光从表面反射。任何被抛光或换句话说有光泽的表面都始终像镜子一样。观察从表面反弹的光称为反射。反射后的光在光线入射到同一表面的相同介质中传播。反射现象不会改变光速,它只会使入射在其上的光的方向反转。这可以在任何粗糙或光滑的表面上观察到。反射射线的路径取决于表面的光滑程度,在光滑表面的情况下,反射射线以与入射角相同的角度出射,在后一种情况下会发生不规则反射,因此反射射线不会t与入射角相同。
反射定律
- 落在反射表面上的光线称为入射光线,而被反射回去的光线称为反射光线。
- 垂直于发生反射的反射面的假想线称为法线。
- 入射角∠i是指入射光线与法线之间的角度。反射角∠r是指反射光线与法线之间的夹角。
反射有两种类型,一种是常规反射,另一种是扩散反射。
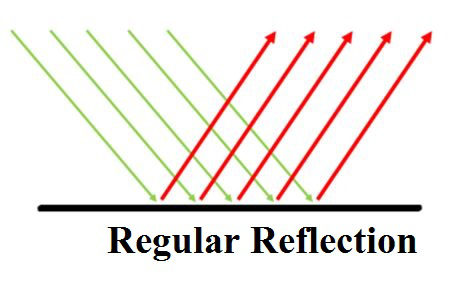
定期反思
从表面反射回来的入射光称为反射。如果反射遵循反射定律发生,则称为正反射。它遵循两个反射定律。来自表面的反射射线形成相同的反射角,该反射角等于入射角。入射点处的入射射线,反射射线和法线都位于同一平面上。在抛光表面具有光泽外观(例如镜子)的情况下,可以观察到这一点。
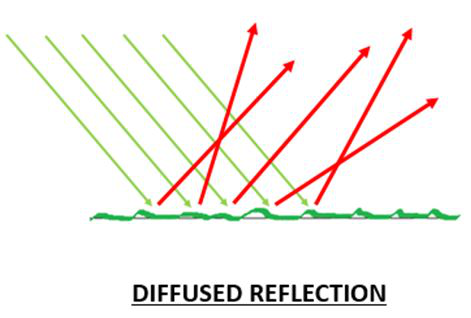
漫反射
从表面返回的入射光称为反射。在漫反射的情况下,不会遵循反射定律发生反射。它不遵循任何反射定律。从表面反射的光线不会形成与入射角相同的反射角。同样,入射光线,反射光线和入射点处的法线,它们三个都不在同一平面上。在未打磨或粗糙的表面(例如纸张,纸板,砂纸,粗糙的纸张等)的情况下,会观察到这种情况。
下表列出了正反射和漫反射之间的区别:
|
Regular Reflection |
Diffused Reflection |
| Light rays fall on a smooth surface. | Light rays fall on an irregular or rough surface. |
| Reflected rays are parallel to each other. | Reflected rays are not parallel to each other. |
| Reflection can be observed clearly. | Reflection cannot be observed clearly. |
| This type of reflection can be seen through polished surfaces, mirror surface, etc. | This type of reflection can be seen on paper, cardboard, or any irregular surface. |
反思中的样本问题
问题1:入射角60°的反射角是多少?
解决方案:
We know that,
∠i = ∠r
Therefore, ∠r = 60°
Hence, the angle of reflection will be 60°.
问题2:50°反射角的入射角是多少?
解决方案:
We know that,
∠i = ∠r
Therefore, ∠i = 50°
Hence, the angle of reflection will be 50°.
问题3:如果镜面和入射光线之间的角度为60°,则入射角为多少?
解决方案:
We know that,
∠i + angle between mirror and incident ray = 90°
Therefore, ∠i + 60° = 90°
Therefore, ∠i = 90° – 60°
Therefore, ∠i = 30°
Hence, the incident angle is 30°
问题3:如果入射光线沿法线入射到镜面中会怎样?
回答:
We know,
∠i = ∠r
If the incident ray fall along the normal then the angle between the incident ray and the normal becomes zero hence, the reflected angle also becomes zero therefore it means that the light doesn’t experience any reflection and travels straight from the surface.
问题4:写出漫反射的两个特征。
回答:
The two characteristics of diffused reflection are:
- Reflected rays are not parallel to each other.
- Reflection cannot be observed clearly.
问题5:陈述两个反射定律。
回答:
Following are the two laws of reflection:
- The Angle of incidence ∠i is always equal to angle of reflection ∠r, ∠i = ∠r
- The incident ray at the polished surface, the reflected ray and the normal which is at the point of incidence, they all lie in the same plane.