Python中动态数组的实现
什么是动态数组?
动态数组类似于数组,但不同之处在于它的大小可以在运行时动态修改。不需要事先指定数组有多大。数组的元素占用一块连续的内存,一旦创建,它的大小就不能改变。动态数组可以在数组填满后分配更大的内存块,将原始数组中的内容复制到这个新空间,并继续填充可用的插槽。

我们将使用一个名为 ctypes of Python的内置库。查看文档以获取更多信息,但它基本上将在此处用作 ctypes 模块中的原始数组。
关于公共方法和私有方法的快速说明,我们可以在方法名称前使用下划线 _来保持它不公开。例如:
class M(object):
def public(self):
print 'Use Tab to see me !'
def _private(self):
print "You won't be able to Tab to see me !"
m = M()
m.public()
Output:
Use Tab to see me!
m._private()
Output:
You won't be able to see me!
动态阵列逻辑实现:
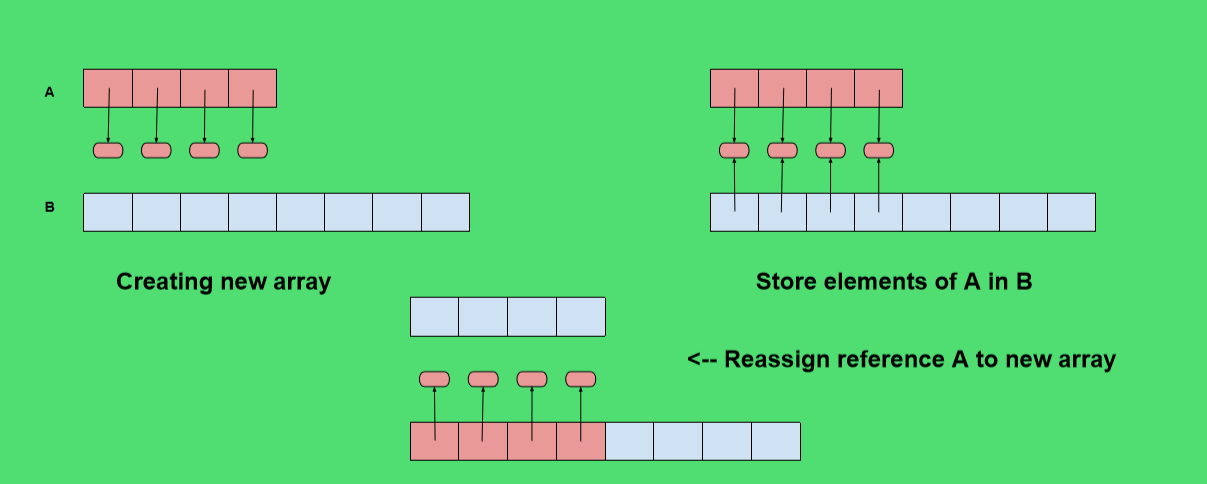
关键是提供方法来增长存储列表元素的数组A。我们实际上不能扩大阵列,它的容量是固定的。如果一次将一个元素附加到列表中,当底层数组已满时,我们需要执行以下步骤。
- 分配一个容量更大的新数组B (新数组的一个常用规则是容量是现有数组的两倍)
- 设置B[i]=A[i] ,对于i=0到n-1 ,其中 n 表示当前的项目数。
- 设置A=B ,即我们因此使用B作为支持列表的数组。
- 在新数组中插入新元素。
动态数组代码实现:
import ctypes
class DynamicArray(object):
'''
DYNAMIC ARRAY CLASS (Similar to Python List)
'''
def __init__(self):
self.n = 0 # Count actual elements (Default is 0)
self.capacity = 1 # Default Capacity
self.A = self.make_array(self.capacity)
def __len__(self):
"""
Return number of elements sorted in array
"""
return self.n
def __getitem__(self, k):
"""
Return element at index k
"""
if not 0 <= k self.n:
print("please enter appropriate index..")
return
if self.n==self.capacity:
self._resize(2*self.capacity)
for i in range(self.n-1,index-1,-1):
self.A[i+1]=self.A[i]
self.A[index]=item
self.n+=1
def delete(self):
"""
This function deletes item from the end of array
"""
if self.n==0:
print("Array is empty deletion not Possible")
return
self.A[self.n-1]=0
self.n-=1
def removeAt(self,index):
"""
This function deletes item from a specified index..
"""
if self.n==0:
print("Array is empty deletion not Possible")
return
if index<0 or index>=self.n:
return IndexError("Index out of bound....deletion not possible")
if index==self.n-1:
self.A[index]=0
self.n-=1
return
for i in range(index,self.n-1):
self.A[i]=self.A[i+1]
self.A[self.n-1]=0
self.n-=1
def _resize(self, new_cap):
"""
Resize internal array to capacity new_cap
"""
B = self.make_array(new_cap) # New bigger array
for k in range(self.n): # Reference all existing values
B[k] = self.A[k]
self.A = B # Call A the new bigger array
self.capacity = new_cap # Reset the capacity
def make_array(self, new_cap):
"""
Returns a new array with new_cap capacity
"""
return (new_cap * ctypes.py_object)()
# Instantiate
arr = DynamicArray()
# Append new element
arr.append(1)
len(arr)
Output:
1# Append new element
arr.append(2)
# Check length
len(arr)
Output:
2# Index
arr[0]
Output:
1arr[1]
Output:
2太棒了,我们制作了自己的动态数组!玩弄它,看看它是如何自动调整大小的。