二进制搜索树(BST)是基于节点的二进制树数据结构,具有以下属性。
•节点的左子树仅包含键值小于节点键值的节点。
•节点的右子树仅包含键大于节点的键的节点。
•左和右子树也都必须是二进制搜索树。
根据以上属性,自然可以得出:
•每个节点(树中的项目)都有一个不同的键。
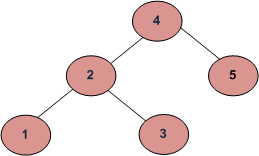
方法1(简单但错误)
以下是一个简单的程序。对于每个节点,请检查其左节点是否小于该节点,而其右节点是否大于该节点。
c
int isBST(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 1;
/* false if left is > than node */
if (node->left != NULL && node->left->data > node->data)
return 0;
/* false if right is < than node */
if (node->right != NULL && node->right->data < node->data)
return 0;
/* false if, recursively, the left or right is not a BST */
if (!isBST(node->left) || !isBST(node->right))
return 0;
/* passing all that, it's a BST */
return 1;
}c
/* Returns true if a binary tree is a binary search tree */
int isBST(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 1;
/* false if the max of the left is > than us */
if (node->left!=NULL && maxValue(node->left) > node->data)
return 0;
/* false if the min of the right is <= than us */
if (node->right!=NULL && minValue(node->right) < node->data)
return 0;
/* false if, recursively, the left or right is not a BST */
if (!isBST(node->left) || !isBST(node->right))
return 0;
/* passing all that, it's a BST */
return 1;
}C++
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child and
a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
/* Constructor that allocates
a new node with the given data
and NULL left and right pointers. */
node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
this->left = NULL;
this->right = NULL;
}
};
int isBSTUtil(node* node, int min, int max);
/* Returns true if the given
tree is a binary search tree
(efficient version). */
int isBST(node* node)
{
return(isBSTUtil(node, INT_MIN, INT_MAX));
}
/* Returns true if the given
tree is a BST and its values
are >= min and <= max. */
int isBSTUtil(node* node, int min, int max)
{
/* an empty tree is BST */
if (node==NULL)
return 1;
/* false if this node violates
the min/max constraint */
if (node->data < min || node->data > max)
return 0;
/* otherwise check the subtrees recursively,
tightening the min or max constraint */
return
isBSTUtil(node->left, min, node->data-1) && // Allow only distinct values
isBSTUtil(node->right, node->data+1, max); // Allow only distinct values
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
node *root = new node(4);
root->left = new node(2);
root->right = new node(5);
root->left->left = new node(1);
root->left->right = new node(3);
if(isBST(root))
cout<<"Is BST";
else
cout<<"Not a BST";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
#include
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
int isBSTUtil(struct node* node, int min, int max);
/* Returns true if the given tree is a binary search tree
(efficient version). */
int isBST(struct node* node)
{
return(isBSTUtil(node, INT_MIN, INT_MAX));
}
/* Returns true if the given tree is a BST and its
values are >= min and <= max. */
int isBSTUtil(struct node* node, int min, int max)
{
/* an empty tree is BST */
if (node==NULL)
return 1;
/* false if this node violates the min/max constraint */
if (node->data < min || node->data > max)
return 0;
/* otherwise check the subtrees recursively,
tightening the min or max constraint */
return
isBSTUtil(node->left, min, node->data-1) && // Allow only distinct values
isBSTUtil(node->right, node->data+1, max); // Allow only distinct values
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(4);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(5);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(3);
if(isBST(root))
printf("Is BST");
else
printf("Not a BST");
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
//Java implementation to check if given Binary tree
//is a BST or not
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
//Root of the Binary Tree
Node root;
/* can give min and max value according to your code or
can write a function to find min and max value of tree. */
/* returns true if given search tree is binary
search tree (efficient version) */
boolean isBST() {
return isBSTUtil(root, Integer.MIN_VALUE,
Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
/* Returns true if the given tree is a BST and its
values are >= min and <= max. */
boolean isBSTUtil(Node node, int min, int max)
{
/* an empty tree is BST */
if (node == null)
return true;
/* false if this node violates the min/max constraints */
if (node.data < min || node.data > max)
return false;
/* otherwise check the subtrees recursively
