可观察对象为有角度的应用程序中的发布者和订阅者之间的数据共享提供支持。与诸如promises之类的技术相比,它是用于事件处理,异步编程和处理多个值的更好的技术。
观测量的一个特点是,它只能由消费者谁订阅了它,即定义用于发布值函数访问,但它没有被订阅的消费者执行的(它可以是任何部件)只通过其客户可以接收通知,直到函数运行或订阅为止。
一个可观察对象可以传递任何类型的多个值。在任何情况下,用于接收值的API都是相同的,并且设置和逻辑均由可观察对象处理。剩下的事情只是关于订阅和取消订阅所需的信息。
观察者:为了处理接收可观察消息,我们需要一个可观察接口,该接口由可观察对象对消息的回调方法组成。一些基本方法如下:
- next:它是每个消息的处理程序,可观察到,执行开始后可能被称为零次或多次。
示例:这是使用观察者的next()方法的简单示例。
javascript
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import {Observable} from 'rxjs';
@Component({
selector: 'app-next-example',
templateUrl: './next-example.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./next-example.component.css']
})
export class NextExampleComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
// Create a new Observable
const sqnc = new Observable(countOnetoTen);
// Execute the Observable and print the
// result of each notification
// next() is a call to countOnetoTen method
// to get the next value from the observable
sqnc.subscribe({
next(num) { console.log(num); }
});
// This function runs when subscribe()
// is called
function countOnetoTen(observer) {
for(var i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
// Calls the next observable
// notification
observer.next(i);
}
// Unsubscribe after completing
// the sequence
return {unsubscribe(){}};
}
}
}javascript
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
@Component({
selector: 'app-error-example',
templateUrl: './error-example.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./error-example.component.css']
})
export class ErrorExampleComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
// Create a new Observable
const sqnc = new Observable(generateError);
// Execute the Observable and print the
// result of each notification
// error() is called when next generate
// some error
sqnc.subscribe({
next(num) { },
error(err) { console.log('Error Somewhere')}
});
// This function runs when subscribe() is called
function generateError(observer){
// Calls the next observable notification
// It generates an error and error is called
observer.next( adddlert("Welcome guest!"));
// Unsubscribe after completing the sequence
return {unsubscribe(){}};
}
}
}javascript
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
@Component({
selector: 'app-complete-example',
templateUrl: './complete-example.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./complete-example.component.css']
})
export class CompleteExampleComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
// Create a new Observable
const sqnc = new Observable(countOnetoTen);
// Execute the Observable and print the
// result of each notification
sqnc.subscribe({
next(num) { console.log(num); },
complete(){console.log("Completed!!!!")}
});
// This function runs when subscribe()
// is called
function countOnetoTen(observer){
for(var i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
// Calls the next observable
// notification
observer.next(i);
}
observer.complete();
// Unsubscribe after completing
// the sequence
return {unsubscribe(){}};
}
}
}javascript
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import {Observable} from "rxjs";
import { CompileTemplateMetadata } from '@angular/compiler';
@Component({
selector: 'app-rt',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'MyFirstApp';
}
// Create a new Observable that will
// deliver the above sequence
const table = new Observable(tableOfTwo);
// Execute the Observable and print the
// result of each notification
// next() is a call to tableOfTwo() method
// to get the next value from the observable
table.subscribe({
next(num) { console.log(num); },
complete() { console.log('Finished sequence'); }
});
// This function runs when subscribe() is called
function tableOfTwo(observer) {
for(var i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
observer.next('2 * ' + i + ' = ' + i*2);
}
observer.complete();
return {unsubscribe(){}};
}javascript
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import {Observable} from 'rxjs';
@Component({
selector: 'app-my-page',
templateUrl: './my-page.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./my-page.component.css']
})
export class MyPageComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
const multiSeq = new Observable(this.multiSeqSubs());
multiSeq.subscribe({
next(num) { console.log('1st subscribe: ' + num); },
complete() { console.log('1st sequence finished.'); }
});
// Subscribe again After 1 seconds.
