珀尔 |构造函数和析构函数
Perl 子例程中的构造函数返回一个对象,该对象是该类的一个实例。在 Perl 中,约定是将构造函数命名为“new” 。与许多其他OOP不同,Perl 不提供任何特殊语法来构造对象。它使用与该特定类显式关联的数据结构(散列、数组、标量)。
构造函数在哈希引用和类名(包名)上使用“bless”函数。
让我们设计一些代码来更好地解释:
注意:由于使用了包,以下代码不会在 Online IDE 上运行。下面的代码是 Perl 类或模块文件。将以下文件另存为 (*.pm) 扩展名。
# Declaring the Package
package Area;
# Declaring the Constructor method
sub new
{
return bless {}, shift; # blessing on the hashed
# reference (which is empty).
}
1;
调用构造方法时,包名“Area”存储在默认数组“@_”中。 “shift”关键字用于从“@_”获取包名并将其传递给“bless”函数。
package Area;
sub new
{
my $class = shift; # defining shift in $myclass
my $self = {}; # the hashed reference
return bless $self, $class;
}
1;
Note: "my" restricts the scope of a variable.Perl 中的属性作为键值对存储在散列引用中。此外,在代码中添加一些属性。
package Area;
sub new
{
my $class = shift;
my $self =
{
length => 2, # storing length
width => 3, # storing width
};
return bless $self, $class;
}
1;
上面的代码(面积类)有两个属性:长度和宽度。为了访问这些属性,设计了另一个 Perl 程序来使用它们。
use strict;
use warnings;
use Area;
use feature qw/say/;
# creating a new Area object
my $area = Area->new;
say $area->{length}; #print the length
say $area->{width}; # print the width
运行代码的步骤:
- 将带有 Package Area 的程序保存在名为Area.pm的文本文件中
注意:文件名应始终与包名相同。 - 现在,保存用于访问包中由名称 *.pl 定义的属性的程序。这里,* 可以是任何名称(在本例中为 test.pl)。
- 使用命令在 Perl 命令行中运行保存为 test.pl 的代码
perl 测试.pl
输出: 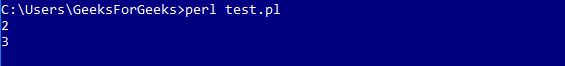
传递动态属性:
使用动态属性更新现有文件:
地区.pm:
package Area;
sub new
{
my ($class, $args) = @_; # since the values will be
# passed dynamically
my $self =
{
length => $args->{length} || 1, # by default the value is 1 (stored)
width => $args->{width} || 1, # by default the value is 1 (stored)
};
return bless $self, $class;
}
# we have added the get_area function to
# calculate the area as well
sub get_area
{
my $self = shift;
# getting the area by multiplication
my $area = $self->{length} * $self->{width};
return $area;
}
1;
测试.pl:
use strict;
use warnings;
use feature qw/say/;
use Area;
# pass length and width arguments
# to the constructor
my $area = Area->new(
{
length => 2, # passing '2' as param of length
width => 2, # passing '2' as param of width
});
say $area->get_area;
现在,参数
length = 2, width = 2传递到包 Area 上,计算 Square 的面积。
The arguments are contained in the default array variable @_ when any subroutine is called
注意:现在按照上面解释的相同过程运行代码。
输出: 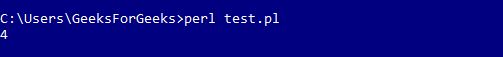
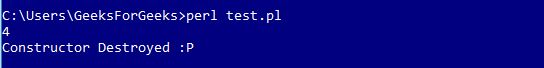
当对象的所有引用超出范围时,Perl 会自动调用析构函数。如果类创建了对象被销毁时需要清理的线程或临时文件,则可以使用析构函数。 Perl 包含一个特殊的方法名称,' DESTROY ' 用于析构函数,必须在析构函数声明时使用。
句法:
sub DESTROY
{
# DEFINE Destructors
my $self = shift;
print "Constructor Destroyed :P";
}
Once this snippet is added to existing file Area.pm.输出会有点像这样: