给定数组arr [] ,任务是使用任何自定义比较器计算每个元素右侧的对数(arr [i],arr [j])。
比较器可以是任何类型,下面给出其中一些–
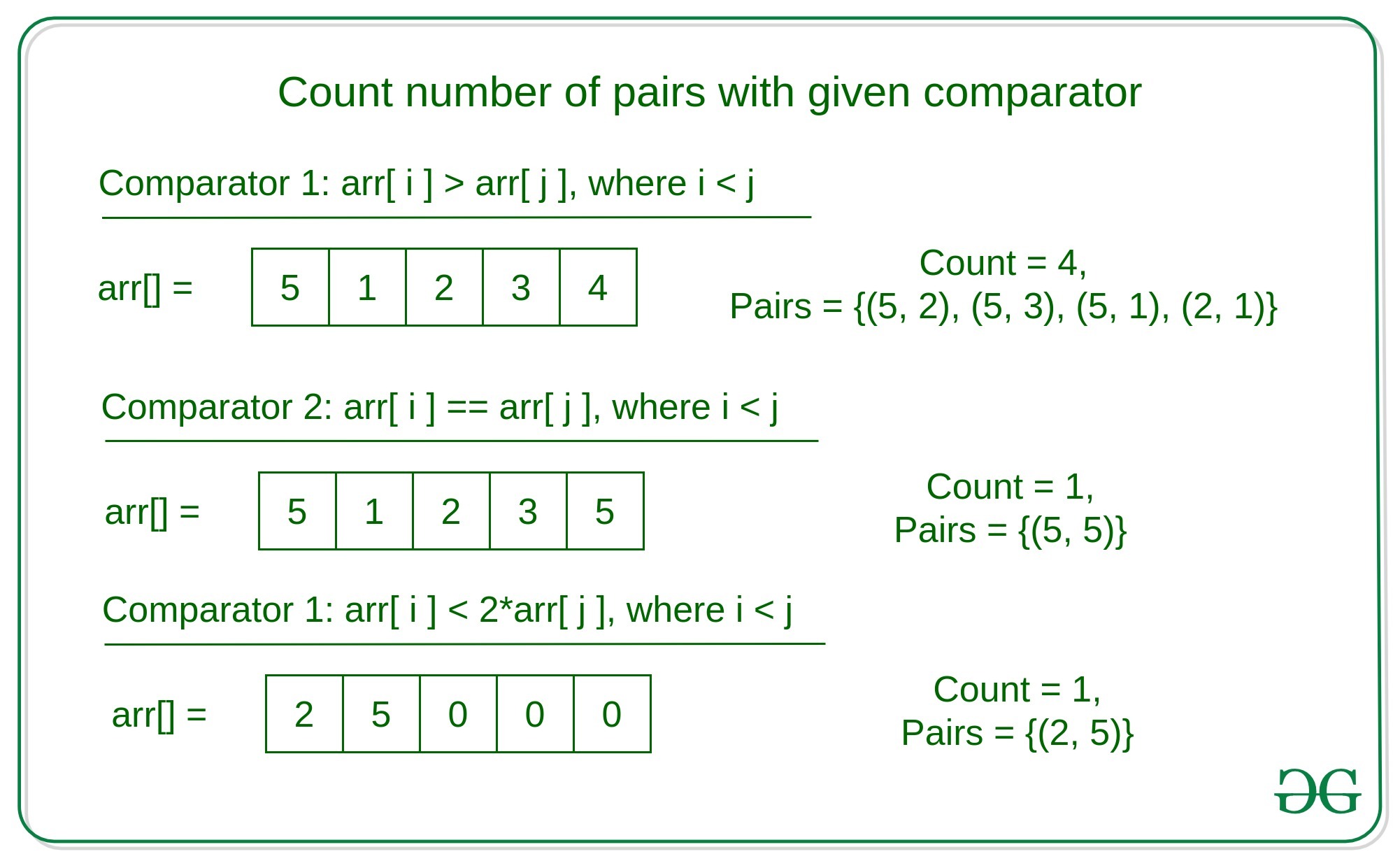
arr[i] > arr[j], where i < j
arr[i] < arr[j], where i 2 * arr[j], where i < j
例子:
Input: arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}, comp = arr[i] > arr[j]
Output: 10
Explanation:
There are 10 such pairs, in which right element is smaller than the left element –
{(5, 4), (5, 3), (5, 2), (5, 1), (4, 3), (4, 2), (4, 1), (3, 2), (3, 1), (2, 1)}
Input: arr[] = {3, 4, 3}, comp = arr[i] == arr[j]
Output: 1
Explanation:
There is only one such pair such that elements are equal. That is (3, 3)
天真的解决方案:遍历每对元素,使i
时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
高效方法:想法是自定义合并排序,以在合并两个子数组时计算此类对。每个数组将有两种计数类型:
- 阵列间对:左子阵列本身中存在的对。
- 阵列内对:在正确的子阵列中存在的对。
对于Left子阵列,可以从下到上递归计算计数,而主要任务是对阵列内对进行计数。
因此,此类对总数可以定义为–
Total Pairs = Inter-Array pairs in Left Sub-array +
Inter-Array pairs in Right Sub-array +
Intra-Array pairs from left to right sub-array
以下是从左子阵列到右子阵列的阵列内阵列对的图示–
- 基本情况:此问题的基本情况将是当两个子阵列中只有一个元素并且我们要检查阵列内对时。然后,检查这两个元素是否形成一对,然后增加计数并将较小的元素放在其位置。
if start1 == end1 and start2 == end2:
if compare(arr, start1, start2):
c += 1
- 递归情况:根据比较器函数,此问题可分为三种类型–
- 当对之间运算符是大于或等于。
- 当对之间运算符是小于或等于。
- 当对之间运算符等于。
因此,可以针对这些对分别计算所有这三种情况。
- 情况1:在大于或等于的情况下,如果我们找到任何这样的对,则该子数组右边的所有元素也将与当前元素形成对。因此,此类对的计数将增加左子数组中剩余的元素数。
if compare(arr, start1, start2):
count += end1 - start1 + 1
- 情况2:在小于或等于的情况下,如果我们找到任何这样的对,则该子数组右边的所有元素也将与当前元素形成对。因此,此类对的计数将增加右侧子数组中剩余的元素数。
if compare(arr, start1, start2):
count += end2 - start2 + 1
- 情况3:在等于的情况下,如果我们找到任何这样的对,那么我们会尝试在while循环的帮助下在左侧子数组中找到所有这样的对。在每个这样的可能对中,将计数增加1。
if compare(arr, start1, start2):
while compare(arr, start1, start2):
count += 1
start1 += 1
- 最后,合并两个子数组,就像在合并排序中那样。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// elements on the right with the given
// custom comparator
#include
using namespace std;
// comparator to check
// if two elements are equal
bool compare(int arr[], int s1, int s2){
if (arr[s1] > arr[s2]){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
// Function to find the Intra-Array
// Count in the two subarrays
int findIntraArrayCount(int arr[], int s1,
int e1, int s2, int e2, int g){
// Base Case
if (s1 == e1 && s2 == e2){
int c = 0;
if (compare(arr, s1, s2)){
c += 1;
}
if (arr[s1] > arr[s2]){
int temp = arr[s1];
arr[s1] = arr[s2];
arr[s2] = temp;
}
return c;
}
// Variable for keeping
// the count of the pair
int c = 0;
int s = s1, e = e2, s3 = s1;
int e3 = e1, s4 = s2, e4 = e2;
