给定一棵具有N个节点的树,任务是找到一个三元组的节点(a,b,c) ,以使连接这些节点的路径中覆盖的节点数最大。 (仅对节点计数一次)。
例子:
Input: N = 4
Edge Set:
1 2
1 3
1 4
Output: (2, 3, 4)
(2, 3, 4) as path between (2, 3) covers nodes 2, 1, 3 and path between (3, 4) covers nodes 3, 1, 4. Hence all nodes are covered.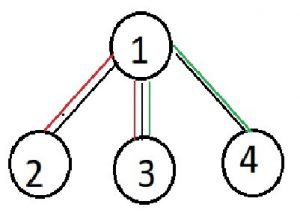
The Red Path in Tree denotes the path between 2 to 3 node which covers node 1, 2, 3. The green path denotes path between (3, 4) which covers node 3, 1, 4.
Input: N = 9
Edge Set :
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
2 7
7 8
4 9
Output: (6, 8, 1)
方法:
- 需要注意的重要一点是,三元组中的两个点必须是树的直径的末端,以覆盖最大的点。
- 我们需要找到最长的支杆直径。
- 现在,对于第3个节点,将DFS应用于每个节点的深度(除选定的Diameter Path以外的所有方向上的DFS),并应用到存在于Diameter路径上的所有节点(距离最远的节点)为被视为第三个节点,因为它覆盖了直径节点已经覆盖的最大节点。使用DFS的树的直径
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
#define ll long long int
#define MAX 100005
using namespace std;
vector adjacent[MAX];
bool visited[MAX];
// To store the required nodes
int startnode, endnode, thirdnode;
int maxi = -1, N;
// Parent array to retrace the nodes
int parent[MAX];
// Visited array to prevent DFS
// in direction on Diameter path
bool vis[MAX];
// DFS function to find the startnode
void dfs(int u, int count)
{
visited[u] = true;
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < adjacent[u].size(); i++) {
if (!visited[adjacent[u][i]]) {
temp++;
dfs(adjacent[u][i], count + 1);
}
}
if (temp == 0) {
if (maxi < count) {
maxi = count;
startnode = u;
}
}
}
// DFS function to find the endnode
// of diameter and maintain the parent array
void dfs1(int u, int count)
{
visited[u] = true;
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < adjacent[u].size(); i++) {
if (!visited[adjacent[u][i]]) {
temp++;
parent[adjacent[u][i]] = u;
dfs1(adjacent[u][i], count + 1);
}
}
if (temp == 0) {
if (maxi < count) {
maxi = count;
endnode = u;
}
}
}
// DFS function to find the end node
// of the Longest Branch to Diameter
void dfs2(int u, int count)
{
visited[u] = true;
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < adjacent[u].size(); i++) {
if (!visited[adjacent[u][i]]
&& !vis[adjacent[u][i]]) {
temp++;
dfs2(adjacent[u][i], count + 1);
}
}
if (temp == 0) {
if (maxi < count) {
maxi = count;
thirdnode = u;
}
}
}
// Function to find the required nodes
void findNodes()
{
// To find start node of diameter
dfs(1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
visited[i] = false;
maxi = -1;
// To find end node of diameter
dfs1(startnode, 0);
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// x is the end node of diameter
int x = endnode;
vis[startnode] = true;
// Mark all the nodes on diameter
// using back tracking
while (x != startnode) {
vis[x] = true;
x = parent[x];
}
maxi = -1;
// Find the end node of longest
// branch to diameter
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (vis[i])
dfs2(i, 0);
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
N = 4;
adjacent[1].push_back(2);
adjacent[2].push_back(1);
adjacent[1].push_back(3);
adjacent[3].push_back(1);
adjacent[1].push_back(4);
adjacent[4].push_back(1);
findNodes();
cout << "(" << startnode << ", " << endnode
<< ", " << thirdnode << ")";
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 100005;
static Vector> adjacent = new
Vector> ();
static boolean visited[] = new boolean[MAX];
// To store the required nodes
static int startnode, endnode, thirdnode;
static int maxi = -1, N;
// Parent array to retrace the nodes
static int parent[] = new int[MAX];
// Visited array to prevent DFS
// in direction on Diameter path
static boolean vis[] = new boolean[MAX];
// DFS function to find the startnode
static void dfs(int u, int count)
{
visited[u] = true;
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < adjacent.get(u).size(); i++)
{
if (!visited[adjacent.get(u).get(i)])
{
temp++;
dfs(adjacent.get(u).get(i), count + 1);
}
}
if (temp == 0)
{
if (maxi < count)
{
maxi = count;
startnode = u;
}
}
}
// DFS function to find the endnode
// of diameter and maintain the parent array
