在本文中,我们将讨论插入排序和选择排序之间的区别:
插入排序是一种简单的排序算法,其工作方式类似于您手中对扑克牌进行排序的方式。该数组实际上被分为一个已排序部分和一个未排序部分。挑选未排序部分中的值,并将其放置在已排序部分中的正确位置。
算法:
要按升序对大小为n的数组进行排序:
- 在数组上从arr [1]迭代到arr [n]。
- 将当前元素(键)与其先前的元素进行比较。
- 如果关键元素小于其前任元素,则将其与之前的元素进行比较。将较大的元素上移一个位置,以为交换的元素留出空间。
下面的图像说明了插入排序:
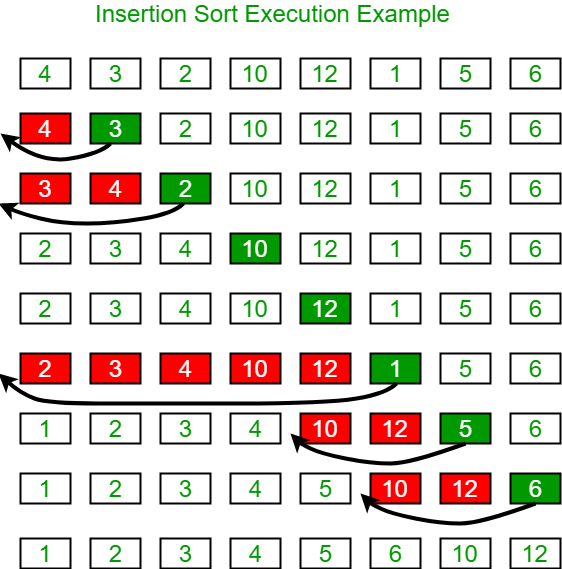
以下是相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program for the insertion sort
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to sort an array using
// insertion sort
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
// Move elements of arr[0..i-1],
// that are greater than key to
// one position ahead of their
// current position
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Function to print an array of size N
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
// Print the array
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function Call
insertionSort(arr, N);
printArray(arr, N);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to sort an array using
// insertion sort
static void insertionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
// Move elements of arr[0..i-1],
// that are greater than key to
// one position ahead of their
// current position
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key)
{
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Function to print an array of size N
static void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
// Print the array
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
int N = arr.length;
// Function Call
insertionSort(arr, N);
printArray(arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by code_hunt.Python3
# Python 3 program for the insertion sort
# Function to sort an array using
# insertion sort
def insertionSort(arr, n):
i = 0
key = 0
j = 0
for i in range(1,n,1):
key = arr[i]
j = i - 1
# Move elements of arr[0..i-1],
# that are greater than key to
# one position ahead of their
# current position
while (j >= 0 and arr[j] > key):
arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
j = j - 1
arr[j + 1] = key
# Function to print an array of size N
def printArray(arr, n):
i = 0
# Print the array
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i],end = " ")
print("\n",end = "")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6]
N = len(arr)
# Function Call
insertionSort(arr, N)
printArray(arr, N)
# This code is contributed by bgangwar59.C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to sort an array using
// insertion sort
static void insertionSort(int[] arr, int n)
{
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
// Move elements of arr[0..i-1],
// that are greater than key to
// one position ahead of their
// current position
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key)
{
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Function to print an array of size N
static void printArray(int[] arr, int n)
{
int i;
// Print the array
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver code
static public void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[] { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
int N = arr.Length;
// Function Call
insertionSort(arr, N);
printArray(arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L VC++
// C++ program for implementation of
// selection sort
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to swap two number
void swap(int* xp, int* yp)
{
int temp = *xp;
*xp = *yp;
*yp = temp;
}
// Function to implement the selection
// sort
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
// One by one move boundary of
// unsorted subarray
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// Find the minimum element
// in unsorted array
min_idx = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
// Swap the found minimum element
// with the first element
swap(&arr[min_idx], &arr[i]);
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function Call
selectionSort(arr, n);
cout << "Sorted array: \n";
// Print the array
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for implementation of
// selection sort
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to implement the selection
// sort
static void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
// One by one move boundary of
// unsorted subarray
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// Find the minimum element
// in unsorted array
min_idx = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
// Swap the found minimum element
// with the first element
int temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx]= arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
// Function to print an array
static void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = arr.length;
// Function Call
selectionSort(arr, n);
System.out.print("Sorted array: \n");
// Print the array
printArray(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995Python3
# Python3 program for implementation of
# selection sort
# Function to implement the selection
# sort
def selectionSort(arr, n):
# One by one move boundary of
# unsorted subarray
for i in range(n - 1):
# Find the minimum element
# in unsorted array
min_idx = i
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx]):
min_idx = j
# Swap the found minimum element
# with the first element
arr[min_idx], arr[i] = arr[i], arr[min_idx]
# Function to print an array
def printArray(arr, size):
for i in range(size):
print(arr[i], end = " ")
print()
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [64, 25, 12, 22, 11]
n = len(arr)
# Function Call
selectionSort(arr, n)
print("Sorted array: ")
# Print the array
printArray(arr, n)
# This code is contributed by ukaspC#
// C# program for implementation of
// selection sort
using System;
public class GFG
{
// Function to implement the selection
// sort
static void selectionSort(int []arr, int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
// One by one move boundary of
// unsorted subarray
