给定一棵二叉树,任务是计算从根到叶的所有路径,从而形成算术级数。
例子:
Input:

Output: 2
Explanation:
The paths that form an AP in the given tree from root to leaf are:
- 1->3->5 (A.P. with common difference 2)
- 1->6->11 (A.P. with common difference 5)
Input:
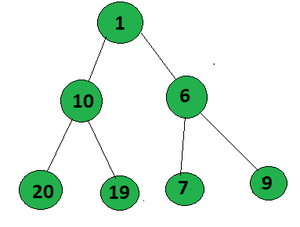
Output: 1
Explanation:
The path that form an AP in the given tree from root to leaf is 1->10->19 (A.P. with difference 9)
方法:该问题可以使用Preorder Traversal来解决。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 对给定的二叉树执行预序遍历。
- 初始化一个数组arr[]来存储路径。
- 初始化count = 0,存储组成AP的路径数
- 到达叶子节点后,检查数组中的当前元素(即从根到叶子路径的节点值)是否形成一个AP 。
- 如果是这样,增加计数
- 在树的完全遍历之后,打印计数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to count
// the path which forms an A.P.
#include
using namespace std;
int count = 0;
// Node structure
struct Node {
int val;
// left and right child of the node
Node *left, *right;
// intializaiton constructor
Node(int x)
{
val = x;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
// Function to check if path
// forma A.P. or not
bool check(vector arr)
{
if (arr.size() == 1)
return true;
// if size of arr is greater than 2
int d = arr[1] - arr[0];
for (int i = 2; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if (arr[i] - arr[i - 1] != d)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the maxmimum
// setbits sum from root to leaf
int countAP(Node* root, vector arr)
{
if (!root)
return 0;
arr.push_back(root->val);
// If the node is a leaf node
if (root->left == NULL
&& root->right == NULL) {
if (check(arr))
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Traverse left subtree
int x = countAP(root->left, arr);
// Traverse the right subtree
int y = countAP(root->right, arr);
return x + y;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(3);
root->right = new Node(6);
root->left->left = new Node(5);
root->left->right = new Node(7);
root->right->left = new Node(11);
root->right->right = new Node(23);
cout << countAP(root, {});
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation to count
// the path which forms an A.P.
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
int count = 0;
// Node structure
static class Node
{
int val;
// left and right child of the node
Node left, right;
// Initialization constructor
Node(int x)
{
val = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
};
// Function to check if path
// forma A.P. or not
static boolean check(Vector arr)
{
if (arr.size() == 1)
return true;
// If size of arr is greater than 2
int d = arr.get(1) - arr.get(0);
for(int i = 2; i < arr.size(); i++)
{
if (arr.get(i) - arr.get(i - 1) != d)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the maxmimum
// setbits sum from root to leaf
static int countAP(Node root,
Vector arr)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
arr.add(root.val);
// If the node is a leaf node
if (root.left == null &&
root.right == null)
{
if (check(arr))
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Traverse left subtree
int x = countAP(root.left, arr);
// Traverse the right subtree
int y = countAP(root.right, arr);
return x + y;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(11);
root.right.right = new Node(23);
System.out.print(countAP(root, new Vector()));
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 Python3
# Python3 implementation to count
# the path which forms an A.P.
# Node structure
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to check if path
# form a A.P. or not
def check(arr):
if len(arr) == 1:
return True
# If size of arr is greater than 2
d = arr[1] - arr[0]
for i in range(2, len(arr)):
if arr[i] - arr[i - 1] != d:
return False
return True
# Function to find the maxmimum
# setbits sum from root to leaf
def countAP(root, arr):
if not root:
return 0
arr.append(root.val)
# If the node is a leaf node
if (root.left == None and
root.right == None):
if check(arr):
return 1
return 0
# Traverse the left subtree
x = countAP(root.left, arr)
# Traverse the right subtree
y = countAP(root.right, arr)
return x + y
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(6)
root.left.left = Node(5)
root.left.right = Node(7)
root.right.left = Node(11)
root.right.right = Node(23)
print(countAP(root, []))
# This code is contributed by stutipathak31janC#
// C# implementation to count
// the path which forms an A.P.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
//int count = 0;
// Node structure
class Node
{
public int val;
// left and right child of the node
public Node left, right;
// Initialization constructor
public Node(int x)
{
val = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
};
// Function to check if path
// forma A.P. or not
static bool check(List arr)
{
if (arr.Count == 1)
return true;
// If size of arr is greater than 2
int d = arr[1] - arr[0];
for(int i = 2; i < arr.Count; i++)
{
if (arr[i] - arr[i - 1] != d)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the maxmimum
// setbits sum from root to leaf
static int countAP(Node root,
List arr)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
arr.Add(root.val);
// If the node is a leaf node
if (root.left == null &&
root.right == null)
{
if (check(arr))
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Traverse left subtree
int x = countAP(root.left, arr);
// Traverse the right subtree
int y = countAP(root.right, arr);
return x + y;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(11);
root.right.right = new Node(23);
Console.Write(countAP(root, new List()));
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey 输出:
2时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(h),其中h是二叉树的高度。
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live