while (s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2){
// Condition when we have to use the
// Greater than comparator
if (g == 1){
if (compare(arr, s1, s2)){
c += e1 - s1 + 1;
s2 += 1;
}
else{
s1 += 1;
}
}
// Condition when we have to use the
// Less than comparator
else if (g == 0){
if (compare(arr, s1, s2)){
c += e2 - s2 + 1;
s1 += 1;
}
else {
s2 += 1;
}
}
// Condition when we have to use the
// Equal to Comparator
else if (g == -1){
if (compare(arr, s1, s2)){
int c1 = 0;
while (s1 <= e1 &&
compare(arr, s1, s2)){
c1 += 1;
s1 += 1;
}
s1 -= 1;
int c2 = 0;
while (s2 <= e2 &&
compare(arr, s1, s2)){
c2 += 1;
s2 += 1;
}
c += c1 * c2;
}
else {
if (arr[s1] > arr[s2]){
s2 += 1;
}
else{
s1 += 1;
}
}
}
}
s1 = s3; e1 = e3;
s2 = s4; e2 = e4;
// Array to store
// the sorted subarray
vector aux;
// Merge the two subarrays
while (s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2){
if (arr[s1] <= arr[s2]){
aux.push_back(arr[s1]);
s1 += 1;
}
else{
aux.push_back(arr[s2]);
s2 += 1;
}
}
// Copy subarray 1 elements
while (s1 <= e1){
aux.push_back(arr[s1]);
s1 += 1;
}
// Copy subarray 2 elements
while (s2 <= e2){
aux.push_back(arr[s2]);
s2 += 1;
}
// Update the original array
for (int i = s; i <= e; i++){
arr[i] = aux[i-s];
}
return c;
}
// Function to find such pairs with
// any custom comparator function
int findElementsOnRight(int arr[], int s,
int e, int g){
if (s >= e){
return 0;
}
int mid = (s+e)/2;
// Recursive call for inter-array
// count of pairs in left subarrays
int c1 = findElementsOnRight(
arr, s, mid, g);
// Recursive call for inter-array
// count of pairs in right sub-arrays
int c2 = findElementsOnRight(
arr, mid + 1, e, g);
// Call for intra-array pairs
int c3 = findIntraArrayCount(
arr, s, mid, mid+1, e, g);
return c1 + c2 + c3;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = {4, 3, 2, 1};
int g = 1;
cout << findElementsOnRight(arr, 0, 3, g);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation to find the
// elements on the right with the given
// custom comparator
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// comparator to check
// if two elements are equal
public static boolean compare(
int[] arr, int s1, int s2){
if (arr[s1] > arr[s2]){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
// Function to find the Intra-Array
// Count in the two subarrays
public static int findIntraArrayCount(
int[] arr, int s1, int e1, int s2,
int e2, int g){
// Base Case
if (s1 == e1 && s2 == e2){
int c = 0;
