// it is not a part of the path
// from root to target
v.removeElementAt(v.size()-1);
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
// Given node
int target = 4;
// Vector to store the path from
// root to the given node
Vector v = new Vector<>();
// Find the path from root to the target node
RootToNode(root, target, v);
int k = 2;
// Print the Kth ancestor
if (k > v.size() - 1 || k <= 0)
System.out.println(-1);
else
System.out.println(v.get(v.size() - 1 - k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# To create a node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to find the path
# from root to the target node
def RootToNode(root, key, v):
if root == None:
return False
# Add current node to the path
v.append(root.data)
# If current node is the target node
if root.data == key:
return True
# If the target node exists in
# the left or the right sub-tree
if (RootToNode(root.left, key, v) or
RootToNode(root.right, key, v)):
return True
# Remove the last inserted node
# as it is not a part of the
# path from root to target
v.pop()
return False
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
# Given node
target, k = 4, 2
# Vector to store the path
# from root to the given node
v = []
# Find the path from root to the target node
RootToNode(root, target, v)
# Print the Kth ancestor
if k > len(v) - 1 or k <= 0:
print(-1)
else:
print(v[len(v) - 1 - k])
# This code is contributed by Rituraj JainC#
// C# implementation of above approach
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
class GFG
{
// Structure of Tree
public class node
{
public node left, right;
public int data;
};
// To create a new node
static node newNode(int data)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.left = temp.right = null;
temp.data = data;
return temp;
}
// Function to find the path from
// root to the target node
static bool RootToNode(node root, int key,
List v)
{
if (root == null)
return false;
// Add current node to the path
v.Add(root.data);
// If current node is the target node
if (root.data == key)
return true;
// If the target node exists in
// the left or the right sub-tree
if (RootToNode(root.left, key, v)
|| RootToNode(root.right, key, v))
return true;
// Remove the last inserted node as
// it is not a part of the path
// from root to target
v.Remove(v.Count-1);
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
// Given node
int target = 4;
// Vector to store the path from
// root to the given node
List v = new List();
// Find the path from root to the target node
RootToNode(root, target, v);
int k = 2;
// Print the Kth ancestor
if (k > v.Count - 1 || k <= 0)
Console.WriteLine(-1);
else
Console.WriteLine(v[v.Count - 1 - k]);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
输出:
1