在C编程中,在运行时使用数组和字符串存储数据是易失的,并在RAM中获取内存。但是将数据永久存储在硬盘中,可以进一步进行操作。因此,其想法是使用CSV文件进行数据存储和操作。不仅CSV,而且其他文件(例如dat , txt和bin)也可以用于数据处理。但CSV文件,顾名思义(C OMMA小号eparated V alues),其中节省了大量的时间在做结构完善的表格式存储数据。
在“关系数据库”中,数据以表格格式存储,因此可以使用CSV文件来创建数据库。
以下是CSV文件的示例:
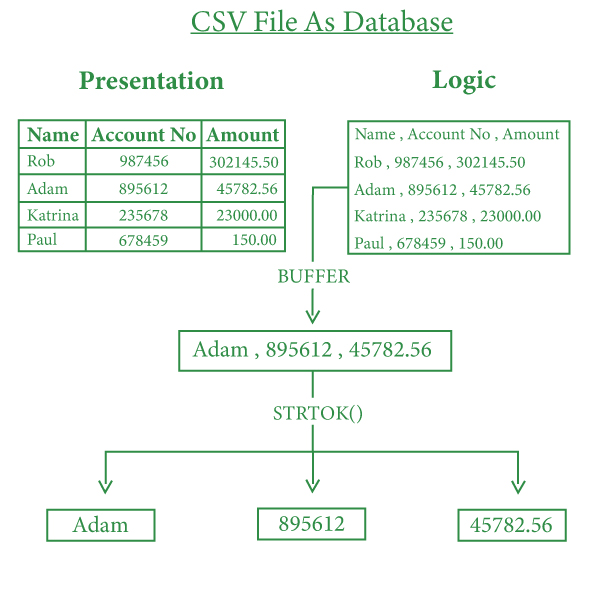
有关文件处理的概念,请参阅C中的基本文件处理。
创建一个字符数组缓冲区(可以称为字符串),该缓冲区获取文件中存在的所有数据,并通过使用File Pointer和fgets()提取数据。使用行和列两个变量,这将维护每个条目的唯一标识。
由于该字符串包含逗号‘,’来分隔值,所以这个想法是使用strtok()函数来分隔值。该函数使用定界符分割字符串,这里我们使用‘,’ 。
数据提取:
数据提取涉及打开现有CSV文件并在控制台上提取和打印整个数据。
方法:
- 使用文件指针打开CSV文件。
- 将整个文件数据提取到char缓冲区数组中。
- 现在初始化值为0的行和列变量。
- 打印用逗号分隔的数据,并增加列变量。
- 当到达行条目的末尾时,将列变量初始化为0并增加行变量。
- 重复步骤4和5,直到指针到达文件的末尾。
- 关闭文件。
以下是相同的程序:
C
// C program for the above approach
#include
#include
#include
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Substitute the full file path
// for the string file_path
FILE* fp = fopen("file_path", "r");
if (!fp)
printf("Can't open file\n");
else {
// Here we have taken size of
// array 1024 you can modify it
char buffer[1024];
int row = 0;
int column = 0;
while (fgets(buffer,
1024, fp)) {
column = 0;
row++;
// To avoid printing of column
// names in file can be changed
// according to need
if (row == 1)
continue;
// Splitting the data
char* value = strtok(buffer, ", ");
while (value) {
// Column 1
if (column == 0) {
printf("Name :");
}
// Column 2
if (column == 1) {
printf("\tAccount No. :");
}
// Column 3
if (column == 2) {
printf("\tAmount :");
}
printf("%s", value);
value = strtok(NULL, ", ");
column++;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Close the file
fclose(fp);
}
return 0;
} C
// C program for the above approach
#include
#include
#include
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Substitute the file_path string
// with full path of CSV file
FILE* fp = fopen("file_path", "a+");
char name[50];
int accountno, amount;
if (!fp) {
// Error in file opening
printf("Can't open file\n");
return 0;
}
// Asking user input for the
// new record to be added
printf("\nEnter Account Holder Name\n");
scanf("%s", &name);
printf("\nEnter Account Number\n");
scanf("%d", &accountno);
printf("\nEnter Available Amount\n");
scanf("%d", &amount);
// Saving data in file
fprintf(fp, "%s, %d, %d\n", name,
accountno, amount);
printf("\nNew Account added to record");
fclose(fp);
return 0;
} 数据添加:
数据添加处理打开一个现有的CSV文件,接收用户输入的数据以将其添加到文件中,然后将该数据添加到CSV文件中。
方法:
- 在附加模式下使用文件指针打开CSV文件,它将指向文件末尾的指针。
- 从用户那里获取临时变量中的Input。
- 使用fprintf()并根据变量的顺序和逗号分隔变量。
- 关闭文件。
例子:
C
// C program for the above approach
#include
#include
#include
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Substitute the file_path string
// with full path of CSV file
FILE* fp = fopen("file_path", "a+");
char name[50];
int accountno, amount;
if (!fp) {
// Error in file opening
printf("Can't open file\n");
return 0;
}
// Asking user input for the
// new record to be added
printf("\nEnter Account Holder Name\n");
scanf("%s", &name);
printf("\nEnter Account Number\n");
scanf("%d", &accountno);
printf("\nEnter Available Amount\n");
scanf("%d", &amount);
// Saving data in file
fprintf(fp, "%s, %d, %d\n", name,
accountno, amount);
printf("\nNew Account added to record");
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
输出:
CSV文件的优点:
- 与.txt和.dat文件的区别在于以表格式存储数据。
- 通过直接的用户交互或通过程序轻松组织数据。
- 在金融行业中广泛使用,以通过Internet存储和传输数据。
- 轻松转换为其他文件和格式。
- 它可以导入或导出到各种平台和界面。
想要从精选的最佳视频中学习和练习问题,请查看《基础知识到高级C的C基础课程》。