毫升 |用于特征选择的额外树分类器
先决条件:决策树分类器
极端随机树分类器(Extra Trees Classifier)是一种集成学习技术,它聚合在“森林”中收集的多个去相关决策树的结果以输出其分类结果。在概念上,它与随机森林分类器非常相似,只是在森林中构建决策树的方式不同。
Extra Trees Forest 中的每个决策树都是从原始训练样本构建的。然后,在每个测试节点,每棵树都提供了来自特征集中的 k 个特征的随机样本,每个决策树必须从中选择最佳特征来根据一些数学标准(通常是基尼指数)分割数据。这种随机的特征样本会导致创建多个去相关的决策树。
为了使用上述森林结构进行特征选择,在森林的构建过程中,对于每个特征,在分割特征的决策中使用的数学标准的归一化总减少量(Gini Index,如果 Gini Index 用于构建森林)被计算。这个值称为特征的基尼重要性。为了进行特征选择,每个特征根据每个特征的基尼重要性按降序排列,用户根据自己的选择选择前k个特征。
考虑以下数据:-

让我们用五棵决策树为上述数据构建一个假设的 Extra Trees Forest,k 的值决定随机特征样本中的特征数量为2 。这里使用的决策标准将是信息增益。首先,我们计算数据的熵。注意计算熵的公式是:-
其中 c 是唯一类标签的数量,并且![]() 是输出标签为 i 的行的比例。
是输出标签为 i 的行的比例。
因此对于给定的数据,熵是:-
![]()
![]()
让决策树构造成这样:-
请注意,信息增益的公式是:-
![]()
因此,

![]()
相似地:
![]()
使用上面给出的公式:-
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
计算每个功能的总信息增益:-
Total Info Gain for Outlook = 0.246+0.246 = 0.492
Total Info Gain for Temperature = 0.029+0.029+0.029 = 0.087
Total Info Gain for Humidity = 0.151+0.151+0.151 = 0.453
Total Info Gain for Wind = 0.048+0.048 = 0.096
因此,根据上述构造的 Extra Trees Forest 确定输出标签的最重要变量是特征“Outlook”。
下面给出的代码将演示如何使用 Extra Trees Classifiers 进行特征选择。
第 1 步:导入所需的库
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier
第 2 步:加载和清理数据
# Changing the working location to the location of the file
cd C:\Users\Dev\Desktop\Kaggle
# Loading the data
df = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
# Separating the dependent and independent variables
y = df['Play Tennis']
X = df.drop('Play Tennis', axis = 1)
X.head()

第 3 步:构建 Extra Trees Forest 并计算各个特征的重要性
# Building the model
extra_tree_forest = ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators = 5,
criterion ='entropy', max_features = 2)
# Training the model
extra_tree_forest.fit(X, y)
# Computing the importance of each feature
feature_importance = extra_tree_forest.feature_importances_
# Normalizing the individual importances
feature_importance_normalized = np.std([tree.feature_importances_ for tree in
extra_tree_forest.estimators_],
axis = 0)
第 4 步:可视化和比较结果
# Plotting a Bar Graph to compare the models
plt.bar(X.columns, feature_importance_normalized)
plt.xlabel('Feature Labels')
plt.ylabel('Feature Importances')
plt.title('Comparison of different Feature Importances')
plt.show()
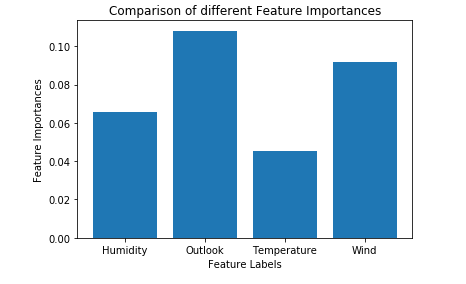
因此,上面给出的输出验证了我们关于使用额外树分类器进行特征选择的理论。由于特征样本的随机性,特征的重要性可能具有不同的值。