给定一个“mx n”矩阵,计算从左上角到达右下角的路径数,最多允许 k 圈。
什么是转?如果我们沿行移动而现在沿列移动,则移动被视为转弯。或者我们沿着列移动,现在沿着行移动。
There are two possible scenarios when a turn can occur
at point (i, j):
Turns Right: (i-1, j) -> (i, j) -> (i, j+1)
Down Right
Turns Down: (i, j-1) -> (i, j) -> (i+1, j)
Right Down例子:
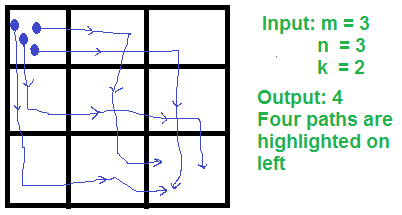
Input: m = 3, n = 3, k = 2
Output: 4
See below diagram for four paths with
maximum 2 turns.
Input: m = 3, n = 3, k = 1
Output: 2
我们强烈建议您将浏览器最小化,然后自己先尝试一下。
这个问题可以使用下面的递归公式递归计算。
countPaths(i, j, k): Count of paths to reach (i,j) from (0, 0)
countPathsDir(i, j, k, 0): Count of paths if we reach (i, j)
along row.
countPathsDir(i, j, k, 1): Count of paths if we reach (i, j)
along column.
The fourth parameter in countPathsDir() indicates direction.
Value of countPaths() can be written as:
countPaths(i, j, k) = countPathsDir(i, j, k, 0) +
countPathsDir(i, j, k, 1)
And value of countPathsDir() can be recursively defined as:
// Base cases
// If current direction is along row
If (d == 0)
// Count paths for two cases
// 1) We reach here through previous row.
// 2) We reach here through previous column, so number of
// turns k reduce by 1.
countPathsDir(i, j, k, d) = countPathsUtil(i, j-1, k, d) +
countPathsUtil(i-1, j, k-1, !d);
// If current direction is along column
Else
// Similar to above
countPathsDir(i, j, k, d) = countPathsUtil(i-1, j, k, d) +
countPathsUtil(i, j-1, k-1, !d);
我们可以使用动态规划在多项式时间内解决这个问题。这个想法是使用一个 4 维表 dp[m][n][k][d],其中 m 是行数,n 是列数,k 是允许的匝数,d 是方向。
下面是基于动态规划的实现。
C++
// C++ program to count number of paths with maximum
// k turns allowed
#include
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100
// table to store results of subproblems
int dp[MAX][MAX][MAX][2];
// Returns count of paths to reach (i, j) from (0, 0)
// using at-most k turns. d is current direction
// d = 0 indicates along row, d = 1 indicates along
// column.
int countPathsUtil(int i, int j, int k, int d)
{
// If invalid row or column indexes
if (i < 0 || j < 0)
return 0;
// If current cell is top left itself
if (i == 0 && j == 0)
return 1;
// If 0 turns left
if (k == 0)
{
// If direction is row, then we can reach here
// only if direction is row and row is 0.
if (d == 0 && i == 0) return 1;
// If direction is column, then we can reach here
// only if direction is column and column is 0.
if (d == 1 && j == 0) return 1;
return 0;
}
// If this subproblem is already evaluated
if (dp[i][j][k][d] != -1)
return dp[i][j][k][d];
// If current direction is row, then count paths for two cases
// 1) We reach here through previous row.
// 2) We reach here through previous column, so number of
// turns k reduce by 1.
if (d == 0)
return dp[i][j][k][d] = countPathsUtil(i, j-1, k, d) +
countPathsUtil(i-1, j, k-1, !d);
// Similar to above if direction is column
return dp[i][j][k][d] = countPathsUtil(i-1, j, k, d) +
countPathsUtil(i, j-1, k-1, !d);
}
// This function mainly initializes 'dp' array as -1 and calls
// countPathsUtil()
int countPaths(int i, int j, int k)
{
// If (0, 0) is target itself
if (i == 0 && j == 0)
return 1;
// Initialize 'dp' array
memset(dp, -1, sizeof dp);
// Recur for two cases: moving along row and along column
return countPathsUtil(i-1, j, k, 1) + // Moving along row
countPathsUtil(i, j-1, k, 0); // Moving along column
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int m = 3, n = 3, k = 2;
cout << "Number of paths is "
<< countPaths(m-1, n-1, k) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to count number of paths
// with maximum k turns allowed
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 100;
// table to store results of subproblems
static int [][][][]dp = new int[MAX][MAX][MAX][2];
// Returns count of paths to reach (i, j) from (0, 0)
// using at-most k turns. d is current direction
// d = 0 indicates along row, d = 1 indicates along
// column.
static int countPathsUtil(int i, int j, int k, int d)
{
// If invalid row or column indexes
if (i < 0 || j < 0)
return 0;
// If current cell is top left itself
if (i == 0 && j == 0)
return 1;
// If 0 turns left
if (k == 0)
{
// If direction is row, then we can reach here
// only if direction is row and row is 0.
if (d == 0 && i == 0) return 1;
// If direction is column, then we can reach here
// only if direction is column and column is 0.
if (d == 1 && j == 0) return 1;
return 0;
}
// If this subproblem is already evaluated
if (dp[i][j][k][d] != -1)
return dp[i][j][k][d];
// If current direction is row,
// then count paths for two cases
// 1) We reach here through previous row.