setTimeout(() => {
multiSeq.subscribe({
next(num) { console.log('2nd subscribe: ' + num); },
complete() { console.log('2nd sequence finished.'); }
});
}, 1000);
}
multiSeqSubs() {
const seq = [];
for (var i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
// Pushes the string onto sequence
seq.push('2 * ' + i + '=' + 2*i)
}
// Keep track of each observer
const obs = [];
// A single time Stamp for one
// set of values being generated,
// multicasted to each subscriber
let timeStamp;
// Return the subscriber function
// (runs when subscribe() function
// is invoked)
return (ob) => {
obs.push(ob);
// When this is the first subscription,
// start the sequence
if (obs.length === 1) {
timeStamp = this.exec_Sequence({
next(val) {
// Iterate through observers
// and notify all subscriptions
obs.forEach(o => o.next(val));
},
complete() {
// Notify all complete callbacks
obs.slice(0).forEach(o => o.complete());
}
}, seq, 0);
}
return {
// Unsubscribe from the observers
unsubscribe() {
obs.splice(obs.indexOf(ob), 1);
// Cleanup
if (obs.length === 0) {
clearTimeout(timeStamp);
}
}
};
};
}
// Executes the sequence
exec_Sequence(observer, sequence, index) {
return setTimeout(() => {
observer.next(sequence[index]);
if (index === sequence.length - 1) {
observer.complete();
} else {
this.exec_Sequence(observer, sequence, ++index);
}
}, 1000);
}
// Create a new Observable that will
// deliver the above sequence
}-
输出:

- 错误:它是每个错误消息的处理程序。错误停止可观察实例的执行。
示例:这是一个示例,该错误是有意在代码中引起的,以了解错误的工作原理。
javascript
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
@Component({
selector: 'app-error-example',
templateUrl: './error-example.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./error-example.component.css']
})
export class ErrorExampleComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
// Create a new Observable
const sqnc = new Observable(generateError);
// Execute the Observable and print the
// result of each notification
// error() is called when next generate
// some error
sqnc.subscribe({
next(num) { },
error(err) { console.log('Error Somewhere')}
});
// This function runs when subscribe() is called
function generateError(observer){
// Calls the next observable notification
// It generates an error and error is called
observer.next( adddlert("Welcome guest!"));
// Unsubscribe after completing the sequence
return {unsubscribe(){}};
}
}
}
-
输出:

- complete:它是一个句柄,用于通知可观察到的执行完成。
示例:此示例说明了complete函数的用法。在观察对象执行完成后,观察者将触发完成通知。
javascript
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
@Component({
selector: 'app-complete-example',
templateUrl: './complete-example.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./complete-example.component.css']
})
export class CompleteExampleComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
// Create a new Observable
const sqnc = new Observable(countOnetoTen);
// Execute the Observable and print the
// result of each notification
sqnc.subscribe({
next(num) { console.log(num); },
complete(){console.log("Completed!!!!")}
});
// This function runs when subscribe()
// is called
function countOnetoTen(observer){
for(var i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
// Calls the next observable
// notification
observer.next(i);
}
observer.complete();
// Unsubscribe after completing
// the sequence
return {unsubscribe(){}};
}
}
}
- 输出:

使可观察:在下面的示例中,我们将使一个简单的可观察到的表2。此代码写在app.component.ts文件中。在使用Observables之前,请通过编写以下代码从rxjs库导入Observables。
import {Observables} from 'rxjs'
javascript
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import {Observable} from "rxjs";
import { CompileTemplateMetadata } from '@angular/compiler';
@Component({
selector: 'app-rt',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'MyFirstApp';
}
// Create a new Observable that will
// deliver the above sequence
const table = new Observable(tableOfTwo);
// Execute the Observable and print the
// result of each notification
// next() is a call to tableOfTwo() method
// to get the next value from the observable
table.subscribe({
next(num) { console.log(num); },
complete() { console.log('Finished sequence'); }
});
// This function runs when subscribe() is called
function tableOfTwo(observer) {
for(var i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
observer.next('2 * ' + i + ' = ' + i*2);
}
observer.complete();
return {unsubscribe(){}};
}
在此代码中, next()用于调用可观察对象的下一个返回值,在可观察对象中,在任务完成之后,它返回取消订阅函数,这导致对可观察对象的取消订阅,因此无法进行更多请求。调用complete()方法时,它将打印字符串“ Finished sequence”。所有功能都显示在控制台中。
输出:
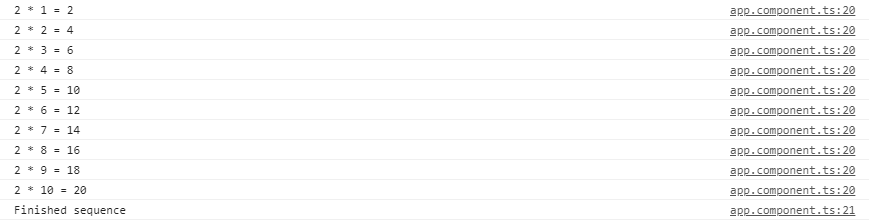
多播:这是一种在一次执行中将可观察到的广播到多个订户列表的实践。通过可观察到的多播,在文档上没有多个侦听器要注册,但是,第一个侦听器被重用并将值发送给每个订户。通过确定是否要多播值的可观察值来完成此操作。
继续上面的示例,现在将执行多播操作,该操作将在两个2序列上转换两个相同的表,并等待一秒钟再执行其他操作。
javascript
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import {Observable} from 'rxjs';
@Component({
selector: 'app-my-page',
templateUrl: './my-page.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./my-page.component.css']
})
export class MyPageComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
const multiSeq = new Observable(this.multiSeqSubs());
multiSeq.subscribe({
next(num) { console.log('1st subscribe: ' + num); },
complete() { console.log('1st sequence finished.'); }
});
// Subscribe again After 1 seconds.
