C / C++中的数组或任何一种编程语言中的数组都是存储在连续内存位置中的相似数据项的集合,并且可以使用数组的索引随机访问元素。它们可用于存储原始数据类型的集合,例如任何特定类型的int,float,double,char等。另外,C / C++中的数组可以存储派生的数据类型,例如结构,指针等。下面给出的是数组的图片表示形式。
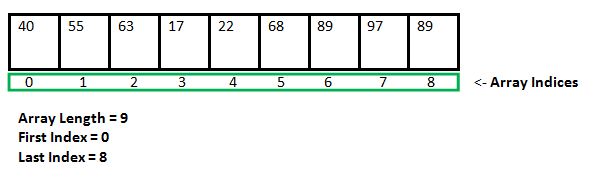
为什么需要数组?
当对象较少时,可以使用普通变量(v1,v2,v3,..),但是如果要存储大量实例,则很难使用普通变量来管理它们。数组的想法是在一个变量中表示许多实例。
C / C++中的数组声明:
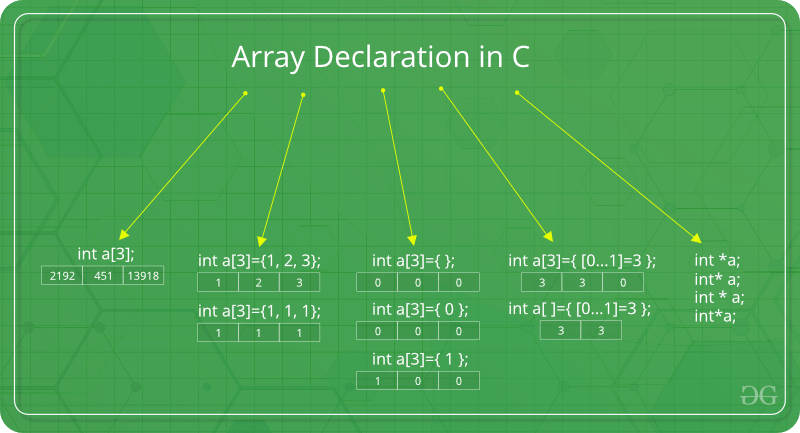
注意:在上面的图片中int a [3] = {[0…1] = 3};自GCC 2.5起,这种声明就已经过时了
我们可以通过多种方式声明数组。可以通过指定其类型和大小,对其进行初始化或同时对两者进行初始化来完成。
通过指定大小声明数组
C
// Array declaration by specifying size
int arr1[10];
// With recent C/C++ versions, we can also
// declare an array of user specified size
int n = 10;
int arr2[n];C
// Array declaration by initializing elements
int arr[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 }
// Compiler creates an array of size 4.
// above is same as "int arr[4] = {10, 20, 30, 40}"C
// Array declaration by specifying size and initializing
// elements
int arr[6] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 }
// Compiler creates an array of size 6, initializes first
// 4 elements as specified by user and rest two elements as
// 0. above is same as "int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 0, 0}"C
#include
int main()
{
int arr[5];
arr[0] = 5;
arr[2] = -10;
arr[3 / 2] = 2; // this is same as arr[1] = 2
arr[3] = arr[0];
printf("%d %d %d %d", arr[0],
arr[1], arr[2], arr[3]);
return 0;
} C++
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[5];
arr[0] = 5;
arr[2] = -10;
// this is same as arr[1] = 2
arr[3 / 2] = 2;
arr[3] = arr[0];
cout << arr[0] << " " << arr[1] << " " << arr[2] << " "
<< arr[3];
return 0;
} C
// This C program compiles fine
// as index out of bound
// is not checked in C.
#include
int main()
{
int arr[2];
printf("%d ", arr[3]);
printf("%d ", arr[-2]);
return 0;
} C++
// This C++ program compiles fine
// as index out of bound
// is not checked in C.