tightening the min/max constraints */
// Allow only distinct values
return (isBSTUtil(node.left, min, node.data-1) &&
isBSTUtil(node.right, node.data+1, max));
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(4);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(3);
if (tree.isBST())
System.out.println("IS BST");
else
System.out.println("Not a BST");
}
}Python
# Python program to check if a binary tree is bst or not
INT_MAX = 4294967296
INT_MIN = -4294967296
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Returns true if the given tree is a binary search tree
# (efficient version)
def isBST(node):
return (isBSTUtil(node, INT_MIN, INT_MAX))
# Retusn true if the given tree is a BST and its values
# >= min and <= max
def isBSTUtil(node, mini, maxi):
# An empty tree is BST
if node is None:
return True
# False if this node violates min/max constraint
if node.data < mini or node.data > maxi:
return False
# Otherwise check the subtrees recursively
# tightening the min or max constraint
return (isBSTUtil(node.left, mini, node.data -1) and
isBSTUtil(node.right, node.data+1, maxi))
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(4)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(5)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(3)
if (isBST(root)):
print "Is BST"
else:
print "Not a BST"
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
using System;
// C# implementation to check if given Binary tree
//is a BST or not
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
//Root of the Binary Tree
public Node root;
/* can give min and max value according to your code or
can write a function to find min and max value of tree. */
/* returns true if given search tree is binary
search tree (efficient version) */
public virtual bool BST
{
get
{
return isBSTUtil(root, int.MinValue, int.MaxValue);
}
}
/* Returns true if the given tree is a BST and its
values are >= min and <= max. */
public virtual bool isBSTUtil(Node node, int min, int max)
{
/* an empty tree is BST */
if (node == null)
{
return true;
}
/* false if this node violates the min/max constraints */
if (node.data < min || node.data > max)
{
return false;
}
/* otherwise check the subtrees recursively
tightening the min/max constraints */
// Allow only distinct values
return (isBSTUtil(node.left, min, node.data - 1) && isBSTUtil(node.right, node.data + 1, max));
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(4);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(3);
if (tree.BST)
{
Console.WriteLine("IS BST");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Not a BST");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13C++
// C++ program to check if a given tree is BST.
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to
left child and a pointer to right child */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left, *right;
};
// Returns true if given tree is BST.
bool isBST(Node* root, Node* l=NULL, Node* r=NULL)
{
// Base condition
if (root == NULL)
return true;
// if left node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. left node's data
// should be less than root's data
if (l != NULL and root->data <= l->data)
return false;
// if right node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. right node's data
// should be greater than root's data
if (r != NULL and root->data >= r->data)
return false;
// check recursively for every node.
return isBST(root->left, l, root) and
isBST(root->right, root, r);
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node *root = newNode(3);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(5);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(4);
if (isBST(root,NULL,NULL))
cout << "Is BST";
else
cout << "Not a BST";
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to check if a given tree is BST.
class Sol
{
// A binary tree node has data, pointer to
//left child && a pointer to right child /
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
// Returns true if given tree is BST.
static boolean isBST(Node root, Node l, Node r)
{
// Base condition
if (root == null)
return true;
// if left node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. left node's data
// should be less than root's data
if (l != null && root.data <= l.data)
return false;
// if right node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. right node's data
// should be greater than root's data
if (r != null && root.data >= r.data)
return false;
// check recursively for every node.
return isBST(root.left, l, root) &&
isBST(root.right, root, r);
}
// Helper function that allocates a new node with the
//given data && null left && right pointers. /
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = newNode(3);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(1);
root.left.right = newNode(4);
if (isBST(root,null,null))
System.out.print("Is BST");
else
System.out.print("Not a BST");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduPython3
""" Program to check if a given Binary
Tree is balanced like a Red-Black Tree """
# Helper function that allocates a new
# node with the given data and None
# left and right poers.
class newNode:
# Construct to create a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Returns true if given tree is BST.
def isBST(root, l = None, r = None):
# Base condition
if (root == None) :
return True
# if left node exist then check it has
# correct data or not i.e. left node's data
# should be less than root's data
if (l != None and root.data <= l.data) :
return False
# if right node exist then check it has
# correct data or not i.e. right node's data
# should be greater than root's data
if (r != None and root.data >= r.data) :
return False
# check recursively for every node.
return isBST(root.left, l, root) and \
isBST(root.right, root, r)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(3)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(5)
root.right.left = newNode(1)
root.right.right = newNode(4)
#root.right.left.left = newNode(40)
if (isBST(root,None,None)):
print("Is BST")
else:
print("Not a BST")
# This code is contributed by
# Shubham Singh(SHUBHAMSINGH10)C#
// C# program to check if a given tree is BST.
using System;
class GFG
{
// A binary tree node has data, pointer to
//left child && a pointer to right child /
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
};
// Returns true if given tree is BST.
static Boolean isBST(Node root, Node l, Node r)
{
// Base condition
if (root == null)
return true;
// if left node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. left node's data
// should be less than root's data
if (l != null && root.data <= l.data)
return false;
// if right node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. right node's data
// should be greater than root's data
if (r != null && root.data >= r.data)
return false;
// check recursively for every node.
return isBST(root.left, l, root) &&
isBST(root.right, root, r);
}
// Helper function that allocates a new node with the
//given data && null left && right pointers. /
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = newNode(3);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(1);
root.left.right = newNode(4);
if (isBST(root,null,null))
Console.Write("Is BST");
else
Console.Write("Not a BST");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarC++
bool isBST(node* root)
{
static node *prev = NULL;
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion
// and keep track of prev node
if (root)
{
if (!isBST(root->left))
return false;
// Allows only distinct valued nodes
if (prev != NULL &&
root->data <= prev->data)
return false;
prev = root;
return isBST(root->right);
}
return true;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendraC
bool isBST(struct node* root)
{
static struct node *prev = NULL;
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion and keep track of prev node
if (root)
{
if (!isBST(root->left))
return false;
// Allows only distinct valued nodes
if (prev != NULL && root->data <= prev->data)
return false;
prev = root;
return isBST(root->right);
}
return true;
}Java
// Java implementation to check if given Binary tree
// is a BST or not
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of the Binary Tree
Node root;
// To keep tract of previous node in Inorder Traversal
Node prev;
boolean isBST() {
prev = null;
return isBST(root);
}
/* Returns true if given search tree is binary
search tree (efficient version) */
boolean isBST(Node node)
{
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion and
// keep a track of previous node
if (node != null)
{
if (!isBST(node.left))
return false;
// allows only distinct values node
if (prev != null && node.data <= prev.data )
return false;
prev = node;
return isBST(node.right);
}
return true;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(4);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(3);
if (tree.isBST())
System.out.println("IS BST");
else
System.out.println("Not a BST");
}
}Python3
# Python implementation to check if
# given Binary tree is a BST or not
# A binary tree node containing data
# field, left and right pointers
class Node:
# constructor to create new node
def __init__(self, val):
self.data = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
# global variable prev - to keep track
# of previous node during Inorder
# traversal
prev = None
# function to check if given binary
# tree is BST
def isbst(root):
# prev is a global variable
global prev
prev = None
return isbst_rec(root)
# Helper function to test if binary
# tree is BST
# Traverse the tree in inorder fashion
# and keep track of previous node
# return true if tree is Binary
# search tree otherwise false
def isbst_rec(root):
# prev is a global variable
global prev
# if tree is empty return true
if root is None:
return True
if isbst_rec(root.left) is False:
return False
# if previous node'data is found
# greater than the current node's
# data return fals
if prev is not None and prev.data > root.data:
return False
# store the current node in prev
prev = root
return isbst_rec(root.right)
# driver code to test above function
root = Node(4)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(5)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(3)
if isbst(root):
print("is BST")
else:
print("not a BST")
# This code is contributed by
# Shweta Singh(shweta44)C#
// C# implementation to check if
// given Binary tree is a BST or not
using System;
/* Class containing left and
right child of current node
and key value*/
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of the Binary Tree
Node root;
// To keep tract of previous node
// in Inorder Traversal
Node prev;
Boolean isBST()
{
prev = null;
return isBST(root);
}
/* Returns true if given search tree is binary
search tree (efficient version) */
Boolean isBST(Node node)
{
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion and
// keep a track of previous node
if (node != null)
{
if (!isBST(node.left))
return false;
// allows only distinct values node
if (prev != null &&
node.data <= prev.data )
return false;
prev = node;
return isBST(node.right);
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(4);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(3);
if (tree.isBST())
Console.WriteLine("IS BST");
else
Console.WriteLine("Not a BST");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiC++
// C++ program to check if a given tree is BST.
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to
left child and a pointer to right child */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
bool isBSTUtil(struct Node* root, Node *&prev)
{
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion and
// keep track of prev node
if (root)
{
if (!isBSTUtil(root->left, prev))
return false;
// Allows only distinct valued nodes
if (prev != NULL && root->data <= prev->data)
return false;
prev = root;
return isBSTUtil(root->right, prev);
}
return true;
}
bool isBST(Node *root)
{
Node *prev = NULL;
return isBSTUtil(root, prev);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node *root = new Node(3);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(5);
root->left->left = new Node(1);
root->left->right = new Node(4);
if (isBST(root))
cout << "Is BST";
else
cout << "Not a BST";
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program to check
# if a given tree is BST.
import math
# A binary tree node has data,
# pointer to left child and
# a pointer to right child
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def isBSTUtil(root, prev):
# traverse the tree in inorder fashion
# and keep track of prev node
if (root != None):
if (isBSTUtil(root.left, prev) == True):
return False
# Allows only distinct valued nodes
if (prev != None and
root.data <= prev.data):
return False
prev = root
return isBSTUtil(root.right, prev)
return True
def isBST(root):
prev = None
return isBSTUtil(root, prev)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(3)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(1)
root.right.right = Node(4)
#root.right.left.left = Node(40)
if (isBST(root) == None):
print("Is BST")
else:
print("Not a BST")
# This code is contributed by SrathoreC#
// C# program to check if a given tree is BST.