setTimeout(() => {
multiSeq.subscribe({
next(num) { console.log('2nd subscribe: ' + num); },
complete() { console.log('2nd sequence finished.'); }
});
}, 1000);
}
multiSeqSubs() {
const seq = [];
for (var i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
// Pushes the string onto sequence
seq.push('2 * ' + i + '=' + 2*i)
}
// Keep track of each observer
const obs = [];
// A single time Stamp for one
// set of values being generated,
// multicasted to each subscriber
let timeStamp;
// Return the subscriber function
// (runs when subscribe() function
// is invoked)
return (ob) => {
obs.push(ob);
// When this is the first subscription,
// start the sequence
if (obs.length === 1) {
timeStamp = this.exec_Sequence({
next(val) {
// Iterate through observers
// and notify all subscriptions
obs.forEach(o => o.next(val));
},
complete() {
// Notify all complete callbacks
obs.slice(0).forEach(o => o.complete());
}
}, seq, 0);
}
return {
// Unsubscribe from the observers
unsubscribe() {
obs.splice(obs.indexOf(ob), 1);
// Cleanup
if (obs.length === 0) {
clearTimeout(timeStamp);
}
}
};
};
}
// Executes the sequence
exec_Sequence(observer, sequence, index) {
return setTimeout(() => {
observer.next(sequence[index]);
if (index === sequence.length - 1) {
observer.complete();
} else {
this.exec_Sequence(observer, sequence, ++index);
}
}, 1000);
}
// Create a new Observable that will
// deliver the above sequence
}
该代码执行相同的功能,即处理多播操作。在这段代码中,我们有一个观察者列表,它取决于编号。多播操作的订阅数。在此,在执行代码期间,我们只有2个正在执行的操作,因此“ obs”列表中只有2个元素。
输出:
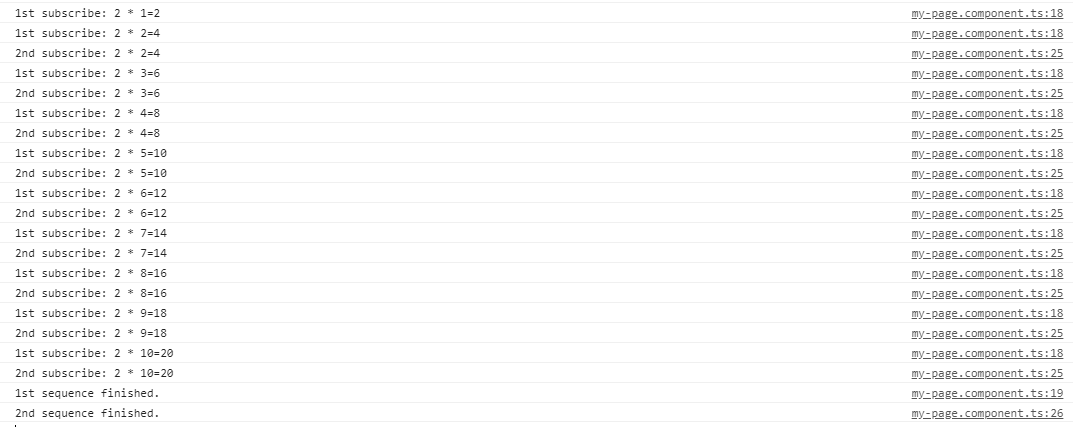
错误处理:
可观察变量产生异步值,因此try / catch不会捕获任何错误,因为它可能导致代码停止运行,而与在该时间实例上运行的其他任务无关。相反,我们通过在观察者上指定错误回调来处理错误。产生错误时,它会导致可观察对象清除订阅并停止为该订阅生成值。可观察对象可以产生值(调用下一个回调),也可以完成,调用完成或错误回调。
错误回调的语法
observable.subscribe({
next(val) { console.log('Next: ' + val)},
error(err) { console.log('Error: ' + err)}
});