给定一个有N个顶点和M个可能包含循环的边的有向图,任务是找到该图在字典上最小的拓扑顺序(如果存在,否则打印-1) (如果该图具有循环)。
逻辑上最小的拓扑顺序是指,如果图中的两个顶点没有任何输入边,则编号较小的顶点应在该顺序中首先出现。
例如,在下面的图像中,许多拓扑排序都是可能的,例如5 2 3 4 0 1,5 0 2 4 3 1 。
但是最小的顺序是4 5 0 2 3 1 。
例子:
Input: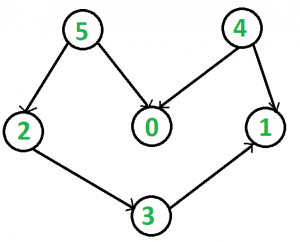
Output: 4 5 0 2 3 1
Even though 5 4 0 2 3 1 is also a valid topological
ordering of the given graph but it is not
lexicographically smallest.
方法:我们将使用经过改进的Kahn算法进行拓扑排序。而不是使用队列,我们将使用多集存储顶点,以确保每次选择顶点时,顶点都是所有元素中最小的。总的时间复杂度变为![]()
下面是上述方法的实现:
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Class to represent a graph
class Graph {
int V; // No. of vertices'
// Pointer to an array containing
// adjacency listsList
list* adj;
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// Function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int u, int v);
// Function to print the required topological
// sort of the given graph
void topologicalSort();
};
// Constructor
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
// Function to add an edge to the graph
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
}
// Function to print the required topological
// sort of the given graph
void Graph::topologicalSort()
{
// Create a vector to store indegrees of all
// the vertices
// Initialize all indegrees to 0
vector in_degree(V, 0);
// Traverse adjacency lists to fill indegrees of
// vertices
// This step takes O(V+E) time
for (int u = 0; u < V; u++) {
list::iterator itr;
for (itr = adj[u].begin(); itr != adj[u].end(); itr++)
in_degree[*itr]++;
}
// Create a set and inserting all vertices with
// indegree 0
multiset s;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (in_degree[i] == 0)
s.insert(i);
// Initialize count of visited vertices
int cnt = 0;
// Create a vector to store result (A topological
// ordering of the vertices)
vector top_order;
// One by one erase vertices from setand insert
// adjacents if indegree of adjacent becomes 0
while (!s.empty()) {
// Extract vertex with minimum number from multiset
// and add it to topological order
int u = *s.begin();
s.erase(s.begin());
top_order.push_back(u);
// Iterate through all its neighbouring nodes
// of erased node u and decrease their in-degree
// by 1
list::iterator itr;
for (itr = adj[u].begin(); itr != adj[u].end(); itr++)
// If in-degree becomes zero, add it to queue
if (--in_degree[*itr] == 0)
s.insert(*itr);
cnt++;
}
// Check if there was a cycle
if (cnt != V) {
cout << -1;
return;
}
// Print topological order
for (int i = 0; i < top_order.size(); i++)
cout << top_order[i] << " ";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Create the graph
Graph g(6);
g.addEdge(5, 2);
g.addEdge(5, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 1);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 1);
// Find the required topological order
g.topologicalSort();
return 0;
}
输出:
4 5 0 2 3 1
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。