左堆是用二叉堆实现的优先级队列。每个节点都有一个与其他节点距离最近的 sValue。现在我们将编写一个Java程序,用于在左侧堆(中序遍历)上执行某些操作,例如插入、删除、清除和检查是否为空。
左树是具有以下特性的二叉树:
- 正常最小堆属性: key(i) >= key(parent(i))
- 左侧较重: dist(right(i)) <= dist(left(i))。这里,dist(i) 是从节点 i 到扩展二叉树表示中的叶节点的最短路径上的边数(在这种表示中,空子节点被视为外部或叶节点)。到后代外部节点的最短路径是通过右孩子。每个子树也是左树并且 dist( i ) = 1 + dist( right( i ) )。
示例:下面的左树显示了使用上述过程为每个节点计算的距离。最右边的节点的等级为 0,因为该节点的右子树为空,并且其父节点的距离为 1,dist( i ) = 1 + dist( right( i ))。每个节点都遵循相同的方法,并计算它们的 s 值(或排名)。
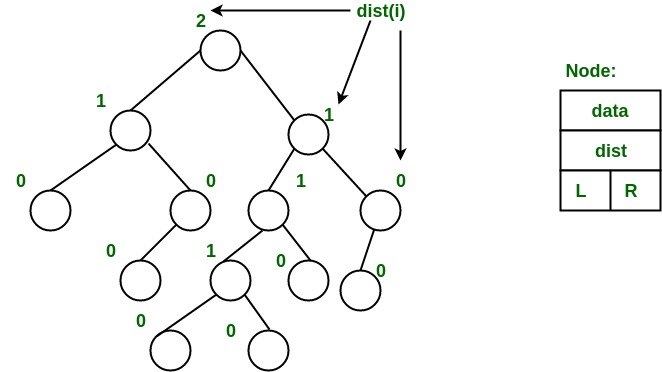
从上面的第二个属性,我们可以得出两个结论:
- 从根到最右边叶子的路径是从根到叶子的最短路径。
- 如果到最右边叶子的路径有 x 个节点,那么左边的堆至少有 2 x – 1 个节点。这意味着对于具有 n 个节点的左侧堆,到最右侧叶子的路径长度为 O(log n)。
例子:
LEFTIST HEAP
Functions to do
2. delete min
3. check empty
4. clear
2
Inorder Traversal: 53 52 54
If you wish to continue type Y or y
y
Functions to do
2. delete min
3. check empty
4. clear
3
Empty status = false
Inorder Traversal: 53 52 54
If you wish to continue type Y or y
y
Functions to do
2. delete min
3. check empty
4. clear
4
Inorder Traversal:
If you wish to continue type Y or y方法:
- 我们将首先使用一个类 Node 并创建它的构造函数和各种参数。
- 然后我们将创建一个类 LeftHeap,在这个类中,我们将创建各种方法并尝试执行它们的操作。
- 我们将创建一个构造函数,在那里我们保持根为空。
- 我们将创建一个方法 isEmpty() 来检查 Heap 是否为空。
- 我们将创建一个方法 clear() 来清除堆。
- 我们创建一个方法来合并:
- 这里我们需要取两个节点,然后我们将检查它们是否为空
- 然后我们将根据我们的方便将值设置为向右或向左。
- 该函数用于查找堆中的最小元素
- 然后我们声明一个名为 del() 的函数。
- 此函数用于查找最小数,然后我们将其删除。
- 然后我们声明 main函数并调用该函数并在 switch case 的帮助下执行操作。执行的操作是检查是否为空或清空堆或删除最小元素。
执行:
Java
// Java Program to Implement Leftist Heap
// Declare all libraries
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
// Class Node
class Node {
// elements, and sValue are the variables in class Node
int element, sValue;
// class has two parameters
Node left, right;
public Node(int element) { this(element, null, null); }
// Function Node where we are using this keyword
// Which will hep us to avoid confusion if we are having
// same elements
public Node(int element, Node left, Node right)
{
this.element = element;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.sValue = 0;
}
}
// Class Left heap
class LeftHeap {
// Now parameter is created named head.
private Node head;
// Its constructor is created named left heap
// Returns null
public LeftHeap() { head = null; }
// Now we will write function to check if the list is
// empty
public boolean isEmpty()
{
// If head is null returns true
return head == null;
}
// Now we will write a function clear
public void clear()
{
// We will put head is null
head = null;
}
// Now Now let us create a function merge which will
// help us merge
public void merge(LeftHeap rhs)
{
// If the present funtion is rhs
// then we return it
if (this == rhs)
return;
// Here we call the function merge
// And make rhs is equal to null
head = merge(head, rhs.head);
rhs.head = null;
}
// Function merge with two Nodes a and b
public Node merge(Node a, Node b)
{
// If A is null
// We return b
if (a == null)
return b;
// If b is null
// we return A
if (b == null)
return a;
// If we put a element greater than b element
if (a.element > b.element) {
// We write the swap code
Node temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
// Now we call the function merge to merge a and b
a.right = merge(a.right, b);
// If a is null we swap rright with left and empty
// right
if (a.left == null) {
a.left = a.right;
a.right = null;
}
// else
// if value in a is less than the svalue of right
// If the condition is satisfied , we swap the left
// with right
else {
if (a.left.sValue < a.right.sValue) {
Node temp = a.left;
a.left = a.right;
a.right = temp;
}
// we store the value in a s Vlaueof right
// SValue
a.sValue = a.right.sValue + 1;
}
// We now returnt the value of a
return a;
}
// Function insert
public void insert(int a)
{
// This root will help us insert a new variable
head = merge(new Node(a), head);
}
// The below function will help us delete minimum
// function present in the Heap
public int del()
{
// If is empty return -1
if (isEmpty())
return -1;
// Now we will store the element in variable and
// Call the merge function to del that is converging
// to head then we return min
int min = head.element;
head = merge(head.left, head.right);
return min;
}
// Function order
// will print the starting and ending points in order.
public void order()
{
order(head);
System.out.println();
}
// Function order with Node r
// If r not equal to r
// It prints all the elements iterating from order left
// to right
private void order(Node r)
{
if (r != null) {
order(r.left);
System.out.print(r.element + " ");
order(r.right);
}
}
}
// Class gfg
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating the scanner object
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("LEFTIST HEAP");
// Creating object for class LeftHeap
LeftHeap h = new LeftHeap();
// Char ch
char ch;
// Now taking the loop
do {
// Now writing down all the functions
System.out.println("Functions to do");
System.out.println("1. insert");
System.out.println("2. delete min");
System.out.println("3. check empty");
System.out.println("4. clear");
// SCnning the choice to be used in switch
int choice = sc.nextInt();
// Using switch
switch (choice) {
// Case 1
// to insert the elements in the heap
// call the insert func
case 1:
System.out.println("Enter integer element to insert");
h.insert(sc.nextInt());
break;
// Delete the minimum element in the func
case 2:
h.del();
break;
// To check the empty status of the heap
case 3:
System.out.println("Empty status = "
+ h.isEmpty());
break;
// Cleaing the heap
case 4:
h.clear();
break;
default:
System.out.println("Wrong entry");
break;
}
// Prints the inorder traversal
// Calling the func
System.out.print("\n Inorder Traversal: ");
h.order();
// Whether to continue or not
System.out.println("\n If you wish to continue type Y or y");
ch = sc.next().charAt(0);
}
// Closing of loop
while (ch == 'Y' || ch == 'y');
}
}输出:

如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live