当看夜空时,在天空中观察到许多天体,例如星星,月亮,卫星等。卫星是绕行星或比行星大的物体旋转或绕行的小物体。最常见的卫星是月球,月球是地球的卫星,因为月球绕其固定轨道绕地球旋转。
月亮是地球的卫星
卫星
人造卫星是自然产生或人造的物体,曾经绕过一个比它大并且绕其轴旋转的行星。太阳系中有包括月球在内的各种卫星。因此,根据卫星的存在,卫星分为两大类:
自然卫星
存在于空间中的任何天体绕大于固定轨道的行星旋转,都被称为自然卫星。太阳系由六个行星卫星系统组成,其中有205颗卫星是自然卫星。类似地,这些卫星更大,并且以更大的半径运行。它们的表面通常由各种气体或落基山脉组成。
e.g. The moon is the natural satellite of Earth similarly, Earth, Jupiter and Venus orbits around the Sun in their fixed orbit.
人造卫星
人们使用火箭制造并发射入轨道的任何物体都称为人造卫星。目前,有超过一千颗活跃的卫星绕地球旋转。卫星的大小,高度和设计取决于卫星的用途。这些卫星还装有精密的仪器和照相机,可以在固定轨道上绕行星旋转,并由来自地球的火箭发射。
e.g. Sputnik-I, launched on 4 October 1957, by the Soviet Union launched as the world’s first artificial satellite. After that USA send Explorer 1. Since then, almost 8,900 satellites from more than 50 countries have been launched. According to an estimate, some 5,000 satellites remain in the orbit. Out of these 5000, about 1,900 were operational, while the rest have exceeded the numbers of their useful lives and become space debris now. These satellites are useless and will revolve until their destruction.
However, Aryabhatta was India’s first satellite launched on 19 April 1975, after that many artificial satellites like INSAT, IRS, Edusat, GSat, Chandrayan etc were launched in later days. Some other examples of artificial satellites on the basis of their uses are: GOES i.e. a weather satellite, ANIK i.e. a communication satellite, GPS i.e. a navigation satellite, TERRIERS i.e. a scientific satellite and MILSTAR i.e. a military satellite.
人造卫星的历史
苏联于1957年10月4日成功发射了第一颗人造卫星。这颗卫星被称为Sputnik-I。 Sputnik-I重达183磅,大约只有板球大小。绕地球运行花了98分钟。人造卫星Sputnik-I的发射被命名为太空时代的开始和跨越1960年代的美苏太空竞赛的开始。同年11月3日,苏联发射了人造卫星Sputnik-II时,又发射了一颗卫星。 Sputnik-II和一只叫莱卡(Laika)的狗一起携带的重物要重得多。
在人造卫星一号和二号卫星之后,美国国防部立即资助了另一个名为冯·布劳恩(Von Braun)的人经营的卫星项目。冯·布劳恩(Von Braun),他的团队和雷德斯通(Redstone)的美国陆军参与了“探索者计划”(Explorer Project)。 1月31日启动了ExplorerI。它由一个小的,具有重要科学意义的有效载荷组成,可用于发现地球周围的电磁辐射带。这些以首席研究员詹姆斯·范·艾伦(James Van Allen)的名字命名。该计划继续创造了一系列成功的轻型科学航天器。
人造卫星的类型
根据人造卫星的运动方向和与地球表面的距离,人造人造卫星大致可分为两类:人造卫星和人造卫星。
1.对地静止卫星:在距地球表面约35、800公里的预定轨道中,与地球旋转方向与地球相同的人造卫星称为对地静止或同步卫星。
2.极地轨道卫星:绕着南北轨道绕过北极和南极并围绕地球表面约500-800 km的人造卫星称为极地卫星。
对地静止卫星
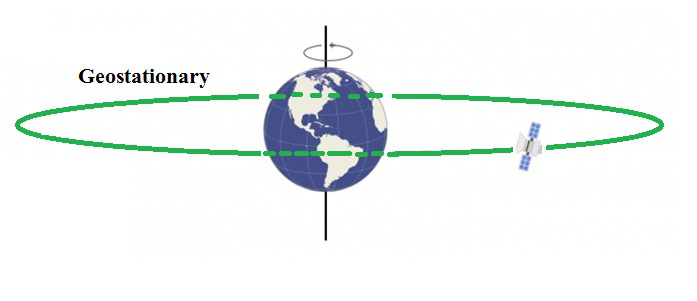
对地静止卫星
- 这些卫星是在约36000公里的轨道上绕地球轨道运行的高轨道卫星。
- 之所以将地球静止卫星称为地球静止卫星,是因为地球静止卫星绕赤道线性轨道旋转,因此地球静止轨道卫星以与地球自转相同的速度绕地球旋转,因此卫星一直都在地球上的同一位置,因此在地球上静止不动。参考地球。
- 同样,对地静止卫星的革命时期大约为24小时,这等于地球的自转周期。
- 这些卫星通常用作通信和气象卫星。
- 这类卫星的例子有印度的INSAT,美国的地球静止运行环境卫星(GEOS),日本的Himawari,欧洲的Meteostat等。
极地卫星
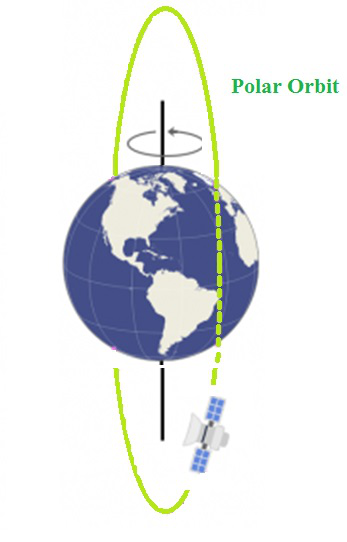
极地卫星
- 这些卫星是低轨道卫星,可在距地球约500-800 km的轨道上绕地球运行。
- 极地轨道卫星靠近或直接越过每个轨道的极点。随着地球在其下方旋转,这意味着极地轨道卫星每次都看到地球的不同部分。
- 同样,对地静止卫星的革命时期大约为24小时,这等于地球的自转周期。
- 此类卫星用于研究宇宙,帮助预报天气,在海洋上转移电话,协助船舶和飞机航行,监控农作物和其他资源以及支持军事活动。
人造卫星的应用
人造卫星的一些重要用途是:
- 电信:卫星通过电话,电视,移动电话,互联网服务等用于电信目的,这些信号是从全球不同位置接收并传输到世界其他地方的。
- 监测:用于确保有关地质和气象领域的重要信息,甚至包括农业监测,即特定区域的作物产量,疾病和歉收。
- 它可以帮助科学家了解干旱和粮食生产的最新情况,并估计这些灾害造成的损失。
- 人造卫星有助于发现地下水储备,并有助于水的管理。
