给定两个数字 n 和 k,其中 n 表示集合中的多个元素,找到多种方法将集合划分为 k 个子集。
例子:
Input: n = 3, k = 2
Output: 3
Explanation: Let the set be {1, 2, 3}, we can partition
it into 2 subsets in following ways
{{1,2}, {3}}, {{1}, {2,3}}, {{1,3}, {2}}
Input: n = 3, k = 1
Output: 1
Explanation: There is only one way {{1, 2, 3}}递归解
- 方法:首先,让我们定义一个递归解来找到第 n 个元素的解。有两种情况。
- 前面的n-1个元素被分成k个分区,即S(n-1,k)路。将第 n 个元素放入前 k 个分区之一。所以, count = k * S(n-1, k)
- 前面的n-1个元素被分成k-1个分区,即S(n-1,k-1)路。将第n个元素放入一个新的分区(单元素分区)。所以, count = S(n-1, k-1)
- 总计数 = k * S(n-1, k) + S(n-1, k-1)。
- 算法:
- 创建一个接受两个参数 n 和 k 的递归函数。该函数将 n 个元素的分区总数返回到 k 个集合中。
- 处理基本情况。如果 n = 0 或 k = 0 或 k > n 返回 0,因为不能有任何子集。如果 n 等于 k 或 k 等于 1,则返回 1。
- 否则计算值如下: S(n, k) = k*S(n-1, k) + S(n-1, k-1) ,即使用递归参数调用递归函数并计算S的值(n, k)。
- 返回总和。
- 执行:
C++
// A C++ program to count number of partitions
// of a set with n elements into k subsets
#include
using namespace std;
// Returns count of different partitions of n
// elements in k subsets
int countP(int n, int k)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0 || k == 0 || k > n)
return 0;
if (k == 1 || k == n)
return 1;
// S(n+1, k) = k*S(n, k) + S(n, k-1)
return k*countP(n-1, k) + countP(n-1, k-1);
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
cout << countP(3, 2);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to count number
// of partitions of a set with
// n elements into k subsets
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// Returns count of different
// partitions of n elements in
// k subsets
public static int countP(int n, int k)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0 || k == 0 || k > n)
return 0;
if (k == 1 || k == n)
return 1;
// S(n+1, k) = k*S(n, k) + S(n, k-1)
return (k * countP(n - 1, k)
+ countP(n - 1, k - 1));
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(countP(3, 2));
}
}
//This code is contributed by Anshika Goyal.Python 3
# A Python3 program to count number
# of partitions of a set with n
# elements into k subsets
# Returns count of different partitions
# of n elements in k subsets
def countP(n, k):
# Base cases
if (n == 0 or k == 0 or k > n):
return 0
if (k == 1 or k == n):
return 1
# S(n+1, k) = k*S(n, k) + S(n, k-1)
return (k * countP(n - 1, k) +
countP(n - 1, k - 1))
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(countP(3, 2))
# This code is contributed
# by Akanksha Rai(Abby_akku)C#
// C# program to count number
// of partitions of a set with
// n elements into k subsets
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns count of different
// partitions of n elements in
// k subsets
public static int countP(int n, int k)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0 || k == 0 || k > n)
return 0;
if (k == 1 || k == n)
return 1;
// S(n+1, k) = k*S(n, k) + S(n, k-1)
return (k * countP(n - 1, k)
+ countP(n - 1, k - 1));
}
// Driver program
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(countP(3, 2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.PHP
$n)
return 0;
if ($k == 1 || $k == $n)
return 1;
// S(n+1, k) = k*S(n, k)
// + S(n, k-1)
return $k * countP($n - 1, $k) +
countP($n - 1, $k - 1);
}
// Driver Code
echo countP(3, 2);
// This code is contributed by aj_36
?>Javascript
C++
// A Dynamic Programming based C++ program to count
// number of partitions of a set with n elements
// into k subsets
#include
using namespace std;
// Returns count of different partitions of n
// elements in k subsets
int countP(int n, int k)
{
// Table to store results of subproblems
int dp[n+1][k+1];
// Base cases
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
dp[i][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
dp[0][k] = 0;
