一个孩子正在n步的楼梯上奔跑,可以一次跳1步,2步或3步。实施一种方法来计算孩子可以上楼梯的多少种方式。
例子:
Input : 4
Output : 7
Explantion:
Below are the four ways
1 step + 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
1 step + 2 step + 1 step
2 step + 1 step + 1 step
1 step + 1 step + 2 step
2 step + 2 step
3 step + 1 step
1 step + 3 step
Input : 3
Output : 4
Explantion:
Below are the four ways
1 step + 1 step + 1 step
1 step + 2 step
2 step + 1 step
3 step有两种方法可以解决此问题:
- 递归方法
- 动态编程
方法1 :递归。
有n个楼梯,允许一个人跳下一个楼梯,跳过一个楼梯或跳过两个楼梯。因此,这里有n个楼梯。因此,如果某人站在第i楼梯,则该人可以移至第i + 1,i + 2,i + 3楼梯。可以形成递归函数,其中在当前索引i处,该函数递归调用第i + 1,i + 2和i + 3个楼梯。
还有另一种形成递归函数。要到达第i阶,一个人必须从第i-1,i-2或i-3阶跳下,或者我是起始阶。
算法:
- 创建一个仅包含一个参数的递归函数(count(int n))。
- 检查基本情况。如果n的值小于0,则返回0;如果n的值等于0,则返回1,因为它是起始楼梯。
- 用值n-1,n-2和n-3递归调用函数,并对返回的值求和,即sum = count(n-1)+ count(n-2)+ count(n-3)
- 返回总和的值。
C++
// C++ Program to find n-th stair using step size
// 1 or 2 or 3.
#include
using namespace std;
class GFG {
// Returns count of ways to reach n-th stair
// using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
public:
int findStep(int n)
{
if (n == 1 || n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n == 2)
return 2;
else
return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2)
+ findStep(n - 1);
}
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
GFG g;
int n = 4;
cout << g.findStep(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by SoM15242 C
// Program to find n-th stair using step size
// 1 or 2 or 3.
#include
// Returns count of ways to reach n-th stair
// using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
int findStep(int n)
{
if (n == 1 || n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n == 2)
return 2;
else
return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2) + findStep(n - 1);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 4;
printf("%d\n", findStep(n));
return 0;
} Java
// Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class GfG {
// Returns count of ways to reach
// n-th stair using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
public static int findStep(int n)
{
if (n == 1 || n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n == 2)
return 2;
else
return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2) + findStep(n - 1);
}
// Driver function
public static void main(String argc[])
{
int n = 4;
System.out.println(findStep(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Sagar Shukla */Python
# Python program to find n-th stair
# using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
# Returns count of ways to reach n-th
# stair using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
def findStep( n) :
if (n == 1 or n == 0) :
return 1
elif (n == 2) :
return 2
else :
return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2) + findStep(n - 1)
# Driver code
n = 4
print(findStep(n))
# This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.C#
// Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
using System;
public class GfG {
// Returns count of ways to reach
// n-th stair using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
public static int findStep(int n)
{
if (n == 1 || n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n == 2)
return 2;
else
return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2) + findStep(n - 1);
}
// Driver function