static void dfs1(int u, int count)
{
visited[u] = true;
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < adjacent.get(u).size(); i++)
{
if (!visited[adjacent.get(u).get(i)])
{
temp++;
parent[adjacent.get(u).get(i)] = u;
dfs1(adjacent.get(u).get(i), count + 1);
}
}
if (temp == 0)
{
if (maxi < count)
{
maxi = count;
endnode = u;
}
}
}
// DFS function to find the end node
// of the Longest Branch to Diameter
static void dfs2(int u, int count)
{
visited[u] = true;
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < adjacent.get(u).size(); i++)
{
if (!visited[adjacent.get(u).get(i)] &&
!vis[adjacent.get(u).get(i)])
{
temp++;
dfs2(adjacent.get(u).get(i), count + 1);
}
}
if (temp == 0)
{
if (maxi < count)
{
maxi = count;
thirdnode = u;
}
}
}
// Function to find the required nodes
static void findNodes()
{
// To find start node of diameter
dfs(1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
visited[i] = false;
maxi = -1;
// To find end node of diameter
dfs1(startnode, 0);
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// x is the end node of diameter
int x = endnode;
vis[startnode] = true;
// Mark all the nodes on diameter
// using back tracking
while (x != startnode)
{
vis[x] = true;
x = parent[x];
}
maxi = -1;
// Find the end node of longest
// branch to diameter
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
if (vis[i])
dfs2(i, 0);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
for(int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
adjacent.add(new Vector());
N = 4;
adjacent.get(1).add(2);
adjacent.get(2).add(1);
adjacent.get(1).add(3);
adjacent.get(3).add(1);
adjacent.get(1).add(4);
adjacent.get(4).add(1);
findNodes();
System.out.print( "(" + startnode + ", " +
endnode + ", " +
thirdnode + ")");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
MAX = 100005
adjacent = [[] for i in range(MAX)]
visited = [False] * MAX
# To store the required nodes
startnode = endnode = thirdnode = None
maxi, N = -1, None
# Parent array to retrace the nodes
parent = [None] * MAX
# Visited array to prevent DFS
# in direction on Diameter path
vis = [False] * MAX
# DFS function to find the startnode
def dfs(u, count):
visited[u] = True
temp = 0
global startnode, maxi
for i in range(0, len(adjacent[u])):
if not visited[adjacent[u][i]]:
temp += 1
dfs(adjacent[u][i], count + 1)
if temp == 0:
if maxi < count:
maxi = count
startnode = u
# DFS function to find the endnode of
# diameter and maintain the parent array
def dfs1(u, count):
visited[u] = True
temp = 0
global endnode, maxi
for i in range(0, len(adjacent[u])):
if not visited[adjacent[u][i]]:
temp += 1
parent[adjacent[u][i]] = u
dfs1(adjacent[u][i], count + 1)
if temp == 0:
if maxi < count:
maxi = count
endnode = u
# DFS function to find the end node
# of the Longest Branch to Diameter
def dfs2(u, count):
visited[u] = True
temp = 0
global thirdnode, maxi
for i in range(0, len(adjacent[u])):
if (not visited[adjacent[u][i]] and
not vis[adjacent[u][i]]):
temp += 1
dfs2(adjacent[u][i], count + 1)
if temp == 0:
if maxi < count:
maxi = count
thirdnode = u
# Function to find the required nodes
def findNodes():
# To find start node of diameter
dfs(1, 0)
global maxi
for i in range(0, N+1):
visited[i] = False
maxi = -1
# To find end node of diameter
dfs1(startnode, 0)
for i in range(0, N+1):
visited[i] = False
# x is the end node of diameter
x = endnode
vis[startnode] = True
# Mark all the nodes on diameter
# using back tracking
while x != startnode:
vis[x] = True
x = parent[x]
maxi = -1
# Find the end node of longest
# branch to diameter
for i in range(1, N+1):
if vis[i]:
dfs2(i, 0)
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 4
adjacent[1].append(2)
adjacent[2].append(1)
adjacent[1].append(3)
adjacent[3].append(1)
adjacent[1].append(4)
adjacent[4].append(1)
findNodes()
print("({}, {}, {})".format(startnode, endnode, thirdnode))
# This code is contributed by Rituraj Jain输出:
(2, 3, 4)
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。