先决条件:IEEE标准754浮点数
给定一个浮点数,任务是通过IEEE 754标准找到该数的十六进制表示形式。
IEEE浮点算术标准(IEEE 754)是浮点计算的技术标准,由电气和电子工程师协会(IEEE)于1985年建立。该标准解决了在各种浮点实现中发现的许多问题,这些问题使它们难以可靠使用并降低了可移植性。 IEEE标准754浮点数是当今计算机上实数的最常见表示形式,包括基于Intel的PC,Mac和大多数Unix平台。 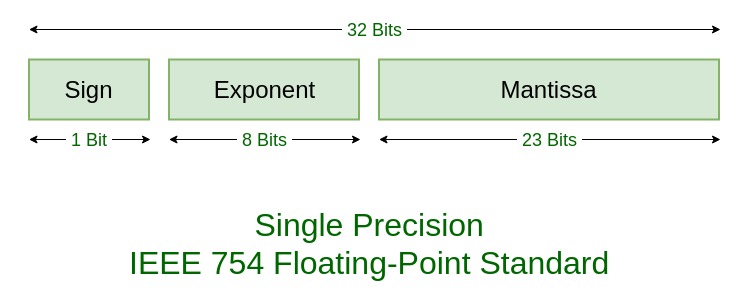
例子 :
Input : -6744.90
Output : C5D2C733
Input : -263.3
Output : C383A666
方法 :
- 检查数字是正数还是负数。将符号另存为0(表示正数)和1(表示负数),然后将数字转换为正数(如果为负数)。
- 将浮点数转换为二进制。
- 将小数部分和整数部分分开。
- 计算指数(E)并将其转换为二进制。
- 找到尾数。
- 合并尾数,指数和尾数的符号。
- 将其转换为十六进制。
让我们编写一个Python程序,以IEEE 754标准将浮点数表示为十六进制。
# Function for converting decimal to binary
def float_bin(my_number, places = 3):
my_whole, my_dec = str(my_number).split(".")
my_whole = int(my_whole)
res = (str(bin(my_whole))+".").replace('0b','')
for x in range(places):
my_dec = str('0.')+str(my_dec)
temp = '%1.20f' %(float(my_dec)*2)
my_whole, my_dec = temp.split(".")
res += my_whole
return res
def IEEE754(n) :
# identifying whether the number
# is positive or negative
sign = 0
if n < 0 :
sign = 1
n = n * (-1)
p = 30
# convert float to binary
dec = float_bin (n, places = p)
dotPlace = dec.find('.')
onePlace = dec.find('1')
# finding the mantissa
if onePlace > dotPlace:
dec = dec.replace(".","")
onePlace -= 1
dotPlace -= 1
elif onePlace < dotPlace:
dec = dec.replace(".","")
dotPlace -= 1
mantissa = dec[onePlace+1:]
# calculating the exponent(E)
exponent = dotPlace - onePlace
exponent_bits = exponent + 127
# converting the exponent from
# decimal to binary
exponent_bits = bin(exponent_bits).replace("0b",'')
mantissa = mantissa[0:23]
# the IEEE754 notation in binary
final = str(sign) + exponent_bits.zfill(8) + mantissa
# convert the binary to hexadecimal
hstr = '0x%0*X' %((len(final) + 3) // 4, int(final, 2))
return (hstr, final)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
print (IEEE754(263.3))
print (IEEE754(-263.3))
输出:
4383A666
C383A666