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// Find the minimum element
// in unsorted array
min_idx = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
// Swap the found minimum element
// with the first element
int temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx]= arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
// Function to print an array
static void printArray(int []arr, int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Console.Write(arr[i]+ " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []arr = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Function Call
selectionSort(arr, n);
Console.Write("Sorted array: \n");
// Print the array
printArray(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1输出:
5 6 11 12 13选择排序算法通过从未排序部分重复查找最小元素(考虑升序)并将其放在开头来对数组进行排序。该算法在给定数组中维护两个子数组。
- 子数组已经排序。
- 剩余的未排序的子数组。
在选择排序的每次迭代中,都会从未排序的子数组中选取最小元素(考虑升序)并将其移至已排序的子数组。
下面是解释上述步骤的示例:
arr[] = 64 25 12 22 11
// Find the minimum element in arr[0...4]
// and place it at beginning
11 25 12 22 64
// Find the minimum element in arr[1...4]
// and place it at beginning of arr[1...4]
11 12 25 22 64
// Find the minimum element in arr[2...4]
// and place it at beginning of arr[2...4]
11 12 22 25 64
// Find the minimum element in arr[3...4]
// and place it at beginning of arr[3...4]
11 12 22 25 64 以下是相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program for implementation of
// selection sort
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to swap two number
void swap(int* xp, int* yp)
{
int temp = *xp;
*xp = *yp;
*yp = temp;
}
// Function to implement the selection
// sort
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
// One by one move boundary of
// unsorted subarray
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// Find the minimum element
// in unsorted array
min_idx = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
// Swap the found minimum element
// with the first element
swap(&arr[min_idx], &arr[i]);
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function Call
selectionSort(arr, n);
cout << "Sorted array: \n";
// Print the array
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for implementation of
// selection sort
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to implement the selection
// sort
static void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
// One by one move boundary of
// unsorted subarray
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// Find the minimum element
// in unsorted array
min_idx = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
// Swap the found minimum element
// with the first element
int temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx]= arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
// Function to print an array
static void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = arr.length;
// Function Call
selectionSort(arr, n);
System.out.print("Sorted array: \n");
// Print the array
printArray(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
Python3
# Python3 program for implementation of
# selection sort
# Function to implement the selection
# sort
def selectionSort(arr, n):
# One by one move boundary of
# unsorted subarray
for i in range(n - 1):
# Find the minimum element
# in unsorted array
min_idx = i
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx]):
min_idx = j
# Swap the found minimum element
# with the first element
arr[min_idx], arr[i] = arr[i], arr[min_idx]
# Function to print an array
def printArray(arr, size):
for i in range(size):
print(arr[i], end = " ")
print()
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [64, 25, 12, 22, 11]
n = len(arr)
# Function Call
selectionSort(arr, n)
print("Sorted array: ")
# Print the array
printArray(arr, n)
# This code is contributed by ukasp
C#
// C# program for implementation of
// selection sort
using System;
public class GFG
{
// Function to implement the selection
// sort
static void selectionSort(int []arr, int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
// One by one move boundary of
// unsorted subarray
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// Find the minimum element
// in unsorted array
min_idx = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
// Swap the found minimum element
// with the first element
int temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx]= arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
// Function to print an array
static void printArray(int []arr, int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Console.Write(arr[i]+ " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []arr = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Function Call
selectionSort(arr, n);
Console.Write("Sorted array: \n");
// Print the array
printArray(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
输出:
Sorted array:
11 12 22 25 64插入排序和选择排序之间的表格差异:
|
|
Insertion Sort | Selection Sort |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Inserts the value in the presorted array to sort the set of values in the array. | Finds the minimum / maximum number from the list and sort it in ascending / descending order. |
| 2. | It is a stable sorting algorithm. | It is an unstable sorting algorithm. |
| 3. | The best-case time complexity is O(N) when the array is already in ascending order. | There is no best case the time complexity is O(N2) in all cases. |
| 4. | The number of comparison operations performed in this sorting algorithm is less than the swapping performed. | The number of comparison operations performed in this sorting algorithm is more than the swapping performed. |
| 5. | It is more efficient than the Selection sort. | It is less efficient than the Insertion sort. |
| 6. | Here the element is known beforehand, and we search for the correct position to place them. | The location where to put the element is previously known we search for the element to insert at that position. |
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。