在本文中,我们将讨论如何使用具有以下功能的循环数组创建动态循环队列:
- Front():从队列中获取最前面的项目。
- Back():从队列中获取最后一项。
- Push(X):在队列的末尾将队列中的X推送。
- Pop():从队列中删除一个元素。
下面是分步说明:
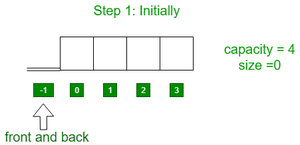
- 最初,队列是空的。
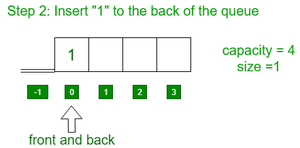
- 将元素1插入到队列的后面。
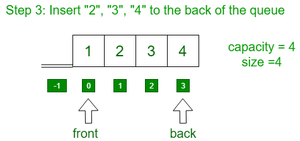
- 将元素2、3、4插入到队列的后面。
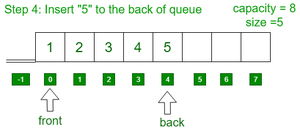
- 将元素5插入到队列的后面。
- 从队列中弹出 4 个元素。
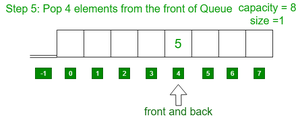
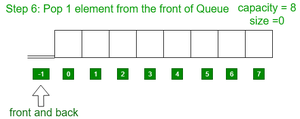
- 从队列中弹出 1 个元素。
方法:这个想法是在每次数组容量已满时将使用的数组大小加倍,并将前一个数组的元素复制到新数组中。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化 4 个变量,比如frontIndex、backIndex、sizeVar和capacity,还有一个数组比如arr[]来实现队列,
- 定义一个函数say Capacity()来查找当前使用的数组的大小:
- 返回容量。
- 定义一个函数say size()来查找队列中元素的数量:
- 返回变量sizeVar。
- 定义一个函数say full()来查找队列是否已满:
- 如果sizeVar等于容量返回true。否则,返回false。
- 定义一个函数say empty()来查找队列是否为空:
- 如果frontIndex和backIndex等于-1,则返回 true。否则,返回false。
- 定义一个函数say Front()来打印队列的前端元素:
- 如果 queue 不是empty() ,则打印arr[frontIndex]的元素。
- 定义一个函数say Back()来打印队列的最后一个元素:
- 如果队列不为空,则打印arr[BackIndex]的元素()。
- 定义一个函数say Push(X)在队列末尾插入一个元素:
- 如果队列已满,则将当前数组的大小加倍,并将前一个数组的元素复制到新数组中。
- 如果 queue 为空(),则分配frontIndex = backIndex = 0 ,然后将X分配给arr[frontIndex]和arr[backIndex] ,然后将sizeVar增加 1。
- 否则,更新backIndex如backIndex =(backIndex + 1)%的容量,然后分配X由一个常用3 [backIndex]和增量sizeVar。
- 定义一个函数say Pop()来删除队列前面的元素:
- 如果队列为空,则打印“下溢”。
- 否则,如果是sizeVar通过一个等于1,则分配-1至frontIndex和backIndex两者结合,然后递减sizeVar。
- 否则,更新frontIndex如frontIndex =(frontIndex + 1)%的容量和减量sizeVar由一个。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Class defination for queue
template
class Queue {
private:
// Stores the frontIndex
int frontIndex;
// Stores the back Index
int backIndex;
// Stores the array
X* arr;
// Stores the sizeof queue
int sizeVar;
// Stores the size of array
int capacityVar = 4;
public:
// Queue class constructor
Queue()
{
arr = new X[capacityVar];
frontIndex = backIndex = -1;
sizeVar = 0;
}
// Function Methods
bool empty();
bool full();
void push(X x);
void pop();
X front();
X back();
int capacity();
int size();
};
// Find the capacity of queue
template
int Queue::capacity()
{
return capacityVar;
}
// Find the number of elements
// present in Queue
template
int Queue::size()
{
return sizeVar;
}
// Function to check if
// Queue is empty or not
template
bool Queue::empty()
{
if (frontIndex == -1
&& backIndex == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Function to check if the queue
// is full or not
template
bool Queue::full()
{
if (sizeVar == capacityVar)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Function to find the front element
// of the queue
template
X Queue::front()
{
// If queue is empty
if (empty()) {
cout << "Queue underflow"
<< endl;
abort();
}
return arr[frontIndex];
}
// Function to find the last element
// of the Queue
template
X Queue::back()
{
if (empty()) {
cout << "Queue underflow"
<< endl;
abort();
}
return arr[backIndex];
}
// Function to insert the element
// to the rear end of the queue
template
void Queue::push(X x)
{
if (full()) {
// If the queue is full, then
// double the capacity
capacityVar = capacityVar * 2;
// Initialize new array of
// double size
X* temp = new X[capacityVar];
// Copy the elements of the
// previous array
for (int i = 0; i < sizeVar; i++)
temp[i] = arr[i];
// Deallocate the memory
// of previous array
delete[] arr;
arr = temp;
}
// If size is zero
if (empty()) {
frontIndex = backIndex = 0;
arr[backIndex] = x;
sizeVar++;
return;
}
// Increment the backIndex
backIndex = (backIndex + 1) % capacityVar;
arr[backIndex] = x;
sizeVar++;
return;
}
// Function to pop an element from
// front end of the queue
template
void Queue::pop()
{
// If queue is empty
if (empty()) {
cout << "Queue underflow"
<< endl;
abort();
}
// If there is only one character
if (frontIndex == backIndex) {
// Mark Queue as empty
// and decrement sizeVar
frontIndex = backIndex = -1;
sizeVar--;
return;
}
// Increment frontIndex cyclically
// using modulo arithmetic
frontIndex = (frontIndex + 1) % capacityVar;
sizeVar--;
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Queue initialization
Queue q;
// Iterate the range [1, 100]
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++)
q.push(i);
// Print the current capacity
cout << "Current capacity "
<< q.capacity() << endl;
// Print current size
cout << "Current size "
<< q.size() << endl;
// Print front elements of queue
cout << "Front element "
<< q.front() << endl;
// Print last element of the queue
cout << "Rear element "
<< q.back() << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "Pop an element" << endl;
// Pop an element from the queue
q.pop();
cout << "Pop an element" << endl;
// Pop an element from the queue
q.pop();
cout << endl;
// Print the current capacity
cout << "Current capacity "
<< q.capacity() << endl;
// Print current size
cout << "Current size "
<< q.size() << endl;
// Print front elements of queue
cout << "Front element "
<< q.front() << endl;
// Print last element of the queue
cout << "Rear element "
<< q.back() << endl;
return 0;
} 输出:
Current capacity 128
Current size 99
Front element 1
Rear element 99
Pop an element
Pop an element
Current capacity 128
Current size 97
Front element 3
Rear element 99时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live