// Fill rest of the entries in dp[][]
// in bottom up manner
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
if (j == 1 || i == j)
dp[i][j] = 1;
else
dp[i][j] = j * dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - 1];
return dp[n][k];
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
cout << countP(5, 2);
return 0;
} Java
// A Dynamic Programming based Java program to count
// number of partitions of a set with n elements
// into k subsets
class GFG{
// Returns count of different partitions of n
// elements in k subsets
static int countP(int n, int k)
{
// Table to store results of subproblems
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][k+1];
// Base cases
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
dp[i][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
dp[0][k] = 0;
// Fill rest of the entries in dp[][]
// in bottom up manner
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
if (j == 1 || i == j)
dp[i][j] = 1;
else
dp[i][j] = j * dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - 1];
return dp[n][k];
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String[] args )
{
System.out.println(countP(5, 2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiPython3
# A Dynamic Programming based Python3 program
# to count number of partitions of a set with
# n elements into k subsets
# Returns count of different partitions
# of n elements in k subsets
def countP(n, k):
# Table to store results of subproblems
dp = [[0 for i in range(k + 1)]
for j in range(n + 1)]
# Base cases
for i in range(n + 1):
dp[i][0] = 0
for i in range(k + 1):
dp[0][k] = 0
# Fill rest of the entries in
# dp[][] in bottom up manner
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, k + 1):
if (j == 1 or i == j):
dp[i][j] = 1
else:
dp[i][j] = (j * dp[i - 1][j] +
dp[i - 1][j - 1])
return dp[n][k]
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(countP(5, 2))
# This code is contributed by
# Surendra_GangwarC#
// A Dynamic Programming based C# program
// to count number of partitions of a
// set with n elements into k subsets
using System;
class GFG
{
// Returns count of different partitions of n
// elements in k subsets
static int countP(int n, int k)
{
// Table to store results of subproblems
int[,] dp = new int[n + 1, k + 1];
// Base cases
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
dp[i, 0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
dp[0, k] = 0;
// Fill rest of the entries in dp[][]
// in bottom up manner
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
if (j == 1 || i == j)
dp[i, j] = 1;
else
dp[i, j] = j * dp[i - 1, j] + dp[i - 1, j - 1];
return dp[n, k];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main( )
{
Console.Write(countP(5, 2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Ita_c.PHP
Javascript
- 输出:
3- 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(2^n)。
对于 n 的每个值,调用两个递归函数。更具体地说,时间复杂度是指数级的。 - 空间复杂度: O(n)(由于调用堆栈)。
- 时间复杂度: O(2^n)。
高效的解决方案
- 方法:上述递归解决方案的时间复杂度是指数级的。可以通过减少重叠的子问题来优化解决方案。下面是countP(10,7) 的递归树。子问题countP(8,6)或CP(8,6)被多次调用。
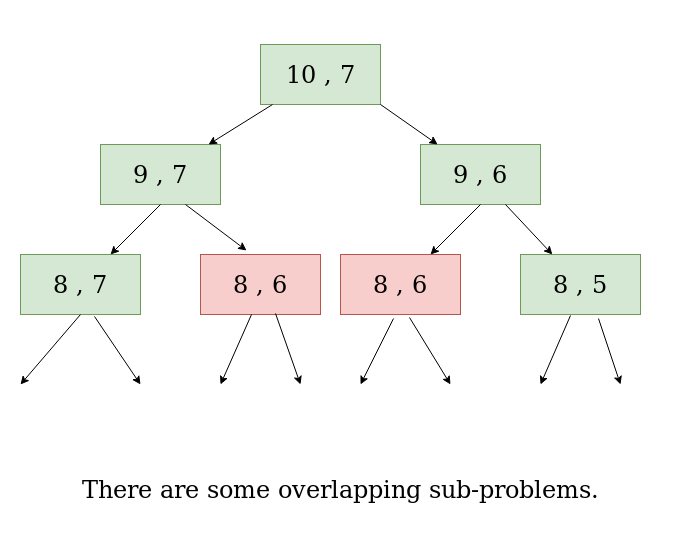
- 所以这个问题具有动态规划问题的两个性质(见类型 1 和类型 2)。与其他典型的动态规划 (DP) 问题一样,可以通过使用所示的递归公式以自下而上的方式构造临时数组dp[][]来避免对相同子问题的重新计算。
接下来是减少子问题以优化问题的复杂性。这可以通过两种方式完成:- 自下而上的方式:这保持递归结构完整,并将值存储在哈希图或二维数组中。然后只计算一次该值,并在下次调用该函数时返回该值。
- 自顶向下方式:这保留了一个大小为 n*k 的二维数组,其中 dp[i][j] 表示将 i 个元素划分为 j 个集合的总数。填写 dp[i][0] 和 dp[0][i] 的基本情况。对于值 (i,j),需要 dp[i-1][j] 和 dp[i-1][j-1] 的值。所以从第 0 行到第 n 行和第 0 列到 k 填充 DP。
- 算法:
- 创建大小为 ( n + 1 )* ( k + 1 ) 的 Dp 数组 dp[n+1][k+1] 。
- 填充基本案例的值。对于从 0 到 n 的所有 i 值填充dp[i][0] = 0并且对于从 0 到 k 的所有 i 值填充dp[0][k] = 0
- 运行一个嵌套循环,外循环从 1 到 n,内循环从 1 到 k。
