前提条件: IEEE标准754浮点数
编写程序以找出给定实际值的32位单精度IEEE 754浮点表示,反之亦然。
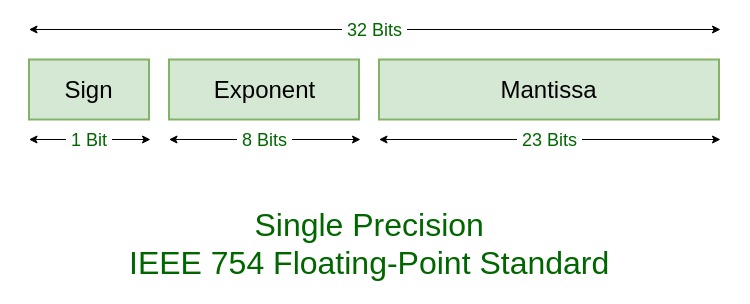
例子:
Input: real number = 16.75
Output: 0 | 10000011 | 00001100000000000000000
Input: floating point number = 0 | 10000011 | 00001100000000000000000
Output: 16.75
方法:
此实现基于C中的联合数据类型,并使用位字段的概念。
当我们不需要通常分配给某些变量的完整内存,但我们想限制这些变量占用的内存量时,便会分配位字段。在C语言中,Union的成员共享公共内存空间,因此我们一次只能访问一个成员。
下面是上述方法的实现:
程序1:将实数值转换为其浮点表示形式
C
// C program to convert a real value
// to IEEE 754 floating point representaion
#include
void printBinary(int n, int i)
{
// Prints the binary representation
// of a number n up to i-bits.
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
if ((n >> k) & 1)
printf("1");
else
printf("0");
}
}
typedef union {
float f;
struct
{
// Order is important.
// Here the members of the union data structure
// use the same memory (32 bits).
// The ordering is taken
// from the LSB to the MSB.
unsigned int mantissa : 23;
unsigned int exponent : 8;
unsigned int sign : 1;
} raw;
} myfloat;
// Function to convert real value
// to IEEE foating point representation
void printIEEE(myfloat var)
{
// Prints the IEEE 754 representation
// of a float value (32 bits)
printf("%d | ", var.raw.sign);
printBinary(var.raw.exponent, 8);
printf(" | ");
printBinary(var.raw.mantissa, 23);
printf("\n");
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Instantiate the union
myfloat var;
// Get the real value
var.f = -2.25;
// Get the IEEE floating point representation
printf("IEEE 754 representation of %f is : \n",
var.f);
printIEEE(var);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python program to convert a real value
# to IEEE 754 Floating Point Representation.
# Function to convert a
# fraction to binary form.
def binaryOfFraction(fraction):
# Declaring an empty string
# to store binary bits.
binary = str()
# Iterating through
# fraction until it
# becomes Zero.
while (fraction):
# Multiplying fraction by 2.
fraction *= 2
# Storing Integer Part of
# Fraction in int_part.
if (fraction >= 1):
int_part = 1
fraction -= 1
else:
int_part = 0
# Adding int_part to binary
# after every iteration.
binary += str(int_part)
# Returning the binary string.
return binary
# Function to get sign bit,
# exp bits and mantissa bits,
# from given real no.
def floatingPoint(real_no):
# Setting Sign bit
# default to zero.
sign_bit = 0
# Sign bit will set to
# 1 for negative no.
if(real_no < 0):
sign_bit = 1
# converting given no. to
# absolute value as we have
# already set the sign bit.
real_no = abs(real_no)
# Converting Integer Part
# of Real no to Binary
int_str = bin(int(real_no))[2 : ]
# Function call to convert
# Fraction part of real no
# to Binary.
fraction_str = binaryOfFraction(real_no - int(real_no))
# Getting the index where
# Bit was high for the first
# Time in binary repres
# of Integer part of real no.
ind = int_str.index('1')
# The Exponent is the no.
# By which we have right
# Shifted the decimal and
# it is given below.
# Also converting it to bias
# exp by adding 127.
exp_str = bin((len(int_str) - ind - 1) + 127)[2 : ]
# getting mantissa string
# By adding int_str and fraction_str.
# the zeroes in MSB of int_str
# have no significance so they
# are ignored by slicing.
mant_str = int_str[ind + 1 : ] + fraction_str
# Adding Zeroes in LSB of
# mantissa string so as to make
# it's length of 23 bits.
mant_str = mant_str + ('0' * (23 - len(mant_str)))
# Returning the sign, Exp
# and Mantissa Bit strings.
return sign_bit, exp_str, mant_str
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Function call to get
# Sign, Exponent and
# Mantissa Bit Strings.
sign_bit, exp_str, mant_str = floatingPoint(-2.250000)
# Final Floating point Representation.
ieee_32 = str(sign_bit) + '|' + exp_str + '|' + mant_str
# Printing the ieee 32 represenation.
print("IEEE 754 representation of -2.250000 is :")
print(ieee_32)C
// C program to convert
// IEEE 754 floating point representaion
// into real value
#include
#include
typedef union {
float f;
struct
{
// Order is important.
// Here the members of the union data structure
// use the same memory (32 bits).
