给定一个三角形金字塔,其顶点标记为O,A,B和C ,数字为N ,任务是找到使从原点O出发的人最初以N步回到原点的方式。在一个步骤中,一个人可以去到它的任何相邻顶点。
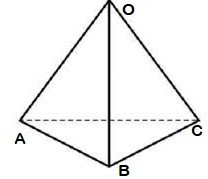
例子:
Input: N = 1
Output: 0
Explanation:
In 1 step, it is impossible to be again at position O.
Input: N = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
The three ways to reach back to O in two steps are:
O->A->O
O->B->O
O->C->O
Input: N = 3
Output: 6
Explanation:
The 6 ways to reach back to O in three steps are:
O->A->B->O
O->A->C->O
O->B->A->O
O->B->C->O
O->C->A->O
O->C->B->O
方法:想法是使用动态编程的概念。
- 将创建一个表T [] [] ,其中行表示路数,而列表示位置。
- 为了填写表格,需要进行一次观察。也就是说,如果我们在上一步中不在O处,则可以返回到位置O。
- 因此,当前步骤中到达原点O的方式数等于之前步骤中人不在原点O上的方式数之和。
- 让我们了解如何为N = 3填充表格:
0 1 2 3 O 1 0 3 6 A 0 1 2 7 B 0 1 2 7 C 0 1 2 7 - 该表的基本情况是当N = 1时。我们可以从O以外的所有位置开始以1步的距离到达原点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
使用制表法
C++
// C++ program for Dynamic
// Programming implementation of
// Number of Path in a Triangular
// pyramid
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to return the number of
// ways we can reach back to the
// initial position O
int count(int n)
{
// If n is 0 then there is
// 1 solution
if (n == 0)
return 1;
// If n is equal to 1
// then we can't reach at position O
if (n == 1)
return 0;
int dp[4][n + 1];
// Initial Conditions
// Represents position O
dp[0][0] = 1;
// Represents position A
dp[1][0] = 0;
// Represents position B
dp[2][0] = 0;
// Represents position C
dp[3][0] = 0;
// Filling the table
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// The number of ways to reach
// a particular position (say X)
// at the i'th step is equivalent
// to the sum of the number
// of ways the person is not at
// position X in the last step.
int countPositionO
= dp[1][i - 1] + dp[2][i - 1]
+ dp[3][i - 1];
int countPositionA
= dp[0][i - 1] + dp[2][i - 1]
+ dp[3][i - 1];
int countPositionB
= dp[0][i - 1] + dp[1][i - 1]
+ dp[3][i - 1];
int countPositionC
= dp[0][i - 1] + dp[1][i - 1]
+ dp[2][i - 1];
dp[0][i] = countPositionO;
dp[1][i] = countPositionA;
dp[2][i] = countPositionB;
dp[3][i] = countPositionC;
}
return dp[0][n];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 3;
cout << count(n) << endl;
n = 4;
cout << count(n) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for dynamic programming
// implementation of number of path in
// a triangular pyramid
class GFG{
// Function to return the number of
// ways we can reach back to the
// initial position O
static int count(int n)
{
// If n is 0 then there is
// 1 solution
if (n == 0)
return 1;
// If n is equal to 1 then we
// can't reach at position O
if (n == 1)
return 0;
int [][]dp = new int[4][n + 1];
// Initial Conditions
// Represents position O
dp[0][0] = 1;
// Represents position A
dp[1][0] = 0;
// Represents position B
dp[2][0] = 0;
// Represents position C
dp[3][0] = 0;
// Filling the table
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// The number of ways to reach
// a particular position (say X)
// at the i'th step is equivalent
// to the sum of the number
// of ways the person is not at
// position X in the last step.
