运算符重载:
C++ provides a special function to change the current functionality of some operators within its class which is often called as operator overloading. Operator Overloading is the method by which we can change the function of some specific operators to do some different task.
这可以通过声明函数来实现,其语法为:
Return_Type classname :: operator op(Argument list)
{
Function Body
}在上面的语法中, Return_Type是要返回到另一个对象的值类型, operator op是函数,其中operator是关键字,而op是要重载的运算符。
操作员函数必须是非静态的(成员函数)或朋友函数。
操作员重载可以通过三种方法来完成,它们是
- 重载一元运算运算符。
- 重载二元运算符。
- 使用朋友函数重载二进制运算符。
以下是定义运算符函数的一些标准/规则:
- 如果是非静态函数,则二元运算符应仅具有一个参数,一元运算符不应具有参数。
- 对于朋友函数,二元运算符应仅具有两个参数,一元运算符应仅具有一个参数。
- 如果实现了运算符重载,则所有类成员对象都应该是公共的。
- 不能重载的运算符是。 。* :: ?:
- 将函数声明为好友函数= () [] ->时,不能使用运算符重载。
请参阅此,以了解更多操作员重载规则
- 重载一元运算符:让我们考虑重载(-)一元运算运算符。在一元运算运算符函数,不应传递任何参数。它仅适用于一个类对象。它是对单个操作数进行操作的运算符的重载。
例子:
假设距离类采用两个成员对象,即英尺和英寸,则创建一个函数,距离对象应通过该函数将英尺和英寸的值减1(具有距离类型的单个操作数)。// C++ program to show unary operator overloading #includeusing namespace std; class Distance { public: // Member Object int feet, inch; // Constructor to initialize the object's value Distance(int f, int i) { this->feet = f; this->inch = i; } // Overloading(-) operator to perform decrement // operation of Distance object void operator-() { feet--; inch--; cout << "\nFeet & Inches(Decrement): " << feet << "'" << inch; } }; // Driver Code int main() { // Declare and Initialize the constructor Distance d1(8, 9); // Use (-) unary operator by single operand -d1; return 0; } 输出:Feet & Inches(Decrement): 7'8在上面的程序中,它表明没有传递任何参数并且没有返回return_type值,因为一元运算运算符对单个操作数起作用。 (-)运算符将功能更改为其成员函数。
注意:
d2 = -d1将不起作用,因为运算符-()不返回任何值。 - 重载二元运算符:在二元运算符重载函数,应传递一个参数。这是对两个操作数进行操作的运算符的重载。
让我们以距离类的相同示例为例,但是这次添加两个距离对象。
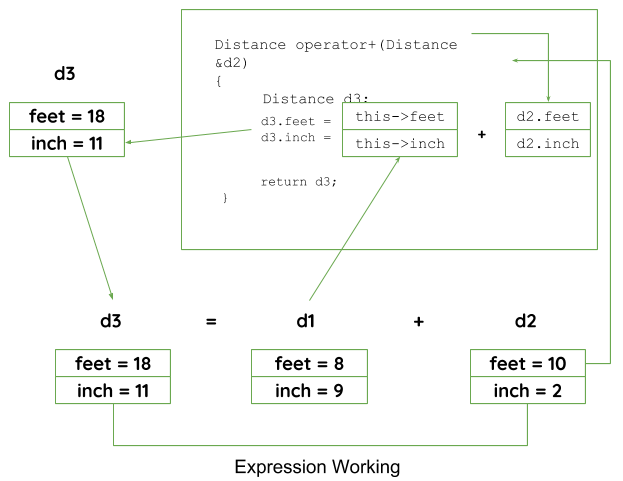
// C++ program to show binary operator overloading #includeusing namespace std; class Distance { public: // Member Object int feet, inch; // No Parameter Constructor Distance() { this->feet = 0; this->inch = 0; } // Constructor to initialize the object's value // Parametrized Constructor Distance(int f, int i) { this->feet = f; this->inch = i; } // Overloading (+) operator to perform addition of // two distance object Distance operator+(Distance& d2) // Call by reference { // Create an object to return Distance d3; // Perform addition of feet and inches d3.feet = this->feet + d2.feet; d3.inch = this->inch + d2.inch; // Return the resulting object return d3; } }; // Driver Code int main() { // Declaring and Initializing first object Distance d1(8, 9); // Declaring and Initializing second object Distance d2(10, 2); // Declaring third object Distance d3; // Use overloaded operator d3 = d1 + d2; // Display the result cout << "\nTotal Feet & Inches: " << d3.feet << "'" << d3.inch; return 0; } 输出:Total Feet & Inches: 18'11在上面的程序中,
见行号26 ,Distance operator+(Distance &d2),这里函数的返回类型是distance,它使用引用调用来传递参数。
见行号49 ,d3 = d1 + d2;在这里,D1调用它的类对象的运算符函数,并采用D2作为参数,通过运算符函数返回的对象,结果将在D3对象反映。二元运算符工作原理图:
- 使用Friend函数重载Binary运算符:在这种方法中,运算符重载函数必须以friend关键字开头,并声明一个函数类范围。请记住,Friend运算符函数在一个二进制运算符采用两个参数,在一个一元运算运算符改变一个参数。所有工作和实现都将与二进制运算符函数相同,只是此函数将在类范围之外实现。
让我们使用friend函数举一个相同的例子。
// C++ program to show binary operator overloading #includeusing namespace std; class Distance { public: // Member Object int feet, inch; // No Parameter Constructor Distance() { this->feet = 0; this->inch = 0; } // Constructor to initialize the object's value // Parametrized Constructor Distance(int f, int i) { this->feet = f; this->inch = i; } // Declaring friend function using friend keyword friend Distance operator+(Distance&, Distance&); }; // Implementing friend function with two parameters Distance operator+(Distance& d1, Distance& d2) // Call by reference { // Create an object to return Distance d3; // Perform addition of feet and inches d3.feet = d1.feet + d2.feet; d3.inch = d1.inch + d2.inch; // Return the resulting object return d3; } // Driver Code int main() { // Declaring and Initializing first object Distance d1(8, 9); // Declaring and Initializing second object Distance d2(10, 2); // Declaring third object Distance d3; // Use overloaded operator d3 = d1 + d2; // Display the result cout << "\nTotal Feet & Inches: " << d3.feet << "'" << d3.inch; return 0; } 输出:Total Feet & Inches: 18'11在这里,在上述程序中,运算符函数由宣称函数作为朋友函数实现类范围之外。
在这些方式中,运算符可以被重载通过改变运算符的功能,以执行某些任务。