// The ordering is taken
// from the LSB to the MSB.
unsigned int mantissa : 23;
unsigned int exponent : 8;
unsigned int sign : 1;
} raw;
} myfloat;
// Function to convert a binary array
// to the corresponding integer
unsigned int convertToInt(int* arr, int low, int high)
{
unsigned f = 0, i;
for (i = high; i >= low; i--) {
f = f + arr[i] * pow(2, high - i);
}
return f;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Get the 32-bit floating point number
unsigned int ieee[32]
= { 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
myfloat var;
// Convert the least significant
// mantissa part (23 bits)
// to corresponding decimal integer
unsigned f = convertToInt(ieee, 9, 31);
// Assign integer representation of mantissa
var.raw.mantissa = f;
// Convert the exponent part (8 bits)
// to a corresponding decimal integer
f = convertToInt(ieee, 1, 8);
// Assign integer representation
// of the exponent
var.raw.exponent = f;
// Assign sign bit
var.raw.sign = ieee[0];
printf("The float value of the given"
" IEEE-754 representation is : \n");
printf("%f", var.f);
} Python3
# Python program to convert
# IEEE 754 floating point representation
# into real value
# Function to convert Binary
# of Mantissa to float value.
def convertToInt(mantissa_str):
# variable to make a count
# of negative power of 2.
power_count = -1
# variable to store
# float value of mantissa.
mantissa_int = 0
# Iterations through binary
# Number. Standard form of
# Mantissa is 1.M so we have
# 0.M therefore we are taking
# negative powers on 2 for
# conversion.
for i in mantissa_str:
# Adding converted value of
# Binary bits in every
# iteration to float mantissa.
mantissa_int += (int(i) * pow(2, power_count))
# count will decrease by 1
# as we move toward right.
power_count -= 1
# returning mantissa in 1.M form.
return (mantissa_int + 1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Floating Point Representation
# to be converted into real
# value.
ieee_32 = '1|10000000|00100000000000000000000'
# First bit will be sign bit.
sign_bit = int(ieee_32[0])
# Next 8 bits will be
# Exponent Bits in Biased
# form.
exponent_bias = int(ieee_32[2 : 10], 2)
# In 32 Bit format bias
# value is 127 so to have
# unbiased exponent
# subtract 127.
exponent_unbias = exponent_bias - 127
# Next 23 Bits will be
# Mantissa (1.M format)
mantissa_str = ieee_32[11 : ]
# Function call to convert
# 23 binary bits into
# 1.M real no. form
mantissa_int = convertToInt(mantissa_str)
# The final real no. obtained
# by sign bit, mantissa and
# Exponent.
real_no = pow(-1, sign_bit) * mantissa_int * pow(2, exponent_unbias)
# Printing the obtained
# Real value of floating
# Point Representaion.
print("The float value of the given IEEE-754 representation is :",real_no)输出:
IEEE 754 representation of -2.250000 is :
1 | 10000000 | 00100000000000000000000
程序2:将浮点表示形式转换为其实际值
C
// C program to convert
// IEEE 754 floating point representaion
// into real value
#include
#include
typedef union {
float f;
struct
{
// Order is important.
// Here the members of the union data structure
// use the same memory (32 bits).
// The ordering is taken
// from the LSB to the MSB.
unsigned int mantissa : 23;
unsigned int exponent : 8;
unsigned int sign : 1;
} raw;
} myfloat;
// Function to convert a binary array
// to the corresponding integer
unsigned int convertToInt(int* arr, int low, int high)
{
unsigned f = 0, i;
for (i = high; i >= low; i--) {
f = f + arr[i] * pow(2, high - i);
}
return f;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Get the 32-bit floating point number
unsigned int ieee[32]
= { 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
myfloat var;
// Convert the least significant
// mantissa part (23 bits)
// to corresponding decimal integer
unsigned f = convertToInt(ieee, 9, 31);
// Assign integer representation of mantissa
var.raw.mantissa = f;
// Convert the exponent part (8 bits)
// to a corresponding decimal integer
f = convertToInt(ieee, 1, 8);
// Assign integer representation
// of the exponent
var.raw.exponent = f;
// Assign sign bit
var.raw.sign = ieee[0];
printf("The float value of the given"
" IEEE-754 representation is : \n");
printf("%f", var.f);
}
Python3
# Python program to convert
# IEEE 754 floating point representation
# into real value
# Function to convert Binary
# of Mantissa to float value.
def convertToInt(mantissa_str):
# variable to make a count
# of negative power of 2.
power_count = -1
# variable to store
# float value of mantissa.
mantissa_int = 0
# Iterations through binary
# Number. Standard form of
# Mantissa is 1.M so we have
# 0.M therefore we are taking
# negative powers on 2 for
# conversion.
for i in mantissa_str:
# Adding converted value of
# Binary bits in every
# iteration to float mantissa.
mantissa_int += (int(i) * pow(2, power_count))
# count will decrease by 1
# as we move toward right.
power_count -= 1
# returning mantissa in 1.M form.
return (mantissa_int + 1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Floating Point Representation
# to be converted into real
# value.
ieee_32 = '1|10000000|00100000000000000000000'
# First bit will be sign bit.
sign_bit = int(ieee_32[0])
# Next 8 bits will be
# Exponent Bits in Biased
# form.
exponent_bias = int(ieee_32[2 : 10], 2)
# In 32 Bit format bias
# value is 127 so to have
# unbiased exponent
# subtract 127.
exponent_unbias = exponent_bias - 127
# Next 23 Bits will be
# Mantissa (1.M format)
mantissa_str = ieee_32[11 : ]
# Function call to convert
# 23 binary bits into
# 1.M real no. form
mantissa_int = convertToInt(mantissa_str)
# The final real no. obtained
# by sign bit, mantissa and
# Exponent.
real_no = pow(-1, sign_bit) * mantissa_int * pow(2, exponent_unbias)
# Printing the obtained
# Real value of floating
# Point Representaion.
print("The float value of the given IEEE-754 representation is :",real_no)
输出:
The float value of the given IEEE-754 representation is :
-2.250000
想要从精选的最佳视频中学习和练习问题,请查看《基础知识到高级C的C基础课程》。