📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-16 07:07:14 🧑 作者: Mango
模型是代表业务逻辑和规则的对象。要创建模型,您应该扩展yii \ base \ Model类或其子类。
属性
属性代表业务数据。可以像访问数组元素或对象属性一样访问它们。每个属性都是模型的可公开访问的属性。要指定模型拥有的属性,您应该覆盖yii \ base \ Model :: attributes()方法。
让我们看一下基本应用程序模板的ContactForm模型。
'Verification Code',
];
}
/**
* Sends an email to the specified email address using the information
collected by this model.
* @param string $email the target email address
* @return boolean whether the model passes validation
*/
public function contact($email) {
if ($this->validate()) {
Yii::$app->mailer->compose()
->setTo($email)
->setFrom([$this->email => $this->name])
->setSubject($this->subject)
->setTextBody($this->body)
->send();
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
?>
第1步-创建一个与下面的代码SiteController称为actionShowContactModel函数。
public function actionShowContactModel() {
$mContactForm = new \app\models\ContactForm();
$mContactForm->name = "contactForm";
$mContactForm->email = "user@gmail.com";
$mContactForm->subject = "subject";
$mContactForm->body = "body";
var_dump($mContactForm);
}
在上面的代码中,我们定义了ContactForm模型,设置属性并在屏幕上显示该模型。
步骤2-现在,如果在Web浏览器的地址栏中键入http:// localhost:8080 / index.php?r = site / show-contact-model ,您将看到以下内容。
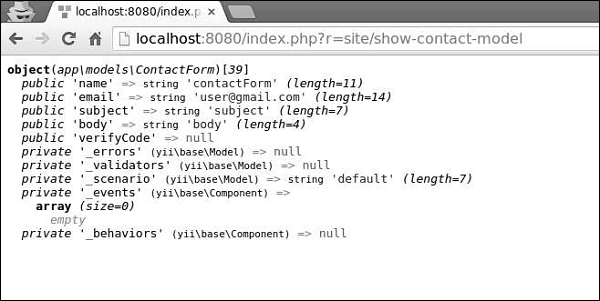
如果您的模型从yii \ base \ Model扩展,则其所有成员变量(公共和非静态)都是属性。 ContactForm模型中有五个属性-名称,电子邮件,主题,正文, verifyCode ,您可以轻松添加新属性。
属性标签
您通常需要显示与属性关联的标签。默认情况下,属性标签由yii \ base \ Model :: generateAttributeLabel()方法自动生成。要手动声明属性标签,您可以覆盖yii \ base \ Model :: attributeLabels()方法。
步骤1-如果打开http:// localhost:8080 / index.php?r = site / contact,您将看到以下页面。
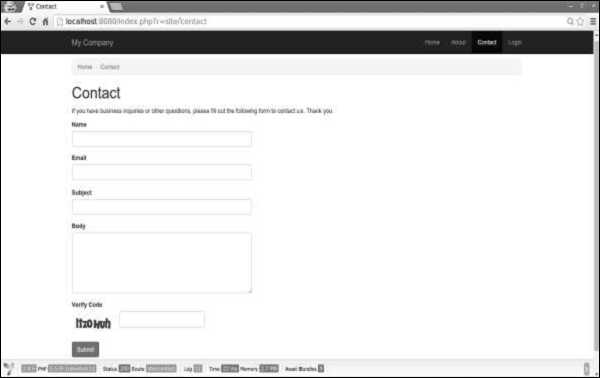
请注意,属性标签与其名称相同。
步骤2-现在,以以下方式修改ContactForm模型中的attributeLabels函数。
public function attributeLabels() {
return [
'name' => 'name overridden',
'email' => 'email overridden',
'subject' => 'subject overridden',
'body' => 'body overridden',
'verifyCode' => 'verifyCode overridden',
];
}
步骤3-如果再次打开http:// localhost:8080 / index.php?r = site / contact ,您将注意到标签已更改,如下图所示。
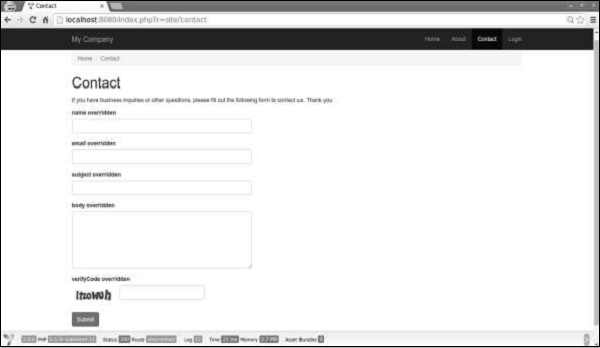
情境
您可以在不同的场景中使用模型。例如,当客人想要发送联系表时,我们需要所有模型属性。当用户想要做同样的事情时,他已经登录了,因此我们不需要他的名字,因为我们可以很容易地从数据库中获取它的名字。
要声明场景,我们应该重写censings()函数。它返回一个数组,其键是方案名称,值是活动属性。活动属性是要验证的属性。他们也可以被大量分配。
步骤1-以以下方式修改ContactForm模型。
['name', 'email', 'subject',
'body', 'verifyCode'],
self::SCENARIO_EMAIL_FROM_USER => ['email' ,'subject', 'body',
'verifyCode'],
];
}
/**
* @return array the validation rules.