using System;
public class GFG
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to
left child and a pointer to right child */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
};
static Node prev;
static Boolean isBSTUtil(Node root)
{
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion and
// keep track of prev node
if (root != null)
{
if (!isBSTUtil(root.left))
return false;
// Allows only distinct valued nodes
if (prev != null &&
root.data <= prev.data)
return false;
prev = root;
return isBSTUtil(root.right);
}
return true;
}
static Boolean isBST(Node root)
{
return isBSTUtil(root);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(3);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(4);
if (isBST(root))
Console.WriteLine("Is BST");
else
Console.WriteLine("Not a BST");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji这种方法是错误的,因为这对于下面的二叉树将返回true(并且下面的树不是BST,因为4在3的左子树中)
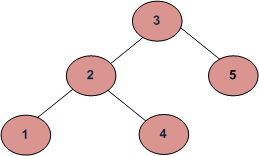
方法2(正确但无效)
对于每个节点,检查左侧子树中的最大值是否小于节点,而右侧子树中的最小值是否大于节点。
C
/* Returns true if a binary tree is a binary search tree */
int isBST(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 1;
/* false if the max of the left is > than us */
if (node->left!=NULL && maxValue(node->left) > node->data)
return 0;
/* false if the min of the right is <= than us */
if (node->right!=NULL && minValue(node->right) < node->data)
return 0;
/* false if, recursively, the left or right is not a BST */
if (!isBST(node->left) || !isBST(node->right))
return 0;
/* passing all that, it's a BST */
return 1;
}
假定您具有辅助函数minValue()和maxValue(),它们从非空树返回最小或最大int值
方法3(正确有效) :
上面的方法2运行缓慢,因为它遍历了树的某些部分。更好的解决方案只对每个节点检查一次。诀窍是编写一个实用程序辅助函数isBSTUtil(struct node * node,int min,int max)遍历树,跟踪缩小的最小和最大允许值,并且只对每个节点查看一次。 min和max的初始值应为INT_MIN和INT_MAX-从那里开始变窄。
注意:如果存在重复的元素,其值为INT_MIN或INT_MAX,则此方法不适用。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child and
a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
/* Constructor that allocates
a new node with the given data
and NULL left and right pointers. */
node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
this->left = NULL;
this->right = NULL;
}
};
int isBSTUtil(node* node, int min, int max);
/* Returns true if the given
tree is a binary search tree
(efficient version). */
int isBST(node* node)
{
return(isBSTUtil(node, INT_MIN, INT_MAX));
}
/* Returns true if the given
tree is a BST and its values
are >= min and <= max. */
int isBSTUtil(node* node, int min, int max)
{
/* an empty tree is BST */
if (node==NULL)
return 1;
/* false if this node violates
the min/max constraint */
if (node->data < min || node->data > max)
return 0;
/* otherwise check the subtrees recursively,
tightening the min or max constraint */
return
isBSTUtil(node->left, min, node->data-1) && // Allow only distinct values
isBSTUtil(node->right, node->data+1, max); // Allow only distinct values
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
node *root = new node(4);
root->left = new node(2);
root->right = new node(5);
root->left->left = new node(1);
root->left->right = new node(3);
if(isBST(root))
cout<<"Is BST";
else
cout<<"Not a BST";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
#include
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
int isBSTUtil(struct node* node, int min, int max);
/* Returns true if the given tree is a binary search tree
(efficient version). */
int isBST(struct node* node)
{
return(isBSTUtil(node, INT_MIN, INT_MAX));
}
/* Returns true if the given tree is a BST and its
values are >= min and <= max. */
int isBSTUtil(struct node* node, int min, int max)
{
/* an empty tree is BST */
if (node==NULL)
return 1;
/* false if this node violates the min/max constraint */
if (node->data < min || node->data > max)
return 0;
/* otherwise check the subtrees recursively,
tightening the min or max constraint */
return
isBSTUtil(node->left, min, node->data-1) && // Allow only distinct values
isBSTUtil(node->right, node->data+1, max); // Allow only distinct values
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(4);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(5);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(3);
if(isBST(root))
printf("Is BST");
else
printf("Not a BST");
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
//Java implementation to check if given Binary tree
//is a BST or not
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
//Root of the Binary Tree
Node root;
/* can give min and max value according to your code or
can write a function to find min and max value of tree. */
/* returns true if given search tree is binary
search tree (efficient version) */
boolean isBST() {
return isBSTUtil(root, Integer.MIN_VALUE,
Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
/* Returns true if the given tree is a BST and its
values are >= min and <= max. */
boolean isBSTUtil(Node node, int min, int max)