if (compare(arr, s1, s2)){
c += 1;
}
if (arr[s1] > arr[s2]){
int temp = arr[s1];
arr[s1] = arr[s2];
arr[s2] = temp;
}
return c;
}
// Variable for keeping
// the count of the pair
int c = 0;
int s = s1, e = e2, s3 = s1;
int e3 = e1, s4 = s2, e4 = e2;
while (s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2){
// Condition when we have to use the
// Greater than comparator
if (g == 1){
if (compare(arr, s1, s2)){
c += e1 - s1 + 1;
s2 += 1;
}
else{
s1 += 1;
}
}
// Condition when we have to use the
// Equal to Comparator
else if (g == 0){
if (compare(arr, s1, s2)){
c += e2 - s2 + 1;
s1 += 1;
}
else {
s2 += 1;
}
}
// Condition when we have to use the
// Equal to Comparator
else if (g == -1){
if (compare(arr, s1, s2)){
int c1 = 0;
while (s1 <= e1 &&
compare(arr, s1, s2)){
c1 += 1;
s1 += 1;
}
s1 -= 1;
int c2 = 0;
while (s2 <= e2 &&
compare(arr, s1, s2)){
c2 += 1;
s2 += 1;
}
c += c1 * c2;
}
else {
if (arr[s1] > arr[s2]){
s2 += 1;
}
else{
s1 += 1;
}
}
}
}
s1 = s3; e1 = e3;
s2 = s4; e2 = e4;
// Array to store
// the sorted subarray
ArrayList aux =
new ArrayList<>();
// Merge the two subarrays
while (s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2){
if (arr[s1] <= arr[s2]){
aux.add(arr[s1]);
s1 += 1;
}
else{
aux.add(arr[s2]);
s2 += 1;
}
}
// Copy subarray 1 elements
while (s1 <= e1){
aux.add(arr[s1]);
s1 += 1;
}
// Copy subarray 2 elements
while (s2 <= e2){
aux.add(arr[s2]);
s2 += 1;
}
// Update the original array
for (int i = s; i <= e; i++){
arr[i] = aux.get(i-s);
}
return c;
}
// Function to find such pairs with
// any custom comparator function
public static int findElementsOnRight(
int[] arr, int s, int e, int g){
if (s >= e){
return 0;
}
int mid = (s+e)/2;
// Recursive call for inter-array
// count of pairs in left subarrays
int c1 = findElementsOnRight(arr, s,
mid, g);
// Recursive call for inter-array
// count of pairs in right sub-arrays
int c2 = findElementsOnRight(arr, mid + 1,
e, g);
// Call for intra-array pairs
int c3 = findIntraArrayCount(arr, s,
mid, mid+1, e, g);
return c1 + c2 + c3;
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args) {
int[] arr = {4, 3, 2, 1};
int g = 1;
System.out.println(
findElementsOnRight(arr, 0, 3, g));
}
} Python3
# Python3 implementation to find the
# elements on the right with the given
# custom comparator
import random, math
from copy import deepcopy as dc
# comparator to check
# if two elements are equal
def compare(arr, s1, s2):
if arr[s1] > arr[s2]:
return True
else:
return False
