给定m和n分别代表芒果数量和人数。任务是计算在n个人之间分配m芒果的方式数量。考虑变量m和n,我们得出4个典型的用例,其中芒果和人被认为是:
1)两者相同
2)分别唯一和相同
3)分别相同和唯一
4)两者都独特
先决条件:二项式系数|排列组合
案例1:在n个相同的人中分配m个相同的芒果
如果我们尝试连续传播m个芒果,我们的目标是将这些m个芒果分配给n个坐在这些芒果之间的人。我们需要做的就是将这m个芒果集中到n个集合中,以便可以将这n个集合中的每一个分别分配给n个人。
为了完成上述任务,我们需要通过使用n-1个分区程序来创建n组芒果来对芒果的初始排列进行分区。在这种情况下,我们需要一起布置m个芒果和n-1个分区。所以我们需要![]() 计算答案的方法。
计算答案的方法。
下图显示了放置3个分区(即P1,P2,P3)后创建的分区排列的示例(一种方式),该分区将所有7个芒果划分为4个不同的分区,以便4个人可以拥有各自分区的自己的部分:
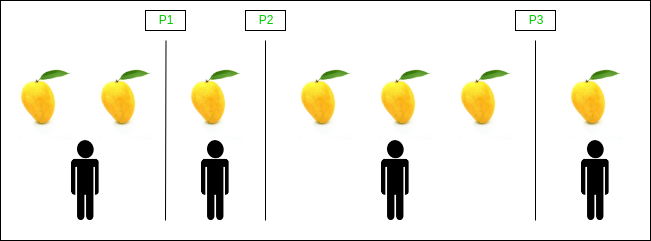
由于所有芒果都被认为是相同的,因此我们划分![]() 经过
经过![]() 扣除重复的条目。同样,我们再次将以上表达式除以
扣除重复的条目。同样,我们再次将以上表达式除以![]() 因为所有人也被认为是相同的。
因为所有人也被认为是相同的。
我们得到的最终表达式是: ![]()
上面的表达式实际上等于二项式系数: ![]()
例子:
Input : m = 3, n = 2
Output : 4
There are four ways
3 + 0, 1 + 2, 2 + 1 and 0 + 3
Input : m = 13, n = 6
Output : 8568
Input : m = 11, n = 3
Output : 78C++
// C++ code for calculating number of ways
// to distribute m mangoes amongst n people
// where all mangoes and people are identical
#include
using namespace std;
// function used to generate binomial coefficient
// time complexity O(m)
int binomial_coefficient(int n, int m)
{
int res = 1;
if (m > n - m)
m = n - m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
res *= (n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res;
}
// helper function for generating no of ways
// to distribute m mangoes amongst n people
int calculate_ways(int m, int n)
{
// not enough mangoes to be distributed
if (m < n)
return 0;
// ways -> (n+m-1)C(n-1)
int ways = binomial_coefficient(n + m - 1, n - 1);
return ways;
}
// Driver function
int main()
{
// m represents number of mangoes
// n represents number of people
int m = 7, n = 5;
int result = calculate_ways(m, n);
printf("%d\n", result);
return 0;
} Java
// Java code for calculating number of ways
// to distribute m mangoes amongst n people
// where all mangoes and people are identical
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// function used to generate binomial coefficient
// time complexity O(m)
public static int binomial_coefficient(int n, int m)
{
int res = 1;
if (m > n - m)
m = n - m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
res *= (n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res;
}
// helper function for generating no of ways
// to distribute m mangoes amongst n people
public static int calculate_ways(int m, int n)
{
// not enough mangoes to be distributed
if (m < n) {
return 0;
}
// ways -> (n+m-1)C(n-1)
int ways = binomial_coefficient(n + m - 1, n - 1);
return ways;
}
// Driver function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// m represents number of mangoes
// n represents number of people
int m = 7, n = 5;
int result = calculate_ways(m, n);
System.out.println(Integer.toString(result));
System.exit(0);
}
}Python3
# Python code for calculating number of ways
# to distribute m mangoes amongst n people
# where all mangoes and people are identical
# function used to generate binomial coefficient
# time complexity O(m)
def binomial_coefficient(n, m):
res = 1
if m > n - m:
m = n - m
