给定一个由N个正整数组成的排序数组arr [] ,任务是最小化将给定数组转换为任意整数X的幂序列所需的每个数组元素的增减总数。
A sequence is called a power sequence of any integer X, if and only if for every ith element (0 ≤ i < N), arr[i] = Xi, where N is length of the given array.
例子:
Input: arr[] = {1, 3, 4}
Output: 1
Explanation: Decreasing arr[1] by 1 modifies array to {1, 2, 4}, which is a power sequence of 2. Therefore, the total number of increments or decrements required is 1.
Input: arr[] = {1, 5, 7}
Output: 6
Explanation:
Operation 1: Decreasing arr[1] by 1 modifies array to {1, 4, 7}
Operation 2: Decreasing arr[1] by 1 modifies array to {1, 3, 7}
Operation 3: Increasing arr[2] by 1 modifies array to {1, 3, 8}
Operation 4: Increasing arr[2] by 1 modifies array to {1, 3, 9}, which is the power sequence of 3. Therefore, the total number of increments or decrements required is 4.
方法:可以根据以下观察结果解决给定问题:
- 由于给定数组需要转换为任意整数X的幂序列,因此数学关系可以写为:
![]()
where, 0 <= i < N, N is the number of elements in the array.
- F(X)的最小值是将其转化成X的功率序列和X的最大值需要可以如下计算操作的最小数量:
=> ![]()
=>![]()
- 因此,其想法是对从1开始的X的所有可能值进行迭代,并检查以下等式是否满足:
![由QuickLaTeX.com渲染 X^{N - 1} \le f(1) + a{[N - 1]}](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Minimum%20increments%20or%20decrements%20required%20to%20convert%20a%20sorted%20array%20into%20a%20power%20sequence_3.jpg)
如果发现为真,则找到的所有可能值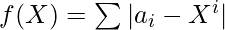 并返回所有获得的值中的最小值。
并返回所有获得的值中的最小值。
请按照以下步骤解决给定的问题:
- 初始化一个变量,例如ans as (数组元素的总和– N) ,该变量存储使数组成为幂序列所需的最小增量或减量。
- 使用变量X循环从1开始的循环,并执行以下步骤:
- 初始化两个变量,例如currCost为0和currPower为1 ,它们存储表达式的总和
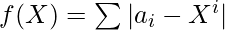 和整数X的幂。
和整数X的幂。 - 迭代[0,N – 1]范围,并将currCost的值更新为currCost + abs(arr [i] – currPower) ,将currPower的值更新为X * currPower 。
- 如果表达
![由QuickLaTeX.com渲染 X^{N - 1} \le ans + a{[N - 1]}](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Minimum%20increments%20or%20decrements%20required%20to%20convert%20a%20sorted%20array%20into%20a%20power%20sequence_6.jpg) 不满意,则跳出循环。否则,将ans的值更新为ans和currCost的最小值。
不满意,则跳出循环。否则,将ans的值更新为ans和currCost的最小值。
- 初始化两个变量,例如currCost为0和currPower为1 ,它们存储表达式的总和
- 完成上述步骤后,将ans的值打印为所需的最小操作数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the minimum number
// of increments or decrements required
// to convert array into a power sequence
int minOperations(int a[], int n)
{
// Initialize the count to f(X) for X = 1
int ans = accumulate(a, a + n, 0) - n;
// Calculate the value of f(X)
// X ^ (n - 1) <= f(1) + a[n - 1]
for (int x = 1;; x++) {
int curPow = 1, curCost = 0;
// Calculate F(x)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
curCost += abs(a[i] - curPow);
curPow *= x;
}
// Check if X ^ (n - 1) > f(1) + a[n - 1]
if (curPow / x > ans + a[n - 1])
break;
// Update ans to store the
// minimum of ans and F(x)
ans = min(ans, curCost);
}
// Return the minimum number
// of operations required
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 5, 7 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << minOperations(arr, N);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
class GFG{
// Function to find the minimum number
// of increments or decrements required
// to convert array into a power sequence
static int minOperations(int a[], int n)
{
// Initialize the count to f(X) for X = 1
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ans += a[i];
}
ans -= n;
// Calculate the value of f(X)
// X ^ (n - 1) <= f(1) + a[n - 1]
for(int x = 1;; x++)
{
int curPow = 1, curCost = 0;
// Calculate F(x)
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
curCost += Math.abs(a[i] - curPow);
curPow *= x;
}
// Check if X ^ (n - 1) > f(1) + a[n - 1]
if (curPow / x > ans + a[n - 1])
break;
// Update ans to store the
// minimum of ans and F(x)
ans = Math.min(ans, curCost);
}
// Return the minimum number
// of operations required
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 5, 7 };
int N = arr.length;
System.out.print(minOperations(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by avijitmondal1998Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to find the minimum number
# of increments or decrements required
# to convert array into a power sequence
def minOperations(a, n):
# Initialize the count to f(X) for X = 1
ans = 0
for i in range(n):
ans += a[i]
ans -= n
# Calculate the value of f(X)
# X ^ (n - 1) <= f(1) + a[n - 1]
x = 1
while(1):
curPow = 1
curCost = 0
# Calculate F(x)
for i in range(n):
curCost += abs(a[i] - curPow)
curPow *= x
# Check if X ^ (n - 1) > f(1) + a[n - 1]
if (curPow / x > ans + a[n - 1]):
break
# Update ans to store the
# minimum of ans and F(x)
ans = min(ans, curCost)
x += 1
# Return the minimum number
# of operations required
return ans
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [1, 5, 7]
N = len(arr)
print(minOperations(arr, N))
# This code is contributed by ipg2016107C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find the minimum number
// of increments or decrements required
// to convert array into a power sequence
static int minOperations(int []a, int n)
{
// Initialize the count to f(X) for X = 1
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ans += a[i];
}
ans -= n;
// Calculate the value of f(X)
// X ^ (n - 1) <= f(1) + a[n - 1]
for(int x = 1;; x++)
{
int curPow = 1, curCost = 0;
// Calculate F(x)
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
curCost += Math.Abs(a[i] - curPow);
curPow *= x;
}
// Check if X ^ (n - 1) > f(1) + a[n - 1]
if (curPow / x > ans + a[n - 1])
break;
// Update ans to store the
// minimum of ans and F(x)
ans = Math.Min(ans, curCost);
}
// Return the minimum number
// of operations required
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = { 1, 5, 7 };
int N = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(minOperations(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29Javascript
4时间复杂度: O(N *(S) (1 /(N – 1)) )
辅助空间: O(1)