给定一棵二叉树,任务是仅使用一次堆栈遍历以先序、后序和中序迭代打印二叉树的所有节点。
例子:
Input:
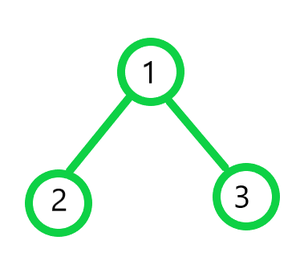
Output:
Preorder Traversal: 1 2 3
Inorder Traversal: 2 1 3
Postorder Traversal: 2 3 1
Input:
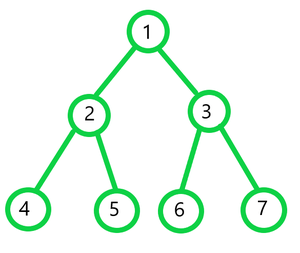
Output:
Preorder traversal: 1 2 3 4 5 3 6 7
Inorder traversal: 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
Post-order traversal: 4 5 2 6 7 3 1
方法:这个问题可以只用一个堆栈来解决。这个想法是通过分配一个值来标记二叉树的每个节点,每个节点称为状态码,值1代表当前正在访问的节点是前序遍历,值2代表当前正在访问的节点是中序遍历和值3表示节点在后序遍历中正在访问。
- 初始化一个 stack < pair < Node*, int>> 说S 。
- 将状态为1的根节点压入堆栈,即{root, 1}。
- 初始化三个整数向量,比如preorder 、 inorder和postorder 。
- 遍历堆栈直到堆栈为空并检查以下条件:
- 如果堆栈的顶部节点的状态是1,那么更新堆栈的顶部节点的状态,以2和顶推节点向量序并插入顶部节点的左子,如果它不是空的堆栈S。
- 如果堆栈的顶部节点的状态为2,则更新堆栈的顶部节点的状态,以3和推入向量序顶部节点,并插入顶部节点的右子,如果它不是空的堆栈S 。
- 如果栈顶节点的状态为3,则按向量后序压入栈顶节点,然后弹出栈顶元素。
- 最后,打印向量preorder 、 inorder和postorder 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of the
// node of a binary tree
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// Function to print all nodes of a
// binary tree in Preorder, Postorder
// and Inorder using only one stack
void allTraversal(Node* root)
{
// Stores preorder traversal
vector pre;
// Stores inorder traversal
vector post;
// Stores postorder traversal
vector in;
// Stores the nodes and the order
// in which they are currently visited
stack > s;
// Push root node of the tree
// into the stack
s.push(make_pair(root, 1));
// Traverse the stack while
// the stack is not empty
while (!s.empty()) {
// Stores the top
// element of the stack
pair p = s.top();
// If the status of top node
// of the stack is 1
if (p.second == 1) {
// Update the status
// of top node
s.top().second++;
// Insert the current node
// into preorder, pre[]
pre.push_back(p.first->data);
// If left child is not NULL
if (p.first->left) {
// Insert the left subtree
// with status code 1
s.push(make_pair(
p.first->left, 1));
}
}
// If the status of top node
// of the stack is 2
else if (p.second == 2) {
// Update the status
// of top node
s.top().second++;
// Insert the current node
// in inorder, in[]
in.push_back(p.first->data);
// If right child is not NULL
if (p.first->right) {
// Insert the right subtree into
// the stack with status code 1
s.push(make_pair(
p.first->right, 1));
}
}
// If the status of top node
// of the stack is 3
else {
// Push the current node
// in post[]
post.push_back(p.first->data);
// Pop the top node
s.pop();
}
}
cout << "Preorder Traversal: ";
for (int i = 0; i < pre.size(); i++) {
cout << pre[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
// Printing Inorder
cout << "Inorder Traversal: ";
for (int i = 0; i < in.size(); i++) {
cout << in[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
// Printing Postorder
cout << "Postorder Traversal: ";
for (int i = 0; i < post.size(); i++) {
cout << post[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Creating the root
struct Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(7);
// Function call
allTraversal(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
class GFG
{
static class Pair
{
Node first;
int second;
public Pair(Node first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Structure of the
// node of a binary tree
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
};
// Function to print all nodes of a
// binary tree in Preorder, Postorder
// and Inorder using only one stack
static void allTraversal(Node root)
{
// Stores preorder traversal
ArrayList pre = new ArrayList<>();
// Stores inorder traversal
ArrayList in = new ArrayList<>();
// Stores postorder traversal
ArrayList post = new ArrayList<>();
// Stores the nodes and the order
// in which they are currently visited
Stack s = new Stack<>();