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[2];
cout << arr[3] << " ";
cout << arr[-2] << " ";
return 0;
} C
#include
int main()
{
// Array declaration by initializing it
// with more elements than specified size.
int arr[2] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
return 0;
} C
// C program to demonstrate that
// array elements are stored
// contiguous locations
#include
int main()
{
// an array of 10 integers.
// If arr[0] is stored at
// address x, then arr[1] is
// stored at x + sizeof(int)
// arr[2] is stored at x +
// sizeof(int) + sizeof(int)
// and so on.
int arr[5], i;
printf("Size of integer in this compiler is %lu\n",
sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
// The use of '&' before a variable name, yields
// address of variable.
printf("Address arr[%d] is %p\n", i, &arr[i]);
return 0;
} C++
// C++ program to demonstrate that array elements
// are stored contiguous locations
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// an array of 10 integers.
// If arr[0] is stored at
// address x, then arr[1] is
// stored at x + sizeof(int)
// arr[2] is stored at x +
// sizeof(int) + sizeof(int)
// and so on.
int arr[5], i;
cout << "Size of integer in this compiler is "
<< sizeof(int) << "\n";
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
// The use of '&' before a variable name, yields
// address of variable.
cout << "Address arr[" << i << "] is " << &arr[i]
<< "\n";
return 0;
} C++
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[6]={11,12,13,14,15,16};
// Way -1
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
cout< 通过初始化元素进行数组声明
C
// Array declaration by initializing elements
int arr[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 }
// Compiler creates an array of size 4.
// above is same as "int arr[4] = {10, 20, 30, 40}"
通过指定大小和初始化元素进行数组声明
C
// Array declaration by specifying size and initializing
// elements
int arr[6] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 }
// Compiler creates an array of size 6, initializes first
// 4 elements as specified by user and rest two elements as
// 0. above is same as "int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 0, 0}"
C / C++中的数组的优点:
- 使用数组索引随机访问元素。
- 使用较少的代码行,因为它创建了多个元素的单个数组。
- 轻松访问所有元素。
- 使用单个循环,遍历数组变得很容易。
- 排序变得很容易,因为可以通过编写更少的代码行来完成排序。
C / C++中数组的缺点:
- 允许输入固定数量的元素,这些元素是在声明时决定的。与链接列表不同,C语言中的数组不是动态的。
- 元素的插入和删除可能会很昂贵,因为需要根据新的内存分配来管理元素。
关于C / C++中的数组的事实:
- 访问数组元素:
数组元素是通过使用整数索引访问的。数组索引从0开始,一直到数组大小减去1。 - 数组的名称也是指向数组第一个元素的指针。
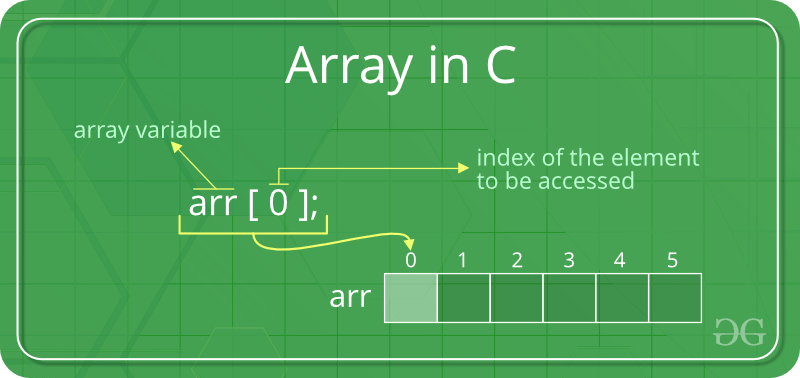
例子:
C
#include
int main()
{
int arr[5];
arr[0] = 5;
arr[2] = -10;
arr[3 / 2] = 2; // this is same as arr[1] = 2
arr[3] = arr[0];
printf("%d %d %d %d", arr[0],
arr[1], arr[2], arr[3]);
return 0;
}
C++
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[5];
arr[0] = 5;
arr[2] = -10;
// this is same as arr[1] = 2
arr[3 / 2] = 2;
arr[3] = arr[0];
cout << arr[0] << " " << arr[1] << " " << arr[2] << " "
<< arr[3];
return 0;
}
没有索引越界检查:
在C / C++中,没有没有超出范围的索引检查,例如,以下程序可以很好地编译,但是在运行时可能会产生意外的输出。
C
// This C program compiles fine
// as index out of bound
// is not checked in C.