- 它还有助于识别飞机,轮船,人和物体的确切位置。
样本问题
问题1:区分天然卫星和人造卫星。
解决方案:
The differences between natural and artificial satellites are,
|
Natural Satellites |
Artificial Satellites |
|
| 1. | These satellites are naturally occurring objects. | They are man-made. |
| 2. | They can not be controlled by humans and so have no use. | They can be controlled by humans and so have wide applications. |
| 3. | The natural satellites can not communicate on earth or with other planets. | The artificial planet can communicate with instruments on earth. |
| 4. | The natural satellite is made up of natural materials like gases, rock, minerals, water, dust etc. | The artificial satellite is made up of metal and other electronics materials. |
| 5. | The natural satellites like Planets are opaque bodies with no light of their own. They also receive heat and light from sun like moon. | The artificial satellites are objects humans propel from earth in order to orbit around the earth, the electrical power required by satellite is provided by panels of solar cells and small nuclear reactors. |
问题2:对地静止卫星和极地轨道卫星是如何彼此不同的。
解决方案:
The difference between the geostationary and polar satellites are as follows:
|
Geostationary Satellites |
Polar-orbiting Satellites |
|
| 1. | Geo-stationary satellites revolve in equatorial orbits. | Polar satellites revolve in polar orbits of the earth. |
| 2. | These satellites complete one circle of the earth in 24 hours. | These satellites take less time to complete one circle of earth. |
| 3. | These satellites are placed at a height of 36000 km from the Earth surface. | These satellites are placed at a height of 500-800 km from Earth surface. |
| 4. | The main use of this satellites is in telecommunication and weather forecasting. |
This satellite is used for remote sensing, weather, science and environment related studies. |
问题3:列出五颗印度人造卫星。
解决方案:
India’s first satellite was Aryabhatta. It was built by ISRO and launched by the Soviet Union on 19 April 1975. It was named after the mathematician Aryabhata. In 1980, Rohini was the first ever satellite to be placed in orbit by an Indian-made launch vehicle, SLV-3. Some other Indian satellites are INSAT, IRS, Kalpana-1, EDUSAT, etc.
问题4:什么是卫星通信?
解决方案:
The technique of transferring data or information from one place to another through a communication satellite is called the satellite communication. The communication satellite is an artificial satellite that is responsible for transmission of signals.
问题5:根据其应用命名更多类型的卫星。
解决方案:
On the basis of the applications of satellites in different fields, the satellites are categorized as:
- Navigation satellites,
- Communication satellites,
- Weather satellites,
- Military satellites,
- Earth Observation satellites,
- Astronomical satellites,
- International Space Station,
- Remote Sensing satellites,
- Navigation satellites,
- Global Positioning satellites etc.