# Function to find the Intra-Array
# Count in the two subarrays
def findIntraArrayCount(arr, s1, \
e1, s2, e2, g):
# Base Case
if s1 == e1 and s2 == e2:
c = 0
if compare(arr, s1, s2):
c += 1
if arr[s1] > arr[s2]:
arr[s1], arr[s2] = arr[s2], arr[s1]
return c
# Variable for keeping
# the count of the pair
c = 0
# Total subarray length
s = dc(s1); e = dc(e2)
# length of subarray 1
s3 = dc(s1); e3 = dc(e1)
# length of subarray 2
s4 = dc(s2); e4 = dc(e2)
while s1 <= e1 and s2 <= e2:
# Condition when we have to use the
# Greater than comparator
if g == 1:
if compare(arr, s1, s2):
c += e1 - s1 + 1
s2 += 1
else:
s1 += 1
# Condition when we have to use the
# Less than comparator
elif g == 0:
if compare(arr, s1, s2):
c += e2 - s2 + 1
s1 += 1
else:
s2 += 1
# Condition when we have to use the
# Equal to Comparator
elif g == -1:
if compare(arr, s1, s2):
c1 = 0
while s1 <= e1 and\
compare(arr, s1, s2):
c1 += 1
s1 += 1
s1 -= 1
c2 = 0
while s2 <= e2 and\
compare(arr, s1, s2):
c2 += 1
s2 += 1
c += c1 * c2
else:
if arr[s1] > arr[s2]:
s2 += 1
else:
s1 += 1
s1 = dc(s3); e1 = dc(e3)
s2 = dc(s4); e2 = dc(e4)
# Array to store the sorted subarray
aux = []
# Merge the two subarrays
while s1 <= e1 and s2 <= e2:
if arr[s1] <= arr[s2]:
aux.append(arr[s1])
s1 += 1
else:
aux.append(arr[s2])
s2 += 1
# Copy subarray 1 elements
while s1 <= e1:
aux.append(arr[s1])
s1 += 1
# Copy subarray 2 elements
while s2 <= e2:
aux.append(arr[s2])
s2 += 1
# Update the original array
for i in range(s, e + 1):
arr[i] = aux[i-s]
return c
# Function to find such pairs with
# any custom comparator function
def findElementsOnRight(arr, s, e, g):
if s >= e:
return 0
mid = (s + e)//2
# Recursive call for inter-array
# count of pairs in left subarrays
c1 = findElementsOnRight(arr, s, \
mid, g)
# Recursive call for inter-array
# count of pairs in right sub-arrays
c2 = findElementsOnRight(arr, mid + 1, \
e, g)
# Call for intra-array pairs
c3 = findIntraArrayCount(arr, s, mid, \
mid + 1, e, g)
return c1 + c2 + c3
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [4, 3, 2, 1]
g = 1
out = findElementsOnRight(arr, 0, \
len(arr)-1, g)
print(out)C#
// C# implementation to find the
// elements on the right with the
// given custom comparator
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// comparator to check
// if two elements are equal
public static bool compare(int[] arr, int s1,
int s2)
{
if (arr[s1] > arr[s2])
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// Function to find the Intra-Array
