图是微积分不可或缺的一部分。它们帮助我们分析函数的行为和限制以及许多其他事情。我们知道一些标准函数的图形,但是有时某些函数是由这些函数的组合组成的,因此很难预测它们的行为。因此,我们使用导数和其他事物来定位其最小值和最大值,然后绘制其图。让我们看看如何进行详细操作。
极大值和极小值
最大值和最小值称为函数的关键点。最大值是高点,最小值是低点。在一个函数,可以存在一个以上的最大和最小点。函数达到最高值和最低值的点称为全局最大值和全局最小值。

我们如何找到这些点?
在任何平滑变化的函数,函数平的点为我们提供了最小值或最大值。现在,这个陈述引起了两个问题。
- 如何识别函数变平的点?
- 假设我们得到一个函数变平的点,即临界点。如何判断是最小还是最大?
为了回答第一个问题,让我们看一下函数的斜率。函数平的点的斜率为零。我们知道,导数不过是函数在特定点的斜率。因此,我们尝试找到导数为零的点。
f’(x)= 0
该方程的解给出了临界点的位置。我们仍然不知道它们是最大值还是最小值。
识别最大和最小值
如下图所示,可以看出,如果导数的符号在临界点之前为正,而在临界点之后为负,则为最大值。同样,如果在临界点之前为负,在临界点之后为正。这是最低要求。最大值和最小值也可以通过二阶导数检验来识别。
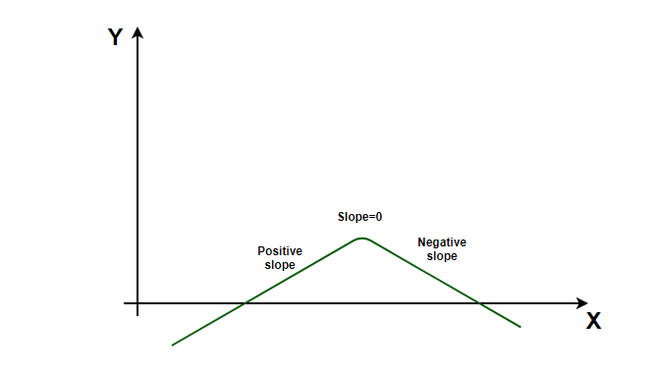
仔细注意该图,可以看到曲线的斜率不断减小,然后变为零,并进一步趋向负值。
Second Derivative Test:
When a function’s slope is zero at x, then the second derivative f” at that point is:
- f” < 0, if it is a maxima.
- f” > 0, if it is a minima.
Note: If the second derivative is zero at the critical points, then the test fails.
分析函数及其导数
一旦有了关于函数的最小值和最大值的信息,就可以开始绘制该函数的图了。假设我们有一个函数f(x),
f(x)= x 2 – 4
步骤1:无症状值
Let’s see the asymptomatic values of the given function, that is the values this function takes at large positive and negative input. The function becomes infinite at large values of input.
步骤2:找出关键点
Putting f'(x) = 0 gives us the position of the critical points for the function. For the given function,
f'(x) = 0
⇒2x = 0
⇒ x = 0.
Thus, x = 0 is a critical point for this function. Now we need to find out whether it is a minimum or a maximum.
步骤3:二阶导数测试
We use the second derivative test mentioned above to find out whether the given critical point is minima or maxima. In the above case,
f”(x) = 2
Notice that, f”(x) > 0. Thus, it must be a minimum.
步骤4:在关键点和根源上重视价值。
Find the value of the function at critical points and find the roots if they exist. The value of the function at x = 0 also should be calculated. These things give us a fair idea about the shape of the graph.
f(0) = -4.

让我们看一些关于这些概念的例子。
样本问题
问题1:找出以下函数的所有关键点,
f(x)= x 3 – 6x 2 + 11x – 6
解决方案:
f(x) = x3 -6x2 +11x – 6
f'(x) = 3x2 -12x +11 = 0
⇒ 3x2 -12x +11 = 0
Using Shree Dharacharya Formula,
x = ![]()
x = ![]()
x = ![]()
x = ![]()
x = ![]()
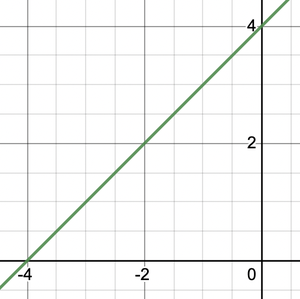
问题2:为f(x)= x + 4绘制图。
解决方案:
Notice that as we increase the values of x on both positive and negative sides, the value of the function goes to positive and negative infinity.
Value of this function at x = 0.
f(0) = 4.
Now let’s look for the critical points.
f'(x) = 1.
There are no critical points, so there are no maxima or minima. Since the derivative is positive and constant, this function is strictly increasing at a constant rate. The constant derivative signifies that the function must be a line which cuts the y-axis at y = 4.
At last let’s look at the point at which the line cuts the x-axis. Putting f(x) =0
0 = x + 4
⇒x = -4
Now we got two points (-4,0) and (0,4). So, the curve will look like.
问题3:给定函数f(x)= x 2 – 4x +4。绘制其图。
解决方案:
We will repeat the same steps for every function.
At x =0. f(x) = 4
Putting f(x) = 0 to find out where the curve intersects the x-axis.
x2 -4x + 4 = 0
⇒ x2 -2x -2x + 4 = 0
⇒ x(x – 2) -2(x – 2) = 0
⇒(x – 2)(x – 2) = 0
x = 2 is the point where the curve the x-axis.
We have both the points now,
f'(x) = 2x – 4 = 0
⇒x = 2
f”(x) = 2 > 0 thus x = 2 is a minima.
So, the graph of the function will look like,

问题4:给定函数f(x)= x 2 -7x +12。绘制其图。
解决方案:
at x = 0 , f(x) = 12.
Putting f(x) = 0,
x2 -7x + 12 =0
⇒ x2 -4x -3x + 12 = 0
⇒x(x – 4) -3(x – 4) = 0
⇒ (x -3) (x -4) = 0
Thus, x = 3 and x = 4 are the roots of this function.
Now let’s find out the critical points and their values.
f'(x) = 2x – 7 = 0d
⇒ x = ![]()
f”(x) = 2 > 0 Thus, the critical point is minima.
So, the graph of this function will look like.

问题5:给定函数f(x)= e x + e -x 。绘制其图。
解决方案:
The given function contains exponential.
At x = 0, f(0) = 2.
At x = ∞ or x = -∞, f(x) = ∞.
Finding out the critical points,
f'(x) = ex – e-x = 0
⇒ ex = e-x
Taking log both sides,
⇒ x = -x
⇒x = 0
Thus, x = 0 is a critical point.
f”(x) = ex + e-x > 0
Thus, x = 0 is a minimum.
f(0) = 2.