*/
public function rules() {
return [
// name, email, subject and body are required
[['name', 'email', 'subject', 'body'], 'required'],
// email has to be a valid email address
['email', 'email'],
// verifyCode needs to be entered correctly
['verifyCode', 'captcha'],
];
}
/**
* @return array customized attribute labels
*/
public function attributeLabels() {
return [
'name' => 'name overridden',
'email' => 'email overridden',
'subject' => 'subject overridden',
'body' => 'body overridden',
'verifyCode' => 'verifyCode overridden',
];
}
/**
* Sends an email to the specified email address using the information
collected by this model.
* @param string $email the target email address
* @return boolean whether the model passes validation
*/
public function contact($email) {
if ($this -> validate()) {
Yii::$app->mailer->compose()
->setTo($email)
->setFrom([$this->email => $this->name])
->setSubject($this->subject)
->setTextBody($this->body)
->send();
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
?>
我们添加了两个方案。一个用于访客,另一个用于经过身份验证的用户。用户通过身份验证后,我们不需要他的名字。
步骤2-现在,修改SiteController的actionContact函数。
public function actionContact() {
$model = new ContactForm();
$model->scenario = ContactForm::SCENARIO_EMAIL_FROM_GUEST;
if ($model->load(Yii::$app->request->post()) && $model->
contact(Yii::$app->params ['adminEmail'])) {
Yii::$app->session->setFlash('contactFormSubmitted');
return $this->refresh();
}
return $this->render('contact', [
'model' => $model,
]);
}
步骤3-在网络浏览器中输入http:// localhost:8080 / index.php?r = site / contact 。您会注意到,当前,所有模型属性都是必需的。
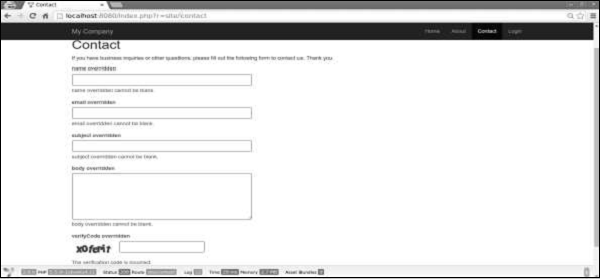
步骤4-如果您在actionContact中更改模型的场景,如以下代码所示,您将发现不再需要name属性。
$model->scenario = ContactForm::SCENARIO_EMAIL_FROM_USER;

大量分配
大规模分配是一种通过单行代码从多个输入属性创建模型的便捷方法。
代码行是-
$mContactForm = new \app\models\ContactForm;
$mContactForm->attributes = \Yii::$app->request->post('ContactForm');
上面给出的代码行等效于-
$mContactForm = new \app\models\ContactForm;
$postData = \Yii::$app->request->post('ContactForm', []);
$mContactForm->name = isset($postData['name']) ? $postData['name'] : null;
$mContactForm->email = isset($postData['email']) ? $postData['email'] : null;
$mContactForm->subject = isset($postData['subject']) ? $postData['subject'] : null;
$mContactForm->body = isset($postData['body']) ? $postData['body'] : null;
前者要干净得多。请注意,大量分配仅适用于安全属性。它们只是scenario()函数列出的当前方案属性。
资料汇出
模型通常需要以不同的格式导出。该模型转换为数组,修改SiteController的actionShowContactModel函数-
public function actionShowContactModel() {
$mContactForm = new \app\models\ContactForm();
$mContactForm->name = "contactForm";
$mContactForm->email = "user@gmail.com";
$mContactForm->subject = "subject";
$mContactForm->body = "body";
var_dump($mContactForm->attributes);
}
在地址栏中输入http:// localhost:8080 / index.php?r = site / show-contact-model ,您将看到以下内容-
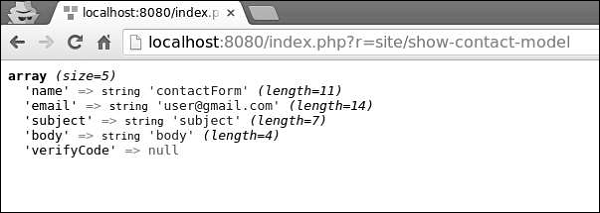
要将模型转换为JSON格式,请按以下方式修改actionShowContactModel函数:
public function actionShowContactModel() {
$mContactForm = new \app\models\ContactForm();
$mContactForm->name = "contactForm";
$mContactForm->email = "user@gmail.com";
$mContactForm->subject = "subject";
$mContactForm->body = "body";
return \yii\helpers\Json::encode($mContactForm);
}
浏览器输出–
{
"name":"contactForm",
"email":"user@gmail.com",
"subject":"subject",
"body":"body ",
"verifyCode":null
}
重要事项
在精心设计的应用程序中,模型通常比控制器快得多。模型应该-
- 包含业务逻辑。
- 包含验证规则。
- 包含属性。
- 未嵌入HTML。
- 不直接访问请求。
- 没有太多的情况。