// 2) We reach here through previous column,
// so number of turns k reduce by 1.
if (d == 0)
return dp[i][j][k][d] = countPathsUtil(i, j - 1, k, d) +
countPathsUtil(i - 1, j, k - 1, d == 1 ? 0 : 1);
// Similar to above if direction is column
return dp[i][j][k][d] = countPathsUtil(i - 1, j, k, d) +
countPathsUtil(i, j - 1, k - 1, d == 1 ? 0 : 1);
}
// This function mainly initializes 'dp' array
// as -1 and calls countPathsUtil()
static int countPaths(int i, int j, int k)
{
// If (0, 0) is target itself
if (i == 0 && j == 0)
return 1;
// Initialize 'dp' array
for(int p = 0; p < MAX; p++)
{
for(int q = 0; q < MAX; q++)
{
for(int r = 0; r < MAX; r++)
for(int s = 0; s < 2; s++)
dp[p][q][r][s] = -1;
}
}
// Recur for two cases: moving along row and along column
return countPathsUtil(i - 1, j, k, 1) + // Moving along row
countPathsUtil(i, j - 1, k, 0); // Moving along column
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int m = 3, n = 3, k = 2;
System.out.println("Number of paths is " +
countPaths(m - 1, n - 1, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi SinghPython3
# Python3 program to count number of paths
# with maximum k turns allowed
MAX = 100
# table to store results of subproblems
dp = [[[[-1 for col in range(2)]
for col in range(MAX)]
for row in range(MAX)]
for row in range(MAX)]
# Returns count of paths to reach
# (i, j) from (0, 0) using at-most k turns.
# d is current direction, d = 0 indicates
# along row, d = 1 indicates along column.
def countPathsUtil(i, j, k, d):
# If invalid row or column indexes
if (i < 0 or j < 0):
return 0
# If current cell is top left itself
if (i == 0 and j == 0):
return 1
# If 0 turns left
if (k == 0):
# If direction is row, then we can reach here
# only if direction is row and row is 0.
if (d == 0 and i == 0):
return 1
# If direction is column, then we can reach here
# only if direction is column and column is 0.
if (d == 1 and j == 0):
return 1
return 0
# If this subproblem is already evaluated
if (dp[i][j][k][d] != -1):
return dp[i][j][k][d]
# If current direction is row,
# then count paths for two cases
# 1) We reach here through previous row.
# 2) We reach here through previous column,
# so number of turns k reduce by 1.
if (d == 0):
dp[i][j][k][d] = countPathsUtil(i, j - 1, k, d) + \
countPathsUtil(i - 1, j, k - 1, not d)
return dp[i][j][k][d]
# Similar to above if direction is column
dp[i][j][k][d] = countPathsUtil(i - 1, j, k, d) + \
countPathsUtil(i, j - 1, k - 1, not d)
return dp[i][j][k][d]
# This function mainly initializes 'dp' array
# as -1 and calls countPathsUtil()
def countPaths(i, j, k):
# If (0, 0) is target itself
if (i == 0 and j == 0):
return 1
# Recur for two cases: moving along row
# and along column
return countPathsUtil(i - 1, j, k, 1) +\
countPathsUtil(i, j - 1, k, 0)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
m = 3
n = 3
k = 2
print("Number of paths is",
countPaths(m - 1, n - 1, k))
# This code is contributed by Ashutosh450C#
// C# program to count number of paths
// with maximum k turns allowed
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 100;
// table to store to store results of subproblems
static int [,,,]dp = new int[MAX, MAX, MAX, 2];
// Returns count of paths to reach (i, j) from (0, 0)
// using at-most k turns. d is current direction
// d = 0 indicates along row, d = 1 indicates along
// column.
static int countPathsUtil(int i, int j, int k, int d)
{
// If invalid row or column indexes
if (i < 0 || j < 0)
return 0;
// If current cell is top left itself
if (i == 0 && j == 0)
return 1;
// If 0 turns left
if (k == 0)
{
// If direction is row, then we can reach here
// only if direction is row and row is 0.
if (d == 0 && i == 0) return 1;
// If direction is column, then we can reach here
// only if direction is column and column is 0.
if (d == 1 && j == 0) return 1;
return 0;
}
// If this subproblem is already evaluated
if (dp[i, j, k, d] != -1)
return dp[i, j, k, d];
// If current direction is row,
// then count paths for two cases
// 1) We reach here through previous row.
// 2) We reach here through previous column,
// so number of turns k reduce by 1.
if (d == 0)
return dp[i, j, k, d] = countPathsUtil(i, j - 1, k, d) +
countPathsUtil(i - 1, j, k - 1,
d == 1 ? 0 : 1);
// Similar to above if direction is column
return dp[i, j, k, d] = countPathsUtil(i - 1, j, k, d) +
countPathsUtil(i, j - 1, k - 1,
d == 1 ? 0 : 1);
}
// This function mainly initializes 'dp' array
// as -1 and calls countPathsUtil()
static int countPaths(int i, int j, int k)
{
// If (0, 0) is target itself
if (i == 0 && j == 0)
return 1;
// Initialize 'dp' array
for(int p = 0; p < MAX; p++)
{
for(int q = 0; q < MAX; q++)
{
for(int r = 0; r < MAX; r++)
for(int s = 0; s < 2; s++)
dp[p, q, r, s] = -1;
}
}
// Recur for two cases: moving along row and along column
return countPathsUtil(i - 1, j, k, 1) + // Moving along row
countPathsUtil(i, j - 1, k, 0); // Moving along column
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int m = 3, n = 3, k = 2;
Console.WriteLine("Number of paths is " +
countPaths(m - 1, n - 1, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992输出:
Number of paths is 4上述解决方案的时间复杂度为 O(m*n*k)
感谢 Gaurav Ahirwar 提出这个解决方案。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。