int countPositionO = dp[1][i - 1] +
dp[2][i - 1] +
dp[3][i - 1];
int countPositionA = dp[0][i - 1] +
dp[2][i - 1] +
dp[3][i - 1];
int countPositionB = dp[0][i - 1] +
dp[1][i - 1] +
dp[3][i - 1];
int countPositionC = dp[0][i - 1] +
dp[1][i - 1] +
dp[2][i - 1];
dp[0][i] = countPositionO;
dp[1][i] = countPositionA;
dp[2][i] = countPositionB;
dp[3][i] = countPositionC;
}
return dp[0][n];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 3;
System.out.print(count(n) + "\n");
n = 4;
System.out.print(count(n) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991Python3
# Python3 program for Dynamic
# Programming implementation of
# Number of Path in a Triangular
# pyramid
# Function to return the number of
# ways we can reach back to the
# initial position O
def count(n):
# If n is 0 then there is
# 1 solution
if (n == 0):
return 1
# If n is equal to 1
# then we can't reach at position O
if (n == 1):
return 0
dp = [[0 for i in range(n + 1)]
for j in range(4)]
# Initial Conditions
# Represents position O
dp[0][0] = 1
# Represents position A
dp[1][0] = 0
# Represents position B
dp[2][0] = 0
# Represents position C
dp[3][0] = 0
# Filling the table
for i in range(1, n + 1):
# The number of ways to reach
# a particular position (say X)
# at the i'th step is equivalent
# to the sum of the number
# of ways the person is not at
# position X in the last step.
countPositionO = (dp[1][i - 1] +
dp[2][i - 1] +
dp[3][i - 1])
countPositionA = (dp[0][i - 1] +
dp[2][i - 1] +
dp[3][i - 1])
countPositionB = (dp[0][i - 1] +
dp[1][i - 1] +
dp[3][i - 1])
countPositionC = (dp[0][i - 1] +
dp[1][i - 1] +
dp[2][i - 1])
dp[0][i] = countPositionO
dp[1][i] = countPositionA
dp[2][i] = countPositionB
dp[3][i] = countPositionC
return dp[0][n]
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 3
print(count(n))
n = 4
print(count(n))
# This code is contributed by ChitraNayalC#
// C# program for dynamic programming
// implementation of number of path in
// a triangular pyramid
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to return the number
// of ways we can reach back to
// the initial position O
static int count(int n)
{
// If n is 0 then there is
// 1 solution
if (n == 0)
return 1;
// If n is equal to 1 then we
// can't reach at position O
if (n == 1)
return 0;
int [,]dp = new int[4, n + 1];
// Initial Conditions
// Represents position O
dp[0, 0] = 1;
// Represents position A
dp[1, 0] = 0;
// Represents position B
dp[2, 0] = 0;
// Represents position C
dp[3, 0] = 0;
// Filling the table
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// The number of ways to reach
// a particular position (say X)
// at the i'th step is equivalent
// to the sum of the number
// of ways the person is not at
// position X in the last step.
int countPositionO = dp[1, i - 1] +
dp[2, i - 1] +
dp[3, i - 1];
int countPositionA = dp[0, i - 1] +
dp[2, i - 1] +
dp[3, i - 1];
int countPositionB = dp[0, i - 1] +
dp[1, i - 1] +
dp[3, i - 1];
int countPositionC = dp[0, i - 1] +
dp[1, i - 1] +
dp[2, i - 1];
dp[0, i] = countPositionO;
dp[1, i] = countPositionA;
dp[2, i] = countPositionB;
dp[3, i] = countPositionC;
}
return dp[0, n];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 3;
Console.Write(count(n) + "\n");
n = 4;
Console.Write(count(n) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991输出:
6
21
时间复杂度: O(N)。
辅助空间复杂度: O(4 * N)
笔记:
- 如果我们为一组查询中的最大表填充表格,则该程序可以更有效地工作,以在对多个查询进行预处理后的恒定时间内找到方法的数量。
- 对于单个查询,也可以使该程序更节省空间。想法是,由于我们只需要先前的步长值即可计算当前的步长值,因此只需采用4个变量来存储先前的步长值,便可以在恒定空间中解决给定的问题。