给定二叉搜索树和排序的子序列。任务是检查给定的排序子序列是否存在于二叉搜索树中。
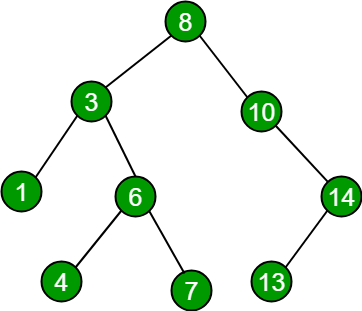
例子:
// For above binary search tree
Input : seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 14}
Output: "Yes"
Input : seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 12, 13}
Output: "No"
一个简单的解决方案是将有序遍历存储在辅助数组中,然后通过将排序后的子序列的元素与tree的有序遍历进行匹配,我们可以确定BST中是否存在子序列。这种方法的时间复杂度为O(n),但需要额外的空间O(n)才能将遍历存储在数组中。
一种有效的解决方案是当我们在序遍历方式BST来匹配的子序列的元素。我们将index作为给定排序子序列的迭代器,并开始对给定bst进行有序遍历,如果当前节点与seq [index]匹配,则将index向前移动索引,并递增1,如果index == n ,则在BST完全遍历之后表示给定子序列的所有元素均已匹配,并在给定BST中作为排序子序列存在。
C++
// C++ program to find if given array exists as a
// subsequece in BST
#include
using namespace std;
// A binary Tree node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to create a new BST node
// with key as given num
struct Node* newNode(int num)
{
struct Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = num;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to insert a given key to BST
struct Node* insert(struct Node* root, int key)
{
if (root == NULL)
return newNode(key);
if (root->data > key)
root->left = insert(root->left, key);
else
root->right = insert(root->right, key);
return root;
}
// function to check if given sorted sub-sequence exist in BST
// index --> iterator for given sorted sub-sequence
// seq[] --> given sorted sub-sequence
void seqExistUtil(struct Node *ptr, int seq[], int &index)
{
if (ptr == NULL)
return;
// We traverse left subtree first in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr->left, seq, index);
// If current node matches with se[index] then move
// forward in sub-sequence
if (ptr->data == seq[index])
index++;
// We traverse left subtree in the end in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr->right, seq, index);
}
// A wrapper over seqExistUtil. It returns true
// if seq[0..n-1] exists in tree.
bool seqExist(struct Node *root, int seq[], int n)
{
// Initialize index in seq[]
int index = 0;
// Do an inorder traversal and find if all
// elements of seq[] were present
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
// index would become n if all elements of
// seq[] were present
return (index == n);
}
// driver program to run the case
int main()
{
struct Node* root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
int seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 14};
int n = sizeof(seq)/sizeof(seq[0]);
seqExist(root, seq, n)? cout << "Yes" :
cout << "No";
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find if given array
// exists as a subsequece in BST
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// A binary Tree node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
//structure of int class
static class INT
{
int a;
}
// A utility function to create a new BST node
// with key as given num
static Node newNode(int num)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = num;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to insert a given key to BST
static Node insert( Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return newNode(key);
if (root.data > key)
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
return root;
}
// function to check if given sorted
// sub-sequence exist in BST index -.
// iterator for given sorted sub-sequence
// seq[] -. given sorted sub-sequence
static void seqExistUtil( Node ptr, int seq[], INT index)
{
if (ptr == null)
return;
// We traverse left subtree
// first in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index);
// If current node matches
// with se[index] then move
// forward in sub-sequence
if (ptr.data == seq[index.a])
index.a++;
// We traverse left subtree
// in the end in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index);
}
// A wrapper over seqExistUtil.
// It returns true if seq[0..n-1]
// exists in tree.
static boolean seqExist( Node root, int seq[], int n)
{
// Initialize index in seq[]
INT index = new INT();
index.a = 0;
// Do an inorder traversal and find if all
// elements of seq[] were present
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
// index would become n if all
// elements of seq[] were present
return (index.a == n);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
int seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 14};
int n = seq.length;
if(seqExist(root, seq, n))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduPython3
# Python3 program to find if given array
# exists as a subsequece in BST
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# A utility function to insert a
# given key to BST
def insert(root, key):
if root == None:
return Node(key)
if root.data > key:
root.left = insert(root.left, key)
else:
root.right = insert(root.right, key)
return root
# function to check if given sorted
# sub-sequence exist in BST index .
# iterator for given sorted sub-sequence
# seq[] . given sorted sub-sequence
def seqExistUtil(ptr, seq, index):
if ptr == None:
return
# We traverse left subtree
# first in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index)
# If current node matches with se[index[0]]
# then move forward in sub-sequence
if ptr.data == seq[index[0]]:
index[0] += 1
# We traverse left subtree in
# the end in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index)
# A wrapper over seqExistUtil. It returns
# true if seq[0..n-1] exists in tree.
def seqExist(root, seq, n):
# Initialize index in seq[]
index = [0]
# Do an inorder traversal and find if
# all elements of seq[] were present
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index)
# index would become n if all elements
# of seq[] were present
if index[0] == n:
return True
else:
return False
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = None
root = insert(root, 8)
root = insert(root, 10)
root = insert(root, 3)
root = insert(root, 6)
root = insert(root, 1)
root = insert(root, 4)
root = insert(root, 7)
root = insert(root, 14)
root = insert(root, 13)
seq = [4, 6, 8, 14]
n = len(seq)
if seqExist(root, seq, n):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by PranchalKC#
// C# program to find if given array
// exists as a subsequece in BST
using System;
class GFG
{
// A binary Tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
};
// structure of int class
public class INT
{
public int a;
}
// A utility function to create a new BST node
// with key as given num
static Node newNode(int num)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = num;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to insert a given key to BST
static Node insert( Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return newNode(key);
if (root.data > key)
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
return root;
}
// function to check if given sorted
// sub-sequence exist in BST index -.
// iterator for given sorted sub-sequence
// seq[] -. given sorted sub-sequence
static void seqExistUtil( Node ptr, int []seq, INT index)
{
if (ptr == null)
return;
// We traverse left subtree
// first in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index);
// If current node matches
// with se[index] then move
// forward in sub-sequence
if (ptr.data == seq[index.a])
index.a++;
// We traverse left subtree
// in the end in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index);
}
// A wrapper over seqExistUtil.
// It returns true if seq[0..n-1]
// exists in tree.
static bool seqExist( Node root, int []seq, int n)
{
// Initialize index in seq[]
INT index = new INT();
index.a = 0;
// Do an inorder traversal and find if all
// elements of seq[] were present
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
// index would become n if all
// elements of seq[] were present
return (index.a == n);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
int []seq = {4, 6, 8, 14};
int n = seq.Length;
if(seqExist(root, seq, n))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */输出:
Yes
时间复杂度: O(n)