// Push root node of the tree
// into the stack
s.push(new Pair(root, 1));
// Traverse the stack while
// the stack is not empty
while (!s.empty())
{
// Stores the top
// element of the stack
Pair p = s.peek();
// If the status of top node
// of the stack is 1
if (p.second == 1)
{
// Update the status
// of top node
s.peek().second++;
// Insert the current node
// into preorder, pre[]
pre.add(p.first.data);
// If left child is not null
if (p.first.left != null)
{
// Insert the left subtree
// with status code 1
s.push(new Pair(p.first.left, 1));
}
}
// If the status of top node
// of the stack is 2
else if (p.second == 2) {
// Update the status
// of top node
s.peek().second++;
// Insert the current node
// in inorder, in[]
in.add(p.first.data);
// If right child is not null
if (p.first.right != null) {
// Insert the right subtree into
// the stack with status code 1
s.push(new Pair(p.first.right, 1));
}
}
// If the status of top node
// of the stack is 3
else {
// Push the current node
// in post[]
post.add(p.first.data);
// Pop the top node
s.pop();
}
}
System.out.print("Preorder Traversal: ");
for (int i : pre) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// Printing Inorder
System.out.print("Inorder Traversal: ");
for (int i : in) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// Printing Postorder
System.out.print("Postorder Traversal: ");
for (int i : post) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating the root
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
// Function call
allTraversal(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev255 Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Structure of the
# node of a binary tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print all nodes of a
# binary tree in Preorder, Postorder
# and Inorder using only one stack
def allTraversal(root):
# Stores preorder traversal
pre = []
# Stores inorder traversal
post = []
# Stores postorder traversal
inn = []
# Stores the nodes and the order
# in which they are currently visited
s = []
# Push root node of the tree
# into the stack
s.append([root, 1])
# Traverse the stack while
# the stack is not empty
while (len(s) > 0):
# Stores the top
# element of the stack
p = s[-1]
#del s[-1]
# If the status of top node
# of the stack is 1
if (p[1] == 1):
# Update the status
# of top node
s[-1][1] += 1
# Insert the current node
# into preorder, pre[]
pre.append(p[0].data)
# If left child is not NULL
if (p[0].left):
# Insert the left subtree
# with status code 1
s.append([p[0].left, 1])
# If the status of top node
# of the stack is 2
elif (p[1] == 2):
# Update the status
# of top node
s[-1][1] += 1
# Insert the current node
# in inorder, in[]
inn.append(p[0].data);
# If right child is not NULL
if (p[0].right):
# Insert the right subtree into
# the stack with status code 1
s.append([p[0].right, 1])
# If the status of top node
# of the stack is 3
else:
# Push the current node
# in post[]
post.append(p[0].data);
# Pop the top node
del s[-1]
print("Preorder Traversal: ",end=" ")
for i in pre:
print(i,end=" ")
print()
# Printing Inorder
print("Inorder Traversal: ",end=" ")
for i in inn:
print(i,end=" ")
print()
# Printing Postorder
print("Postorder Traversal: ",end=" ")
for i in post:
print(i,end=" ")
print()
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Creating the root
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
# Function call
allTraversal(root)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29.输出:
Preorder Traversal: 1 2 4 5 3 6 7
Inorder Traversal: 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
Postorder Traversal: 4 5 2 6 7 3 1时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live