给定的无环无向图的二进制树的根的形式在顶点1和值在每个顶点[1,N]由阵列ARR []表示时,任务是找到根的数量含有叶的路径至多 m 个值为K 的连续节点。
例子:
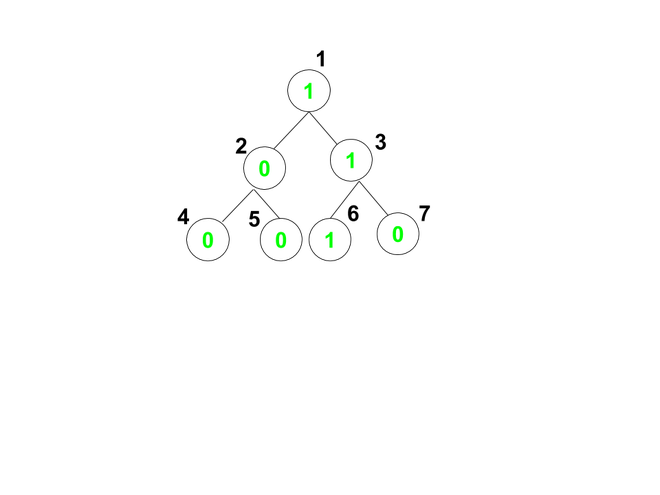
Input: arr[] = {1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0}, K = 1, M = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
Path 1 : 1 -> 2 -> 4 contains maximum 1 consecutive K
Path 2 : 1 -> 2 -> 5 contains maximum 1 consecutive K
Path 3 : 1 -> 3 -> 6 contains maximum 3 consecutive K
Path 4 : 1 -> 3 -> 7 contains maximum 2 consecutive K
Since the given value of M is 2, therefore there are 3 paths that contains atmost 2 consecutive K.
Input: arr[] = {2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 4, 3, 5, 2}, K = 2, M = 2
Output: 3
方法:
可以使用深度优先搜索方法解决该问题:
- 深度优先搜索可用于遍历从根顶点开始的所有路径。
- 每次如果当前节点的值为K ,则增加计数。
- 否则,将计数设置为0 。
- 如果计数超过M ,则返回。
- 否则,遍历其相邻节点并重复上述步骤。
- 最后,打印获得的计数值。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
2
/ \
1 3
/ \ / \
2 1 2 1
/ \ / \
4 3 5 2
Java
// C++ Program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Initialize the adjacency
// list and visited array
vector adj[100005];
int visited[100005] = { 0 };
int ans = 0;
// Function to find the number of root to
// leaf paths that contain atmost m
// consecutive nodes with value k
void dfs(int node, int count, int m,
int arr[], int k)
{
// Mark the current node
// as visited
visited[node] = 1;
// If value at current node is k
if (arr[node - 1] == k) {
// Increment counter
count++;
}
else {
count = 0;
}
// If count is greater than m
// return from that path
if (count > m) {
return;
}
// Path is allowed if size of present node
// becomes 0 i.e it has no child root and
// no more than m consecutive 1's
if (adj[node].size() == 1 && node != 1) {
ans++;
}
for (auto x : adj[node]) {
if (!visited[x]) {
dfs(x, count, m, arr, k);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int N = 7, K = 2, M = 2;
// Desigining the tree
adj[1].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(1);
adj[1].push_back(3);
adj[3].push_back(1);
adj[2].push_back(4);
adj[4].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(5);
adj[5].push_back(2);
adj[3].push_back(6);
adj[6].push_back(3);
adj[3].push_back(7);
adj[7].push_back(3);
// Counter counts no.
// of consecutive nodes
int counter = 0;
dfs(1, counter, M, arr, K);
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
} Python3
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Initialize the adjacency
// list and visited array
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector []adj = new Vector[100005];
static int []visited = new int[100005];
static int ans = 0;
// Function to find the number of root to
// leaf paths that contain atmost m
// consecutive nodes with value k
static void dfs(int node, int count, int m,
int arr[], int k)
{
// Mark the current node
// as visited
visited[node] = 1;
// If value at current node is k
if (arr[node - 1] == k)
{
// Increment counter
count++;
}
else
{
count = 0;
}
// If count is greater than m
// return from that path
if (count > m)
{
return;
}
// Path is allowed if size of present node
// becomes 0 i.e it has no child root and
// no more than m consecutive 1's
if (adj[node].size() == 1 && node != 1)
{
ans++;
}
for(int x : adj[node])
{
if (visited[x] == 0)
{
dfs(x, count, m, arr, k);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int N = 7, K = 2, M = 2;
for(int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector();
// Desigining the tree
adj[1].add(2);
adj[2].add(1);
adj[1].add(3);
adj[3].add(1);
adj[2].add(4);
adj[4].add(2);
adj[2].add(5);
adj[5].add(2);
adj[3].add(6);
adj[6].add(3);
adj[3].add(7);
adj[7].add(3);
// Counter counts no.
// of consecutive nodes
int counter = 0;
dfs(1, counter, M, arr, K);
System.out.print(ans + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar C#
# Python3 Program to implement
# the above approach
# Initialize the adjacency
# list and visited array
adj = [[] for i in range(100005)]
visited = [ 0 for i in range(100005)]
ans = 0;
# Function to find the number of root to
# leaf paths that contain atmost m
# consecutive nodes with value k
def dfs(node, count, m, arr, k):
global ans
# Mark the current node
# as visited
visited[node] = 1;
# If value at current
# node is k
if (arr[node - 1] == k):
# Increment counter
count += 1;
else:
count = 0;
# If count is greater than m
# return from that path
if (count > m):
return;
# Path is allowed if size
# of present node becomes 0
# i.e it has no child root and
# no more than m consecutive 1's
if (len(adj[node]) == 1 and node != 1):
ans += 1
for x in adj[node]:
if (not visited[x]):
dfs(x, count, m, arr, k);
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
N = 7
K = 2
M = 2
# Desigining the tree
adj[1].append(2);
adj[2].append(1);
adj[1].append(3);
adj[3].append(1);
adj[2].append(4);
adj[4].append(2);
adj[2].append(5);
adj[5].append(2);
adj[3].append(6);
adj[6].append(3);
adj[3].append(7);
adj[7].append(3);
# Counter counts no.
# of consecutive nodes
counter = 0;
dfs(1, counter, M, arr, K);
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56输出:
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Initialize the adjacency
// list and visited array
static List []adj = new List[100005];
static int []visited = new int[100005];
static int ans = 0;
// Function to find the number of root to
// leaf paths that contain atmost m
// consecutive nodes with value k
static void dfs(int node, int count, int m,
int []arr, int k)
{
// Mark the current node
// as visited
visited[node] = 1;
// If value at current node is k
if (arr[node - 1] == k)
{
// Increment counter
count++;
}
else
{
count = 0;
}
// If count is greater than m
// return from that path
if (count > m)
{
return;
}
// Path is allowed if size of present node
// becomes 0 i.e it has no child root and
// no more than m consecutive 1's
if (adj[node].Count == 1 && node != 1)
{
ans++;
}
foreach(int x in adj[node])
{
if (visited[x] == 0)
{
dfs(x, count, m, arr, k);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []arr = { 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int K = 2, M = 2;
for(int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List();
// Desigining the tree
adj[1].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(1);
adj[1].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(1);
adj[2].Add(4);
adj[4].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(5);
adj[5].Add(2);
adj[3].Add(6);
adj[6].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(7);
adj[7].Add(3);
// Counter counts no.
// of consecutive nodes
int counter = 0;
dfs(1, counter, M, arr, K);
Console.Write(ans + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar 时间复杂度: O(V + E)
辅助空间: O(V)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live