#include
int main()
{
int arr[2];
printf("%d ", arr[3]);
printf("%d ", arr[-2]);
return 0;
}
C++
// This C++ program compiles fine
// as index out of bound
// is not checked in C.
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[2];
cout << arr[3] << " ";
cout << arr[-2] << " ";
return 0;
}
-449684907 4195777 在C语言中,使用比指定大小更多的元素初始化数组不是编译器错误。例如,下面的程序可以正常编译并仅显示警告。
C
#include
int main()
{
// Array declaration by initializing it
// with more elements than specified size.
int arr[2] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
return 0;
}
警告:
prog.c: In function 'main':
prog.c:7:25: warning: excess elements in array initializer
int arr[2] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
^
prog.c:7:25: note: (near initialization for 'arr')
prog.c:7:29: warning: excess elements in array initializer
int arr[2] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
^
prog.c:7:29: note: (near initialization for 'arr')
prog.c:7:33: warning: excess elements in array initializer
int arr[2] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
^
prog.c:7:33: note: (near initialization for 'arr')- 注意:该程序无法在C++中编译。如果将上述程序另存为.cpp,则程序会生成编译器错误“错误:’int [2]’的初始化函数太多” 。
元素存储在连续的内存位置
例子:
C
// C program to demonstrate that
// array elements are stored
// contiguous locations
#include
int main()
{
// an array of 10 integers.
// If arr[0] is stored at
// address x, then arr[1] is
// stored at x + sizeof(int)
// arr[2] is stored at x +
// sizeof(int) + sizeof(int)
// and so on.
int arr[5], i;
printf("Size of integer in this compiler is %lu\n",
sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
// The use of '&' before a variable name, yields
// address of variable.
printf("Address arr[%d] is %p\n", i, &arr[i]);
return 0;
}
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate that array elements
// are stored contiguous locations
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// an array of 10 integers.
// If arr[0] is stored at
// address x, then arr[1] is
// stored at x + sizeof(int)
// arr[2] is stored at x +
// sizeof(int) + sizeof(int)
// and so on.
int arr[5], i;
cout << "Size of integer in this compiler is "
<< sizeof(int) << "\n";
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
// The use of '&' before a variable name, yields
// address of variable.
cout << "Address arr[" << i << "] is " << &arr[i]
<< "\n";
return 0;
}
Size of integer in this compiler is 4
Address arr[0] is 0x7ffe75c32210
Address arr[1] is 0x7ffe75c32214
Address arr[2] is 0x7ffe75c32218
Address arr[3] is 0x7ffe75c3221c
Address arr[4] is 0x7ffe75c32220遍历数组的另一种方法
C++
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[6]={11,12,13,14,15,16};
// Way -1
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
cout< 11 12 13 14 15 16
By Other Method:
11 12 13 14 15 16 数组与指针
数组和指针是两个不同的东西(我们可以通过应用sizeof进行检查)。发生混乱是因为数组名称指示第一个元素的地址,并且数组始终作为指针传递(即使我们使用方括号)。请参阅C中的指针和数组之间的区别?更多细节。
C++中的向量是什么?
C++中的向量是STL中的一个代表数组的类。向量比普通阵列的优势在于,
- 声明向量时,我们不需要传递大小作为额外的参数,即向量支持动态大小(我们不必最初指定向量的大小)。我们还可以调整向量的大小。
- 向量具有许多内置函数,例如删除元素等。
要了解有关vector提供的功能的更多信息,请参考C++中的vector以获得更多详细信息。