绝对最小值和最大值
有时我们会遇到具有丘陵和山谷的函数。多项式函数通常有多个山丘和山谷点。我们知道这些点是函数的临界点,可以分为最大值或最小值。山点称为最大值,谷点称为最小值。由于存在多个最大值和最小值,因此我们必须确定函数占据最小值的点,最大值称为全局最大值和全局最小值。
临界点和极值定理
假设我们有一个函数f(x),临界点是函数的导数变为零的点。这些点可以是最大值或最小值。临界点是最小值或最大值由二阶导数检验确定。由于函数的导数可能不止一个点为零,因此可能不止一个最小值或最大值。下图显示了一个具有多个临界点的函数。
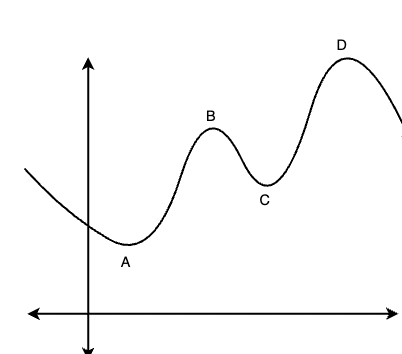
请注意,点 A、C 是最小值,点 B、D 是最大值。 B 和 C 分别称为局部最大值和局部最小值。这意味着这些点在其本地是最大和最小的,但不一定在全局级别上。点 A 和 D 称为全局最小值和全局最大值。
Let’s say we have a function f(x) which is twice differentiable. Its critical points are given by the f'(x) = 0. Second Derivative Test allows us to check whether the calculated critical point is minima or maxima.
- If f”(x) > 0, then the point x is a maxima.
- If f”(x) < 0, then the point x is a minima.
现在,这个测试告诉我们哪个点是最小值或最大值,但它仍然无法为我们提供有关全局最大值和全局最小值的信息。极值定理来拯救我们。
极值定理
极值定理保证函数在特定条件下的最大值和最小值。这个定理没有告诉我们极值点会存在哪里,这个定理告诉我们它们会存在。该定理指出,
If a function f(x) is continuous on a closed interval [a, b], then f(x) has both at least one maximum and minimum value on [a, b].
封闭区间内的绝对最小值和最大值
现在要找到任何区间的极值点,我们需要遵循一些基本步骤。假设我们有一个函数f(x) 和一个区域 D。我们想在这个区间内找到函数的极值。
Step 1: Find the critical points of the function in the interval D,
f'(x) = 0
Step 2: Find the value of the function at the extreme points of interval D.
Step 3: The largest value and smallest value found in the above two steps are the absolute maximum and absolute minimum of the function.
整个域中的绝对最小值和最大值
整个域中函数的绝对最小值和最大值是函数在任何地方定义的最高和最低值。一个函数可以同时具有最大值和最小值,可以是其中之一,也可以没有。例如,一条直线在两个方向上都延伸到无穷远,因此它既没有最大值也没有最小值。我们需要按照与上一个案例类似的一些步骤来找出整个域的绝对最大值和最小值。
Step 1: Find the critical points of the function wherever it is defined.
Step 2: Find the value of the function at these extreme points.
Step 3: Check for the value of the function when x tends to infinity and negative infinity. Also, check for the points of discontinuity.
Step 4: Maximum and minimum of all these values give us the absolute maximum and absolute minimum for the function in its entire domain.
让我们看一些示例问题
示例问题
问题1:求函数f(x) = 5x + 2在区间[0,2]中的绝对最大值和绝对最小值。
解决方案:
The first step is to find the critical points by differentiating the function f(x),
f'(x) = 5
This equation has no roots, therefore there are no critical points which means no maxima or minima. This function is continuously increasing. Thus, the maxima and minima will occur at the end points of the interval.
f(0) = 2
f(2) = 12
Thus, f(0) is the minimum and f(2) is the maximum value of the function.
问题2:在区间[0,2]中求函数f(x) = x 2 – 2x + 5的绝对最大值和绝对最小值。
解决方案:
The first step is to find the critical points by differentiating the function f(x),
f'(x) = 2x – 2
f'(x) = 0
⇒ 2x – 2 = 0
⇒ x = 1
This, x = 1 is the critical point of the function.
f(1) = (1)2 – 2(1) + 5
⇒f(1) = 1 – 2 + 5
⇒f(1) = 4
Checking the end points of the interval,
f(0) = 5
f(2) = 5
Out of all these values, we can conclude that,
x = 1 is the minima and x = 2,0 is the maxima.
Thus, absolute maximum and absolute minimum values of the function are 5 and 4 respectively.