public static void Main()
{
int n = 4;
Console.WriteLine(findStep(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by vt_m */PHP
Javascript
C++
// A C++ program to count number of ways
// to reach n't stair when
#include
using namespace std;
// A recursive function used by countWays
int countWays(int n)
{
int res[n + 1];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2]
+ res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int n = 4;
cout << countWays(n);
return 0;
}
//This code is contributed by shubhamsingh10 C
// A C program to count number of ways
// to reach n't stair when
#include
// A recursive function used by countWays
int countWays(int n)
{
int res[n + 1];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2]
+ res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int n = 4;
printf("%d", countWays(n));
return 0;
} Java
// Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class GfG {
// A recursive function used by countWays
public static int countWays(int n)
{
int[] res = new int[n + 1];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2]
+ res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver function
public static void main(String argc[])
{
int n = 4;
System.out.println(countWays(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Sagar Shukla */Python
# Python program to find n-th stair
# using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
# A recursive function used by countWays
def countWays(n) :
res = [0] * (n + 2)
res[0] = 1
res[1] = 1
res[2] = 2
for i in range(3, n + 1) :
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2] + res[i - 3]
return res[n]
# Driver code
n = 4
print(countWays(n))
# This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.C#
// Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
using System;
public class GfG {
// A recursive function used by countWays
public static int countWays(int n)
{
int[] res = new int[n + 2];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2]
+ res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver function
public static void Main()
{
int n = 4;
Console.WriteLine(countWays(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by vt_m */PHP
Javascript
C++
#include
#define k 3
using namespace std;
// Multiply Two Matrix Function
vector> multiply(vector> A, vector> B) {
// third matrix to store multiplication of Two matrix9*
vector> C(k + 1, vector(k + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
for (int x = 1; x <= k; x++) {
C[i][j] = (C[i][j] + (A[i][x] * B[x][j]));
}
}
}
return C;
}
// Optimal Way For finding pow(t,n)
// If n Is Odd then It Will be t*pow(t,n-1)
// else return pow(t,n/2)*pow(t,n/2)
vector> pow(vector> t, int n) {
// base Case
if (n == 1) {
return t;
}
// Recurrence Case
if (n & 1) {
return multiply(t, pow(t, n - 1));
} else {
vector> X = pow(t, n / 2);
return multiply(X, X);
}
}
int compute(int n) {
// base Case
if (n == 0) return 1;
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
// Function Vector(indexing 1 )
// that is [1,2]
int f1[k + 1] = {};
f1[1] = 1;
f1[2] = 2;
f1[3] = 4;
// Constucting Transformation Matrix that will be
/*[[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[3,2,1]]
*/
vector> t(k + 1, vector(k + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
if (i < k) {
// Store 1 in cell that is next to diagonal of Matrix else Store 0 in
// cell
if (j == i + 1) {
t[i][j] = 1;
} else {
t[i][j] = 0;
}
continue;
}
// Last Row - store the Coefficients in reverse order
t[i][j] = 1;
}
}
// Computing T^(n-1) and Setting Tranformation matrix T to T^(n-1)
t = pow(t, n - 1);
int sum = 0;
// Computing first cell (row=1,col=1) For Resultant Matrix TXF
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sum += t[1][i] * f1[i];
}
return sum;
}
int main() {
int n = 4;
cout << compute(n) << endl;
n = 5;
cout << compute(n) << endl;
n = 10;
cout << compute(n) << endl;
return 0;
} 输出 :
7在职的:
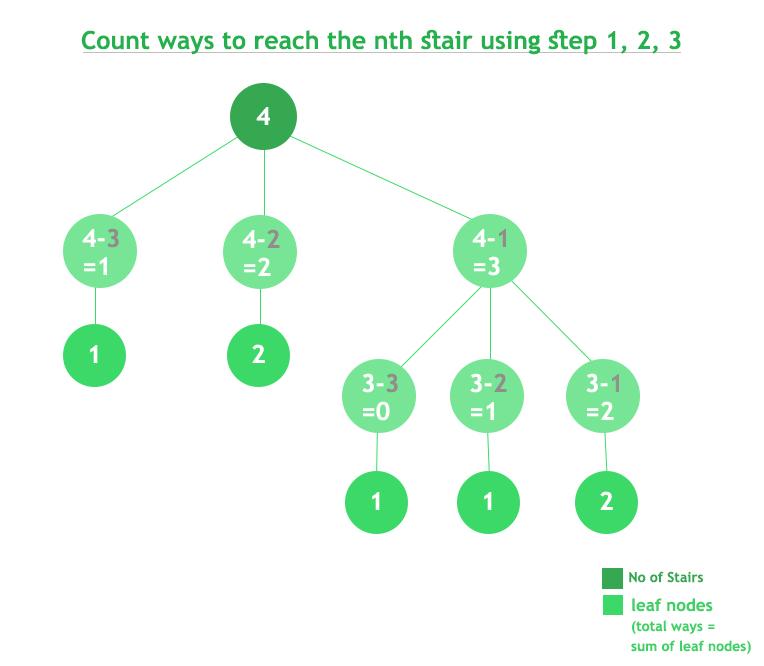
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(3 n )。
上述解决方案的时间复杂度是指数的,上限接近O(3 n )。从每个状态,调用3个递归函数。因此,n个状态的上限为O(3 n )。 - 空间复杂度: O(1)。
由于不需要额外的空间。
注意:可以使用动态编程来优化程序的时间复杂度。
方法2 :动态编程。
这个想法是相似的,但是可以观察到有n个状态,但是递归函数被称为3 ^ n次。这意味着某些状态会被反复调用。因此,想法是存储状态值。这可以通过两种方式完成。
- 自上而下的方法:第一种方法是保持递归结构完整,只将值存储在HashMap中,每当再次调用该函数时,都将返回值存储而不进行计算()。
- 自下而上的方法:第二种方法是占用大小为n的额外空间,并开始计算从1、2 ..到n的状态值,即计算i,i + 1,i + 2的值,然后使用它们来计算计算i + 3的值。
算法:
- 创建一个大小为n + 1的数组,并使用1、1、2(基本情况)初始化前三个变量。
- 从3到n运行一个循环。
- 对于每个索引i,第i个位置的计算机值分别为dp [i] = dp [i-1] + dp [i-2] + dp [i-3]。
- 打印dp [n]的值,作为达到第n步的方式的计数。
C++
// A C++ program to count number of ways
// to reach n't stair when
#include
using namespace std;
// A recursive function used by countWays
int countWays(int n)
{
int res[n + 1];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2]
+ res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int n = 4;
cout << countWays(n);
return 0;
}
//This code is contributed by shubhamsingh10
C
// A C program to count number of ways
// to reach n't stair when
#include
// A recursive function used by countWays
int countWays(int n)
{
int res[n + 1];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2]
+ res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int n = 4;
printf("%d", countWays(n));
return 0;
}
Java
// Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class GfG {
// A recursive function used by countWays
public static int countWays(int n)
{
int[] res = new int[n + 1];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2]
+ res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver function
public static void main(String argc[])
{
int n = 4;
System.out.println(countWays(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Sagar Shukla */
Python
# Python program to find n-th stair
# using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
# A recursive function used by countWays
def countWays(n) :
res = [0] * (n + 2)
res[0] = 1
res[1] = 1
res[2] = 2
for i in range(3, n + 1) :
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2] + res[i - 3]
return res[n]
# Driver code
n = 4
print(countWays(n))
# This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
C#
// Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
using System;
public class GfG {
// A recursive function used by countWays
public static int countWays(int n)
{
int[] res = new int[n + 2];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2]
+ res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver function
public static void Main()
{
int n = 4;
Console.WriteLine(countWays(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by vt_m */
的PHP
Java脚本
输出 :
7- 在职的:
1 -> 1 -> 1 -> 1
1 -> 1 -> 2
1 -> 2 -> 1
1 -> 3
2 -> 1 -> 1
2 -> 2
3 -> 1