{
/* an empty tree is BST */
if (node == null)
return true;
/* false if this node violates the min/max constraints */
if (node.data < min || node.data > max)
return false;
/* otherwise check the subtrees recursively
tightening the min/max constraints */
// Allow only distinct values
return (isBSTUtil(node.left, min, node.data-1) &&
isBSTUtil(node.right, node.data+1, max));
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(4);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(3);
if (tree.isBST())
System.out.println("IS BST");
else
System.out.println("Not a BST");
}
}
Python
# Python program to check if a binary tree is bst or not
INT_MAX = 4294967296
INT_MIN = -4294967296
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Returns true if the given tree is a binary search tree
# (efficient version)
def isBST(node):
return (isBSTUtil(node, INT_MIN, INT_MAX))
# Retusn true if the given tree is a BST and its values
# >= min and <= max
def isBSTUtil(node, mini, maxi):
# An empty tree is BST
if node is None:
return True
# False if this node violates min/max constraint
if node.data < mini or node.data > maxi:
return False
# Otherwise check the subtrees recursively
# tightening the min or max constraint
return (isBSTUtil(node.left, mini, node.data -1) and
isBSTUtil(node.right, node.data+1, maxi))
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(4)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(5)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(3)
if (isBST(root)):
print "Is BST"
else:
print "Not a BST"
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
C#
using System;
// C# implementation to check if given Binary tree
//is a BST or not
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
//Root of the Binary Tree
public Node root;
/* can give min and max value according to your code or
can write a function to find min and max value of tree. */
/* returns true if given search tree is binary
search tree (efficient version) */
public virtual bool BST
{
get
{
return isBSTUtil(root, int.MinValue, int.MaxValue);
}
}
/* Returns true if the given tree is a BST and its
values are >= min and <= max. */
public virtual bool isBSTUtil(Node node, int min, int max)
{
/* an empty tree is BST */
if (node == null)
{
return true;
}
/* false if this node violates the min/max constraints */
if (node.data < min || node.data > max)
{
return false;
}
/* otherwise check the subtrees recursively
tightening the min/max constraints */
// Allow only distinct values
return (isBSTUtil(node.left, min, node.data - 1) && isBSTUtil(node.right, node.data + 1, max));
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(4);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(3);
if (tree.BST)
{
Console.WriteLine("IS BST");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Not a BST");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
输出:
IS BST时间复杂度: O(n)
辅助空间:如果不考虑函数调用堆栈的大小,则为O(1),否则为O(n)简化方法3
我们可以使用NULL指针而不是INT_MIN和INT_MAX值来简化方法2。
C++
// C++ program to check if a given tree is BST.
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to
left child and a pointer to right child */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left, *right;
};
// Returns true if given tree is BST.
bool isBST(Node* root, Node* l=NULL, Node* r=NULL)
{
// Base condition
if (root == NULL)
return true;
// if left node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. left node's data
// should be less than root's data
if (l != NULL and root->data <= l->data)
return false;
// if right node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. right node's data
// should be greater than root's data
if (r != NULL and root->data >= r->data)
return false;
// check recursively for every node.
return isBST(root->left, l, root) and
isBST(root->right, root, r);
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node *root = newNode(3);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(5);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(4);
if (isBST(root,NULL,NULL))
cout << "Is BST";
else
cout << "Not a BST";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to check if a given tree is BST.
class Sol
{
// A binary tree node has data, pointer to
//left child && a pointer to right child /
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
// Returns true if given tree is BST.
static boolean isBST(Node root, Node l, Node r)
{
// Base condition
if (root == null)
return true;
// if left node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. left node's data
// should be less than root's data
if (l != null && root.data <= l.data)
return false;
// if right node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. right node's data
// should be greater than root's data
if (r != null && root.data >= r.data)
return false;
// check recursively for every node.
