给定两个整数N和B ,任务是打印指针的最大索引,从第0个索引开始可以到达一个自然数数组(即0、1、2、3、4、5…),例如arr [] ,在N步中不将自己放置在索引B的任何位置。
In each step, the pointer can move from the Current Index to a Jumping Index or can remain at the Current Index.
Jumping Index = Current Index + Step Number
例子:
Input: N = 3, B = 2
Output: 6
Explanation:
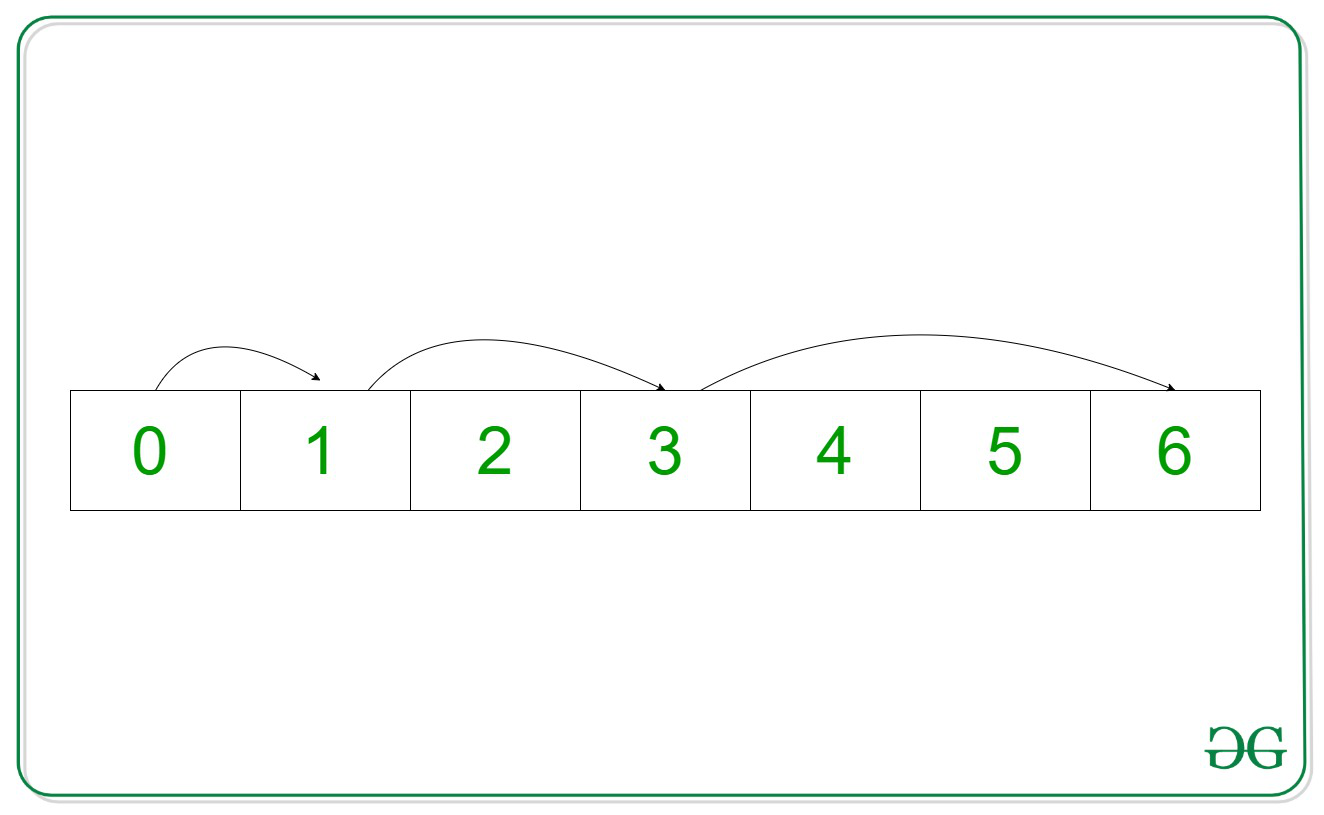
Step 1:
Current Index = 0
Step Number = 1
Jumping Index = 0 + 1 = 1
Step 2:Current Index = 1
Step Number = 2
Jumping Index = 1 + 2 = 3
Step 3:
Current Index = 3
Step Number = 3
Jumping Index = 3 + 3 = 6
Therefore, the maximum index that can be reached is 6.
Input: N = 3, B = 1
Output: 5
Explanation:

Step 1:
Current Index = 0
Step Number = 1
Jumping Index = 0 + 1 = 1But this is bad index. So pointer remains at the Current Index.
Step 2:
Current Index = 0
Step Number = 2
Jumping Index = 0 + 2 = 2
Step 3:
Current Index = 2
Step Number = 3
Jumping Index = 2 + 3 = 5
Therefore, the maximum index that can be reached is 5.
