对流
它可能已经看到,如果将一杯热茶放在桌子上很长时间,它就会冷却下来。这是由于热量散失到环境中。因此,传热被描述为热量或热能从一个物理系统到另一个物理系统的传输。因此,当两个物体有温差时,热量会从热的物体传递到较冷的物体。传导、对流和辐射是三种最常见的传热方式。我们将在这篇文章中讨论通过对流进行的热传递。
对流
The action of heat transmission through movement of major number of molecules inside fluids such as gases and liquids is known as convection.
物品和流体之间的初始热传递是通过传导发生的,但大部分热传递是由于流体运动而发生的。
固体不会经历对流,因为它们的基本粒子不会移动。固体中的热扩散过程称为热传导。在正常情况下,气体和液体是不良的热导体,但是,它们可以通过对流快速传递热量。

对流换热:它是如何工作的?
对流是固体与与固体接触的液体或流体之间的热传递过程。当通过屏障将热量从一种液体传递到另一种液体时,对流是必不可少的。对流热传递通过热扩散(流体分子运动)或平流发生,其中热量通过流体中热流的整体运动传递。
当任何流体从下方加热时,就会发生热膨胀。随着温度升高,流体的密度在较低层中降低。流体中较热、密度较小的部分由于浮力而上升,并被密度较大、较冷的流体所取代。当这部分升温时,它也上升并被上层较冷的层取代,并重复该过程。这样,对流被用来传递热量。
对流类型
对流可分为两种:
- 自然对流
- 强制对流
自然对流: 当温差发生时,会引起密度差,产生浮力,发生对流。这个过程被称为自然对流。海洋风是自然对流的一个例子。
强制对流:当利用泵或风扇等外部源产生对流时,就会发生强制对流。利用间歇泉或热水器快速加热水,以及在温暖的夏季使用风扇,都是强制对流的例子。
牛顿冷却定律
在典型情况下,对流热传递与组件之间的温差成正比。牛顿冷却定律已经说明了这种现象,该定律指出:
The rate of heat transmission from anybody to its surroundings by convection is related to temperature difference between them. The difference in temperature should be minimal, and the radiating surface’s nature should stay unchanged.
牛顿冷却定律与强制对流有关,写成:
P = dq⁄dt = hA(Ts-Tf)
where, P = dq⁄dt is the heat transfer rate, h is the heat-transfer coefficient of convection, A is the surface area of body which is exposed, Ts is the body temperature and Tf is the fluid temperature.
The heat-transfer coefficient value depends on the various factors:
- Viscosity
- Density
- Specific heat capacity
- Thermal conductivity
对流的例子
- 温暖的水在接近赤道时流向两极,而较冷的水则流向赤道。
- 温血动物使用对流来循环血液,这有助于调节体温。
- 海陆风现象是自然对流最普遍的例子之一。
海风:白天有海风。水和土地都被太阳加热。因为水的加热能力比陆地高,它接收到更多的太阳能,但升温速度要慢得多。结果,陆地上方的温度升高,加热了周围环境中的空气。
暖空气由于密度较低而膨胀,导致沿岸陆地上空出现低压区域。同时,水处于相当高的压力下。由于空气中的压力差,空气从海洋流向陆地。结果,一股意想不到的风被称为海风。
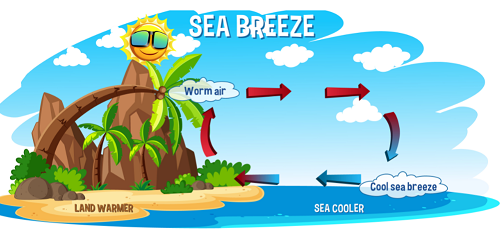
海风
陆风:当夜间情况发生变化时,就会出现这些现象。随着日落,陆地和海洋开始变冷。由于热容量的变化,与水相比,土地的热量散失更快。相比之下,水温变高,导致那里的气压低。这会在海岸外产生凉爽的风,称为陆风。

陆风
示例问题
问题1:对流在我们的日常生活中扮演什么角色?
回答:
In the following situations, convection is used:
- When water is heated to a certain temperature, the water molecules expand and circulate in the vicinity. As a result of the heat being transported to different sections of the pot, the cold water begins to sink while the heated water rises.
- The air within the hot air balloon is continuously heated, making it warmer. The balloon, like the warm air, rises.
- In the afternoon, the land near the sea is warmer than in the evening. By the concept of convection, heated air rises and is replaced by colder air. Similarly, the air near the water is warmer than the air near the coast at night. This happens because heated air rises and is replaced by cold air.
问题2:为什么固体材料不经历对流?
回答:
Convection is the process of heat transfer through movement of particles. Since, the solid particles do not move, convection is not possible in solid materials.
问题3:对流发生的过程是什么?
回答:
When transferring heat from one liquid to another through a barrier, convection is essential. Convectional heat transfer occurs either through thermal diffusion (fluid molecule motion) or advection, in which heat is transferred through the bulk motion of heat currents in the fluid.
问题 4:“自由”或“自然”对流是什么意思?
回答:
The mechanism of heat transmission is considered to be free or natural convection if the fluid motion is caused by a change in density caused by temperature gradients.
问题5:自然对流或诱导对流,哪个具有更高的传热系数?这背后的原因是什么?
回答:
Since the convection heat transfer coefficient is primarily determined by characteristics such as fluid density, velocity, and viscosity, it is generally larger in forced convection than in natural convection.