- 对于索引 i 和 j(分别为外循环和内循环),计算dp[i][j] = j * dp[i – 1][j] + dp[i – 1][j – 1]并且如果 j = = 1 或 i == j,计算 dp[i][j] = 1。
- 打印值 dp[n][k]
- 执行:
C++
// A Dynamic Programming based C++ program to count
// number of partitions of a set with n elements
// into k subsets
#include
using namespace std;
// Returns count of different partitions of n
// elements in k subsets
int countP(int n, int k)
{
// Table to store results of subproblems
int dp[n+1][k+1];
// Base cases
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
dp[i][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
dp[0][k] = 0;
// Fill rest of the entries in dp[][]
// in bottom up manner
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
if (j == 1 || i == j)
dp[i][j] = 1;
else
dp[i][j] = j * dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - 1];
return dp[n][k];
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
cout << countP(5, 2);
return 0;
}
Java
// A Dynamic Programming based Java program to count
// number of partitions of a set with n elements
// into k subsets
class GFG{
// Returns count of different partitions of n
// elements in k subsets
static int countP(int n, int k)
{
// Table to store results of subproblems
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][k+1];
// Base cases
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
dp[i][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
dp[0][k] = 0;
// Fill rest of the entries in dp[][]
// in bottom up manner
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
if (j == 1 || i == j)
dp[i][j] = 1;
else
dp[i][j] = j * dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - 1];
return dp[n][k];
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String[] args )
{
System.out.println(countP(5, 2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
蟒蛇3
# A Dynamic Programming based Python3 program
# to count number of partitions of a set with
# n elements into k subsets
# Returns count of different partitions
# of n elements in k subsets
def countP(n, k):
# Table to store results of subproblems
dp = [[0 for i in range(k + 1)]
for j in range(n + 1)]
# Base cases
for i in range(n + 1):
dp[i][0] = 0
for i in range(k + 1):
dp[0][k] = 0
# Fill rest of the entries in
# dp[][] in bottom up manner
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, k + 1):
if (j == 1 or i == j):
dp[i][j] = 1
else:
dp[i][j] = (j * dp[i - 1][j] +
dp[i - 1][j - 1])
return dp[n][k]
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(countP(5, 2))
# This code is contributed by
# Surendra_Gangwar
C#
// A Dynamic Programming based C# program
// to count number of partitions of a
// set with n elements into k subsets
using System;
class GFG
{
// Returns count of different partitions of n
// elements in k subsets
static int countP(int n, int k)
{
// Table to store results of subproblems
int[,] dp = new int[n + 1, k + 1];
// Base cases
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
dp[i, 0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
dp[0, k] = 0;
// Fill rest of the entries in dp[][]
// in bottom up manner
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
if (j == 1 || i == j)
dp[i, j] = 1;
else
dp[i, j] = j * dp[i - 1, j] + dp[i - 1, j - 1];
return dp[n, k];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main( )
{
Console.Write(countP(5, 2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Ita_c.
PHP
Javascript
- 输出:
15- 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n*k)。
填充了大小为 n*k 的 2D dp 数组,因此时间复杂度为 O(n*k)。 - 空间复杂度: O(n*k)。
需要额外的 2D DP 阵列。
- 时间复杂度: O(n*k)。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。