// Count in the two subarrays
public static int findIntraArrayCount(int[] arr, int s1,
int e1, int s2,
int e2, int g)
{
// Base Case
if (s1 == e1 && s2 == e2)
{
int cc = 0;
if (compare(arr, s1, s2))
{
cc += 1;
}
if (arr[s1] > arr[s2])
{
int temp = arr[s1];
arr[s1] = arr[s2];
arr[s2] = temp;
}
return cc;
}
// Variable for keeping
// the count of the pair
int c = 0;
int s = s1, e = e2, s3 = s1;
int e3 = e1, s4 = s2, e4 = e2;
while (s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2)
{
// Condition when we have to use the
// Greater than comparator
if (g == 1)
{
if (compare(arr, s1, s2))
{
c += e1 - s1 + 1;
s2 += 1;
}
else
{
s1 += 1;
}
}
// Condition when we have to use the
// Equal to Comparator
else if (g == 0)
{
if (compare(arr, s1, s2))
{
c += e2 - s2 + 1;
s1 += 1;
}
else
{
s2 += 1;
}
}
// Condition when we have to use the
// Equal to Comparator
else if (g == -1)
{
if (compare(arr, s1, s2))
{
int c1 = 0;
while (s1 <= e1 &&
compare(arr, s1, s2))
{
c1 += 1;
s1 += 1;
}
s1 -= 1;
int c2 = 0;
while (s2 <= e2 &&
compare(arr, s1, s2))
{
c2 += 1;
s2 += 1;
}
c += c1 * c2;
}
else
{
if (arr[s1] > arr[s2])
{
s2 += 1;
}
else
{
s1 += 1;
}
}
}
}
s1 = s3; e1 = e3;
s2 = s4; e2 = e4;
// Array to store
// the sorted subarray
List aux = new List();
// Merge the two subarrays
while (s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2)
{
if (arr[s1] <= arr[s2])
{
aux.Add(arr[s1]);
s1 += 1;
}
else
{
aux.Add(arr[s2]);
s2 += 1;
}
}
// Copy subarray 1 elements
while (s1 <= e1)
{
aux.Add(arr[s1]);
s1 += 1;
}
// Copy subarray 2 elements
while (s2 <= e2)
{
aux.Add(arr[s2]);
s2 += 1;
}
// Update the original array
for(int i = s; i <= e; i++)
{
arr[i] = aux[i-s];
}
return c;
}
// Function to find such pairs with
// any custom comparator function
public static int findElementsOnRight(int[] arr, int s,
int e, int g)
{
if (s >= e)
{
return 0;
}
int mid = (s + e) / 2;
// Recursive call for inter-array
// count of pairs in left subarrays
int c1 = findElementsOnRight(arr, s,
mid, g);
// Recursive call for inter-array
// count of pairs in right sub-arrays
int c2 = findElementsOnRight(arr, mid + 1,
e, g);
// Call for intra-array pairs
int c3 = findIntraArrayCount(arr, s, mid,
mid + 1, e, g);
return c1 + c2 + c3;
}
// Driver code
static public void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 4, 3, 2, 1 };
int g = 1;
Console.WriteLine(findElementsOnRight(
arr, 0, 3, g));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat 6
时间复杂度:上述方法需要O(N * logN)个时间。
辅助空间: O(N)