So Total ways: 7- 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
只需要遍历数组一次。因此,时间复杂度为O(n)。 - 空间复杂度: O(n)。
要将值存储在DP中,需要n个额外的空间。
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
方法3:矩阵求幂(O(logn)方法)
矩阵幂运算是解决DP问题的数学方法,具有更好的时间复杂度。矩阵幂运算技术具有大小为KXK的变换矩阵和函数向量(KX 1)。通过将变换矩阵的n-1次幂乘以函数向量,得到结果向量,将其表示为大小为KX 1的Res。给定n值。该方法将采用O(K ^ 3logn)时间复杂度,即找到变换矩阵的(n-1)次幂的复杂度。
关键条款:
K = F(n)依赖的项,从递归关系中我们可以说F(n)依赖于F(n-1)和F(n-2)。 => K = 3
F1 =包含前K个项的F(n)值的向量(一维数组)。由于K = 3 => F1将具有前2个项的F(n)值。 F1 = [1,2,4]
T =转换矩阵,是大小为KXK的2D矩阵,由对角后的所有1组成,除最后一行外其余全部为零。最后一行将具有所有K个项的系数,其中F(n)依赖于逆序。 => T = [[0 1 0],[0 0 1],[1 1 1]]。
算法:
1)Take Input N
2)If N < K then Return Precalculated Answer //Base Condition
3)construct F1 Vector and T (Transformation Matrix)
4)Take N-1th power of T by using Optimal Power(T,N) Methods and assign it in T
5)return (TXF)[1]有关最佳功率(T,N)方法的信息,请参阅以下文章:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/write-ac-program-to-calculate-powxn/
C++
#include
#define k 3
using namespace std;
// Multiply Two Matrix Function
vector> multiply(vector> A, vector> B) {
// third matrix to store multiplication of Two matrix9*
vector> C(k + 1, vector(k + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
for (int x = 1; x <= k; x++) {
C[i][j] = (C[i][j] + (A[i][x] * B[x][j]));
}
}
}
return C;
}
// Optimal Way For finding pow(t,n)
// If n Is Odd then It Will be t*pow(t,n-1)
// else return pow(t,n/2)*pow(t,n/2)
vector> pow(vector> t, int n) {
// base Case
if (n == 1) {
return t;
}
// Recurrence Case
if (n & 1) {
return multiply(t, pow(t, n - 1));
} else {
vector> X = pow(t, n / 2);
return multiply(X, X);
}
}
int compute(int n) {
// base Case
if (n == 0) return 1;
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
// Function Vector(indexing 1 )
// that is [1,2]
int f1[k + 1] = {};
f1[1] = 1;
f1[2] = 2;
f1[3] = 4;
// Constucting Transformation Matrix that will be
/*[[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[3,2,1]]
*/
vector> t(k + 1, vector(k + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
if (i < k) {
// Store 1 in cell that is next to diagonal of Matrix else Store 0 in
// cell
if (j == i + 1) {
t[i][j] = 1;
} else {
t[i][j] = 0;
}
continue;
}
// Last Row - store the Coefficients in reverse order
t[i][j] = 1;
}
}
// Computing T^(n-1) and Setting Tranformation matrix T to T^(n-1)
t = pow(t, n - 1);
int sum = 0;
// Computing first cell (row=1,col=1) For Resultant Matrix TXF
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sum += t[1][i] * f1[i];
}
return sum;
}
int main() {
int n = 4;
cout << compute(n) << endl;
n = 5;
cout << compute(n) << endl;
n = 10;
cout << compute(n) << endl;
return 0;
}
7
13
274Explanation:
We Know For This Question
Transformation Matrix M= [[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Functional Vector F1 = [1,2,4]
for n=2 :
ans = (M X F1)[1]
ans = [2,4,7][1]
ans = 2 //[2,4,7][1] = First cell value of [2,4,7] i.e 2
for n=3 :
ans = (M X M X F1)[1] //M^(3-1) X F1 = M X M X F1
ans = (M X [2,4,7])[1]
ans = [4,7,13][1]
ans = 4
for n = 4 :
ans = (M^(4-1) X F1)[1]
ans = (M X M X M X F1) [1]
ans = (M X [4,7,13])[1]
ans = [7,13,24][1]
ans = 7
for n = 5 :
ans = (M^4 X F1)[1]
ans = (M X [7,13,24])[1]
ans = [13,24,44][1]
ans = 13时间复杂度:
O(K^3log(n)) //For Computing pow(t,n-1)
For this question K is 3
So Overall Time Complexity is O(27log(n))=O(logn)