for i in range(0, m):
res *= (n - i)
res /= (i + 1)
return res
# helper function for generating no of ways
# to distribute m mangoes amongst n people
def calculate_ways(m, n):
# not enough mangoes to be distributed
if m (n + m-1)C(n-1)
ways = binomial_coefficient(n + m-1, n-1)
return int(ways)
# Driver function
if __name__ == '__main__':
# m represents number of mangoes
# n represents number of people
m = 7 ;n = 5
result = calculate_ways(m, n)
print(result) C#
// C# code for calculating number
// of ways to distribute m mangoes
// amongst n people where all mangoes
// and people are identical
using System;
class GFG
{
// function used to generate
// binomial coefficient
// time complexity O(m)
public static int binomial_coefficient(int n,
int m)
{
int res = 1;
if (m > n - m)
m = n - m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
res *= (n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res;
}
// helper function for generating
// no of ways to distribute m
// mangoes amongst n people
public static int calculate_ways(int m, int n)
{
// not enough mangoes
// to be distributed
if (m < n)
{
return 0;
}
// ways -> (n+m-1)C(n-1)
int ways = binomial_coefficient(n + m - 1,
n - 1);
return ways;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// m represents number of mangoes
// n represents number of people
int m = 7, n = 5;
int result = calculate_ways(m, n);
Console.WriteLine(result.ToString());
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by SubhadeepPHP
$n - $m)
$m = $n - $m;
for ($i = 0; $i < $m; ++$i)
{
$res *= ($n - $i);
$res /= ($i + 1);
}
return $res;
}
// Helper function for generating
// no of ways to distribute m.
// mangoes amongst n people
function calculate_ways($m, $n)
{
// not enough mangoes to
// be distributed
if ($m < $n)
return 0;
// ways -> (n+m-1)C(n-1)
$ways = binomial_coefficient($n + $m - 1,
$n - 1);
return $ways;
}
// Driver Code
// m represents number of mangoes
// n represents number of people
$m = 7;
$n = 5;
$result = calculate_ways($m, $n);
echo $result;
// This code is contributed
// by Shivi_Aggarwal
?>Javascript
输出:
330时间复杂度: O(n)
辅助空间: O(1)
案例2:在n个相同的人中分配m个独特的芒果
在这种情况下,要计算在n个相同的人中分配m个独特的芒果的方式数量,我们只需要将最后一个表达式相乘即可![]() 我们在案例1中计算出
我们在案例1中计算出![]() 。
。
所以我们对这种情况的最终表达是![]()
证明:
在第一种情况下,最初我们得到表达式![]() 而不删除重复的条目。
而不删除重复的条目。
在这种情况下,我们只需要划分![]() 因为在这种情况下,所有芒果都被认为是唯一的。
因为在这种情况下,所有芒果都被认为是唯一的。
因此,我们将表达式表示为: ![]()
分子和分母都乘以![]() ,
,
我们得到![]()
在哪里![]() ===
=== ![]()
时间复杂度: O(max(n,m))
辅助空间: O(1)
案例3:在n个独特的人中分配m个相同的芒果
在这种情况下,要计算在n个唯一的人中分配m个相同的芒果的方式,我们只需要将最后一个表达式相乘即可![]() 我们在案例1中计算出
我们在案例1中计算出![]() 。
。
所以我们对这种情况的最终表达是![]()
证明:
该证明与最后一种情况的证明非常相似。
在第一种情况下,最初我们得到表达式![]() 而不删除重复的条目。
而不删除重复的条目。
在这种情况下,我们只需要划分![]() 因为在这种情况下所有人都被认为是独一无二的。
因为在这种情况下所有人都被认为是独一无二的。
因此,我们将表达式表示为: ![]()
分子和分母都乘以![]() ,
,
我们得到![]()
在哪里![]() ===
=== ![]()
时间复杂度: O(n)
辅助空间: O(1)
有关如何计算的参考![]() 请参阅此处的数字阶乘
请参阅此处的数字阶乘
案例4:在n个独特的人中分配m个独特的芒果
在这种情况下,我们需要将在情况1中获得的表达式乘以两个![]() 和
和![]() 。
。
在情况2和情况3中定义了两个乘法的证明。
因此,在这种情况下,我们的最终表达式是![]()
时间复杂度: O(n + m)
辅助空间: O(1)