return isBST(root.left, l, root) &&
isBST(root.right, root, r);
}
// Helper function that allocates a new node with the
//given data && null left && right pointers. /
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = newNode(3);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(1);
root.left.right = newNode(4);
if (isBST(root,null,null))
System.out.print("Is BST");
else
System.out.print("Not a BST");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Python3
""" Program to check if a given Binary
Tree is balanced like a Red-Black Tree """
# Helper function that allocates a new
# node with the given data and None
# left and right poers.
class newNode:
# Construct to create a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Returns true if given tree is BST.
def isBST(root, l = None, r = None):
# Base condition
if (root == None) :
return True
# if left node exist then check it has
# correct data or not i.e. left node's data
# should be less than root's data
if (l != None and root.data <= l.data) :
return False
# if right node exist then check it has
# correct data or not i.e. right node's data
# should be greater than root's data
if (r != None and root.data >= r.data) :
return False
# check recursively for every node.
return isBST(root.left, l, root) and \
isBST(root.right, root, r)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(3)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(5)
root.right.left = newNode(1)
root.right.right = newNode(4)
#root.right.left.left = newNode(40)
if (isBST(root,None,None)):
print("Is BST")
else:
print("Not a BST")
# This code is contributed by
# Shubham Singh(SHUBHAMSINGH10)
C#
// C# program to check if a given tree is BST.
using System;
class GFG
{
// A binary tree node has data, pointer to
//left child && a pointer to right child /
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
};
// Returns true if given tree is BST.
static Boolean isBST(Node root, Node l, Node r)
{
// Base condition
if (root == null)
return true;
// if left node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. left node's data
// should be less than root's data
if (l != null && root.data <= l.data)
return false;
// if right node exist then check it has
// correct data or not i.e. right node's data
// should be greater than root's data
if (r != null && root.data >= r.data)
return false;
// check recursively for every node.
return isBST(root.left, l, root) &&
isBST(root.right, root, r);
}
// Helper function that allocates a new node with the
//given data && null left && right pointers. /
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = newNode(3);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(1);
root.left.right = newNode(4);
if (isBST(root,null,null))
Console.Write("Is BST");
else
Console.Write("Not a BST");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
输出 :
Not a BST感谢Abhinesh Garhwal建议上述解决方案。
方法4(使用有序遍历)
感谢LJW489建议这种方法。
1)对给定的树进行有序遍历,并将结果存储在临时数组中。
2)此方法假定树中没有重复的值
3)检查temp数组是否按升序排序,如果是,则树为BST。
时间复杂度:O(n)
我们可以避免使用辅助阵列。在进行有序遍历时,我们可以跟踪先前访问的节点。如果当前访问的节点的值小于先前的值,则树不是BST。感谢ygos进行此空间优化。
C++
bool isBST(node* root)
{
static node *prev = NULL;
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion
// and keep track of prev node
if (root)
{
if (!isBST(root->left))
return false;
// Allows only distinct valued nodes
if (prev != NULL &&
root->data <= prev->data)
return false;
prev = root;
return isBST(root->right);
}
return true;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
bool isBST(struct node* root)
{
static struct node *prev = NULL;
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion and keep track of prev node
if (root)
{
if (!isBST(root->left))
return false;
// Allows only distinct valued nodes
if (prev != NULL && root->data <= prev->data)
return false;
prev = root;
return isBST(root->right);
}
return true;
}
Java
// Java implementation to check if given Binary tree
// is a BST or not
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of the Binary Tree
Node root;
// To keep tract of previous node in Inorder Traversal
Node prev;
boolean isBST() {
prev = null;
return isBST(root);
}
/* Returns true if given search tree is binary
search tree (efficient version) */
boolean isBST(Node node)
{
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion and
// keep a track of previous node
if (node != null)
{
if (!isBST(node.left))
return false;
// allows only distinct values node
if (prev != null && node.data <= prev.data )
return false;
prev = node;
return isBST(node.right);
}
return true;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(4);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(3);
if (tree.isBST())
System.out.println("IS BST");
else
System.out.println("Not a BST");
}
}
Python3
# Python implementation to check if
# given Binary tree is a BST or not
# A binary tree node containing data
# field, left and right pointers
class Node:
# constructor to create new node
def __init__(self, val):
self.data = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
# global variable prev - to keep track
# of previous node during Inorder
# traversal
prev = None
# function to check if given binary
# tree is BST
def isbst(root):
# prev is a global variable
global prev
prev = None
return isbst_rec(root)
# Helper function to test if binary
# tree is BST
# Traverse the tree in inorder fashion
# and keep track of previous node
# return true if tree is Binary
# search tree otherwise false
def isbst_rec(root):
# prev is a global variable
global prev
# if tree is empty return true
if root is None:
return True
if isbst_rec(root.left) is False:
return False
# if previous node'data is found
# greater than the current node's
# data return fals
if prev is not None and prev.data > root.data:
return False
# store the current node in prev
prev = root
return isbst_rec(root.right)
# driver code to test above function
root = Node(4)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(5)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(3)
if isbst(root):
print("is BST")
else:
print("not a BST")
# This code is contributed by
# Shweta Singh(shweta44)
C#
// C# implementation to check if
// given Binary tree is a BST or not
using System;
/* Class containing left and
right child of current node
and key value*/
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of the Binary Tree
Node root;
// To keep tract of previous node
// in Inorder Traversal
Node prev;
Boolean isBST()
{
prev = null;
return isBST(root);
}
/* Returns true if given search tree is binary
search tree (efficient version) */
Boolean isBST(Node node)
{
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion and
// keep a track of previous node
if (node != null)
{
if (!isBST(node.left))
return false;
// allows only distinct values node
if (prev != null &&
node.data <= prev.data )
return false;
prev = node;
return isBST(node.right);
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(4);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(3);
if (tree.isBST())
Console.WriteLine("IS BST");
else
Console.WriteLine("Not a BST");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
也可以通过使用对上一个节点的引用作为参数来避免使用静态变量。
C++
// C++ program to check if a given tree is BST.
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to
left child and a pointer to right child */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
bool isBSTUtil(struct Node* root, Node *&prev)
{
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion and
// keep track of prev node
if (root)
{
if (!isBSTUtil(root->left, prev))
return false;
// Allows only distinct valued nodes
if (prev != NULL && root->data <= prev->data)
return false;
prev = root;
return isBSTUtil(root->right, prev);
}
return true;
}
bool isBST(Node *root)
{
Node *prev = NULL;
return isBSTUtil(root, prev);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node *root = new Node(3);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(5);
root->left->left = new Node(1);
root->left->right = new Node(4);
if (isBST(root))
cout << "Is BST";
else
cout << "Not a BST";
return 0;
}
Python3
# Python3 program to check
# if a given tree is BST.
import math
# A binary tree node has data,
# pointer to left child and
# a pointer to right child
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def isBSTUtil(root, prev):
# traverse the tree in inorder fashion
# and keep track of prev node
if (root != None):
if (isBSTUtil(root.left, prev) == True):
return False
# Allows only distinct valued nodes
if (prev != None and
root.data <= prev.data):
return False
prev = root
return isBSTUtil(root.right, prev)
return True
def isBST(root):
prev = None
return isBSTUtil(root, prev)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(3)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(1)
root.right.right = Node(4)
#root.right.left.left = Node(40)
if (isBST(root) == None):
print("Is BST")
else:
print("Not a BST")
# This code is contributed by Srathore
C#
// C# program to check if a given tree is BST.
using System;
public class GFG
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to
left child and a pointer to right child */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
};
static Node prev;
static Boolean isBSTUtil(Node root)
{
// traverse the tree in inorder fashion and
// keep track of prev node
if (root != null)
{
if (!isBSTUtil(root.left))
return false;
// Allows only distinct valued nodes
if (prev != null &&
root.data <= prev.data)
return false;
prev = root;
return isBSTUtil(root.right);
}
return true;
}
static Boolean isBST(Node root)
{
return isBSTUtil(root);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(3);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(4);
if (isBST(root))
Console.WriteLine("Is BST");
else
Console.WriteLine("Not a BST");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
输出:
Not a BST