问题 3:求函数f(x) = x 3 – 2x 2 + 5 在区间 [-2,2] 内的绝对最大值和绝对最小值。
解决方案:
The first step is to find the critical points by differentiating the function f(x),
f'(x) = 3x2 – 4x
f'(x) = x(3x – 4)
⇒ x(3x – 4) = 0
⇒ x = 0 and ![]()
This, x = 0 and ![]() are the critical points of the function.
are the critical points of the function.
f(0) = 5
⇒f(1) = ![]()
⇒f(1) = ![]()
⇒f(1) =
⇒f(1) = ![]()
⇒f(1) = ![]()
⇒f(1) = ![]()
Checking the end points of the interval,
f(-2) = (-2)3 – 2(-2)2+ 5
⇒ f(-2) = -8 -2(4) + 5
⇒f(-2) = -16 + 5
⇒f(-2) = -11
f(2) = (2)3 – 2(2)2+ 5
⇒ f(2) = 5
Out of all these values, we can conclude that,
x = -2 is the minima and x = 0, 2 is the maxima.
Thus, absolute maximum and absolute minimum values of the function are 5 and 4 respectively.
问题 4:求函数f(x) = 的绝对最大值和绝对最小值![]() 在区间 [0,1] 内。
在区间 [0,1] 内。
解决方案:
The first step is to find the critical points by differentiating the function f(x),
f'(x) = ![]()
This equation will not be zero for any value of x in the interval. So, it is monotonically increasing or decreasing in the interval. Checking at the boundary points.
f(0) = ![]()
f(1) = ![]()
Out of all these values, we can conclude that,
x = 1 is the minima and x = 0 is the maxima.
Thus, absolute maximum and absolute minimum values of the function are ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
问题 5:求函数f(x) = 2e x – 2 在区间 [0,1] 中的绝对最大值和绝对最小值。
解决方案:
The first step is to find the critical points by differentiating the function f(x),
f'(x) = 2ex
This equation will not be zero for any value of x in the interval. So, it is monotonically increasing or decreasing in the interval. Checking at the boundary points.
f(1) = 2e1 – 2
⇒f(1) = 2e – 2
f(0) = 2(1) – 2
⇒f(0) = 0
Out of all these values, we can conclude that,
x = 0 is the minima and x = 1 is the maxima.
Thus, absolute maximum and absolute minimum values of the function are 2e – 2 and 0 respectively.
问题6:求函数f(x) = x 2 – x 在区间[0,1]中的绝对最大值和绝对最小值。
解决方案:
The first step is to find the critical points by differentiating the function f(x),
f'(x) = 2x – 2
f'(x) = 0
⇒ 2x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = ![]()
This, x = ![]() is the critical point of the function.
is the critical point of the function.
f(![]() ) =
) = ![]()
⇒f(![]() ) =
) = ![]()
⇒f(![]() ) =
) = ![]()
Checking the end points of the interval,
f(0) = 0
f(1) = 0
Out of all these values, we can conclude that,
x = ![]() is the minima and x = 1,0 is the maxima.
is the minima and x = 1,0 is the maxima.
Thus, absolute maximum and absolute minimum values of the function are 0 and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
问题 7:求函数f(x) = x 4 + 2x 2的绝对最大值和最小值。
解决方案:
Since no interval is given, we need to calculate the minimum and the maximum value of the function on it’s domain which is R. First let’s check for the critical points.
f(x) = x4 – 2x2
⇒ f'(x) = 4x3 – 4x
f'(x) = 0
⇒ 4x3 – 4x = 0
⇒ 4x(x2 – 1) = 0
The critical points are x = 0, 1, -1.
Now since it’s a polynomial function there are no discontinuities. Let’s check for the asymptomatic values of the function.
When x ⇢ ∞, f(x) ⇢ ∞ similarly,
x ⇢ -∞, f(x) ⇢ ∞
So, there is no maximum value for the function. For minimum value, let’s check on the critical points.
x = 0,-1 and 1
f(0) = 0
f(1) = 3
f(-1) = 3
Thus, minimum value is f(0) = 0.
问题 8:求函数f(x) = 的绝对最小值和最大值![]() .
.
解决方案:
Since no interval is given, we need to calculate the minimum and the maximum value of the function on its domain which is R – {-3}. First let’s check for the critical points.
f(x) = ![]()
f'(x) = ![]()
There is no point in the function’s domain where f'(x) = 0.
So now we need to check for the values of the function when x tends to infinity.
As x ⇢ -∞ or x ⇢ ∞. f(x) ⇢ 0. And as x ⇢ -3, f (x) ⇢ ∞
Thus, there is no maximum value and the minimum value exists when x ⇢ ∞ or -∞ and f(x) ⇢ 0.