给定一个由空单元(用“ 1”表示)和障碍物(用“ 0”表示)组成的N * N网格,任务是找到可以放置镜子以观察东侧的空单元的数量从南侧看网格。
例子:
Input: mat[][] = {
{1, 1, 1},
{1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1}}
Output: 2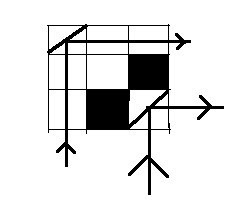
On clearly observing the image above, it can be seen that the mirror can be placed in only the cell (0, 0) and the cell (2, 2). If any other cell is chosen then the path of light is obstructed by the obstacles.
Input: mat[][] = {
{0, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 1}}
Output: 6
幼稚的方法:提到镜子只有在其右侧和下方的所有单元都为空时才能放置在一个空单元中。天真的方法是单独检查每个单元格是否满足条件。这种方法将花费O(n 3 )时间。
高效方法:创建两个布尔数组row [] []和col [] [] ,如果第j列(包括它)之后的第i行中的所有单元格均为1,则将存储row [i] [j]如果第i行(包括它)之后的第j列中的所有单元格均为1 ,则col [i] [j]将存储true,否则col [i] [j]将存储false。现在,对于每个单元格mat [i] [j],如果row [i] [j]和col [i] [j]均为true,则当前单元格有效,否则无效。计算所有此类有效单元格并最后打印计数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 3;
// Function to return the number of cells
// in which mirror can be placed
int numberOfCells(int mat[][N])
{
bool row[N][N] = { { false } };
bool col[N][N] = { { false } };
// Update the row array where row[i][j]
// will store whether the current row i
// contains all 1s in the columns
// starting from j
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = N - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (mat[i][j] == 1) {
row[i][j] = (j + 1 < N)
? row[i][j + 1]
: true;
}
else {
row[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
// Update the column array where col[i][j]
// will store whether the current column j
// contains all 1s in the rows starting from i
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (mat[i][j] == 1) {
col[i][j] = (i + 1 < N)
? col[i + 1][j]
: true;
}
else {
col[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
// To store the required result
int cnt = 0;
// For every cell except the last
// row and the last column
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N - 1; j++) {
// If the current cell is not blocked
// and the light can travel from the
// next row and the next column
// then the current cell is valid
if (row[i][j]
&& col[i][j]) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
// For the last column
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (col[i][N - 1])
cnt++;
}
// For the last row, note that the last column
// is not taken into consideration as the bottom
// right element has already been considered
// in the last column previously
for (int j = 0; j < N - 1; j++) {
if (row[N - 1][j])
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int mat[][N] = { { 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 1 } };
cout << numberOfCells(mat);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int N = 3;
// Function to return the number of cells
// in which mirror can be placed
static int numberOfCells(int mat[][])
{
boolean [][]row = new boolean[N][N];
boolean [][]col = new boolean[N][N];
// Update the row array where row[i][j]
// will store whether the current row i
// contains all 1s in the columns
// starting from j
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = N - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (mat[i][j] == 1)
{
row[i][j] = (j + 1 < N) ? row[i][j + 1]
: true;
}
else
{
row[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
// Update the column array where col[i][j]
// will store whether the current column j
// contains all 1s in the rows starting from i
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (mat[i][j] == 1)
{
col[i][j] = (i + 1 < N) ? col[i + 1][j]
: true;
}
else
{
col[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
// To store the required result
int cnt = 0;
// For every cell except the last
// row and the last column
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N - 1; j++)
{
// If the current cell is not blocked
// and the light can travel from the
// next row and the next column
// then the current cell is valid
if (row[i][j] && col[i][j])
{
cnt++;
}
}
}
// For the last column
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (col[i][N - 1])
cnt++;
}
// For the last row, note that the last column
// is not taken into consideration as the bottom
// right element has already been considered
// in the last column previously
for (int j = 0; j < N - 1; j++)
{
if (row[N - 1][j])
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int mat[][] = { { 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 1 } };
System.out.print(numberOfCells(mat));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
N = 3
# Function to return the number of cells
# in which mirror can be placed
def numberOfCells(mat):
row = [[ False for i in range(N)]
for i in range(N)]
col = [[ False for i in range(N)]
for i in range(N)]
# Update the row array where row[i][j]
# will store whether the current row i
# contains all 1s in the columns
# starting from j
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N - 1, -1, -1):
if (mat[i][j] == 1):
if j + 1 < N:
row[i][j] = row[i][j + 1]
else:
row[i][j] = True
else :
row[i][j] = False
# Update the column array where col[i][j]
# will store whether the current column j
# contains all 1s in the rows starting from i
for j in range(N):
for i in range(N - 1, -1, -1):
if (mat[i][j] == 1):
if i + 1 < N:
col[i][j] = col[i + 1][j]
else:
col[i][j] = True
else:
col[i][j] = False
# To store the required result
cnt = 0
# For every cell except the last
# row and the last column
for i in range(N - 1):
for j in range(N - 1):
# If the current cell is not blocked
# and the light can travel from the
# next row and the next column
# then the current cell is valid
if (row[i][j] and col[i][j]):
cnt += 1
# For the last column
for i in range(N):
if (col[i][N - 1]):
cnt += 1
# For the last row, note that the last column
# is not taken into consideration as the bottom
# right element has already been considered
# in the last column previously
for j in range(N - 1):
if (row[N - 1][j]):
cnt += 1
return cnt
# Driver code
mat = [[0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1]]
print(numberOfCells(mat))
# This code is contributed by Mohit KumarC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int N = 3;
// Function to return the number of cells
// in which mirror can be placed
static int numberOfCells(int [,]mat)
{
bool [,]row = new bool[N, N];
bool [,]col = new bool[N, N];
// Update the row array where row[i,j]
// will store whether the current row i
// contains all 1s in the columns
// starting from j
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = N - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (mat[i, j] == 1)
{
row[i, j] = (j + 1 < N) ? row[i, j + 1]
: true;
}
else
{
row[i, j] = false;
}
}
}
// Update the column array where col[i,j]
// will store whether the current column j
// contains all 1s in the rows starting from i
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (mat[i, j] == 1)
{
col[i, j] = (i + 1 < N) ? col[i + 1, j]
: true;
}
else
{
col[i, j] = false;
}
}
}
// To store the required result
int cnt = 0;
// For every cell except the last
// row and the last column
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N - 1; j++)
{
// If the current cell is not blocked
// and the light can travel from the
// next row and the next column
// then the current cell is valid
if (row[i, j] && col[i, j])
{
cnt++;
}
}
}
// For the last column
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (col[i, N - 1])
cnt++;
}
// For the last row, note that the last column
// is not taken into consideration as the bottom
// right element has already been considered
// in the last column previously
for (int j = 0; j < N - 1; j++)
{
if (row[N - 1, j])
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]mat = {{ 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 1 }};
Console.Write(numberOfCells(mat));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar6
时间复杂度: O(n 2 )
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。