天真的方法:解决问题的最简单方法是通过为每个当前索引考虑两种可能性来计算最大索引,即按步号移动指针或通过保留当前索引来生成指针,并生成所有可能的组合。最后,打印获得的最大索引。
时间复杂度: O(N 3 )
辅助空间: O(1)
高效方法:
计算在给定步骤内可以达到的最大索引。如果通过避免不良索引可以从最大索引中获得第0个索引,请打印结果。否则,通过将最大索引递减1来重复此过程。
步骤如下:
- 通过计算前N个自然数的总和来计算N步可达到的最大索引。
- 将计算出的最大索引的值分配给“当前索引” 。
- 保持递减当前索引的步数和步数1,直到其中之一变为负数为止。
- 每次递减后,请检查“当前索引”是否等于B。如果发现是真的,请还原对“当前索引”所做的更改。
- 如果当前索引成功达到0 ,则打印最大索引的当前值作为答案。
- 否则,将最大索引的值减1,然后从步骤2开始重复。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the maximum
// index the pointer can reach
void maximumIndex(int N, int B)
{
int max_index = 0;
// Calculate maximum possible
// index that can be reached
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
max_index += i;
}
int current_index = max_index, step = N;
while (1) {
// Check if current index and step
// both are greater than 0 or not
while (current_index > 0 && N > 0) {
// Decrement current_index by step
current_index -= N;
// Check if current index is
// equal to B or not
if (current_index == B) {
// Restore to previous index
current_index += N;
}
// Decrement step by one
N--;
}
// If it reaches the 0th index
if (current_index <= 0) {
// Print result
cout << max_index << endl;
break;
}
// If max index fails to
// reach the 0th index
else {
N = step;
// Store max_index - 1 in current index
current_index = max_index - 1;
// Decrement max index
max_index--;
// If current index is equal to B
if (current_index == B) {
current_index = max_index - 1;
// Decrement current index
max_index--;
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 3, B = 2;
maximumIndex(N, B);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find the maximum
// index the pointer can reach
static void maximumIndex(int N,
int B)
{
int max_index = 0;
// Calculate maximum possible
// index that can be reached
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
max_index += i;
}
int current_index = max_index,
step = N;
while (true)
{
// Check if current index
// and step both are greater
// than 0 or not
while (current_index > 0 &&
N > 0)
{
// Decrement current_index
// by step
current_index -= N;
// Check if current index
// is equal to B or not
if (current_index == B)
{
// Restore to previous
// index
current_index += N;
}
// Decrement step by one
N--;
}
// If it reaches the 0th index
if (current_index <= 0)
{
// Print result
System.out.print(max_index + "\n");
break;
}
// If max index fails to
// reach the 0th index
else
{
N = step;
// Store max_index - 1 in
// current index
current_index = max_index - 1;
// Decrement max index
max_index--;
// If current index is
// equal to B
if (current_index == B)
{
current_index = max_index - 1;
// Decrement current index
max_index--;
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 3, B = 2;
maximumIndex(N, B);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to find the maximum
# index the pointer can reach
def maximumIndex(N, B):
max_index = 0
# Calculate maximum possible
# index that can be reached
for i in range(1, N + 1):
max_index += i
current_index = max_index
step = N
while (1):
# Check if current index and step
# both are greater than 0 or not
while (current_index > 0 and N > 0):
# Decrement current_index by step
current_index -= N
# Check if current index is
# equal to B or not
if (current_index == B):
# Restore to previous index
current_index += N
# Decrement step by one
N -= 1
# If it reaches the 0th index
if (current_index <= 0):
# Print result
print(max_index)
break
# If max index fails to
# reach the 0th index
else:
N = step
# Store max_index - 1 in current index
current_index = max_index - 1
# Decrement max index
max_index -= 1
# If current index is equal to B
if (current_index == B):
current_index = max_index - 1
# Decrement current index
max_index -= 1
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 3
B = 2
maximumIndex(N, B)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program for the
// above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find the maximum
// index the pointer can reach
static void maximumIndex(int N,
int B)
{
int max_index = 0;
// Calculate maximum possible
// index that can be reached
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
max_index += i;
}
int current_index = max_index,
step = N;
while (true)
{
// Check if current index
// and step both are greater
// than 0 or not
while (current_index > 0 &&
N > 0)
{
// Decrement current_index
// by step
current_index -= N;
// Check if current index
// is equal to B or not
if (current_index == B)
{
// Restore to previous
// index
current_index += N;
}
// Decrement step by one
N--;
}
// If it reaches the 0th index
if (current_index <= 0)
{
// Print result
Console.Write(max_index + " ");
break;
}
// If max index fails to
// reach the 0th index
else
{
N = step;
// Store max_index - 1 in
// current index
current_index = max_index - 1;
// Decrement max index
max_index--;
// If current index is
// equal to B
if (current_index == B)
{
current_index = max_index - 1;
// Decrement current index
max_index--;
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main (String[] args)
{
int N = 3, B = 2;
maximumIndex(N, B);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeatJavascript
6时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
辅助空间: O(1)