给定一棵二叉树,任务是计算给定二叉树中偶数路径的数量。偶数路径是根到叶路径仅包含所有偶数节点的路径。
例子:
Input: Below is the given Binary Tree:
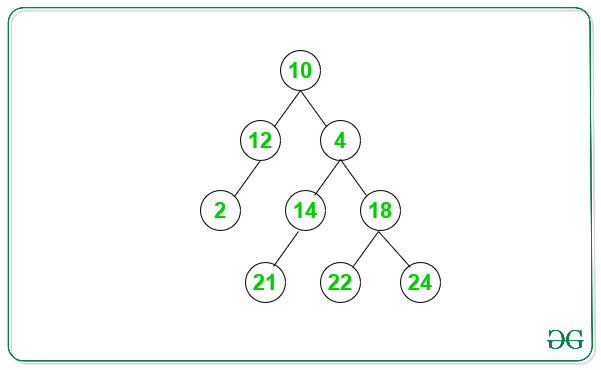
Output: 3
Explanation:
There are 3 even path for the above Binary Tree:
1. 10->12->2
2. 10->4->18->22
3. 10->4->18->24
Input: Below is the given Binary Tree:

Output: 2
Explanation:
There are 2 even path for the above Binary Tree:
1. 8->2->4
2. 8->16->6->28
朴素的方法:想法是生成所有的根到叶路径,并检查每条路径中的所有节点是否为偶数。计算其中包含偶数节点的所有路径并返回计数。上面的实现需要额外的空间来存储路径。
高效的方法:这个想法是使用预序树遍历。在给定二叉树的前序遍历期间,请执行以下操作:
- 如果节点的当前值为奇数或指针变为NULL,则返回计数。
- 如果当前节点是叶节点,则将计数加 1。
- 递归调用与更新的计左和右子树。
- 在全递归调用之后,count 的值是给定二叉树的偶数路径数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// A Tree node
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Utility function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
// Utility function to count the even path
// in a given Binary tree
int evenPaths(struct Node* node, int count)
{
// Base Condition, when node pointer
// becomes null or node value is odd
if (node == NULL || (node->key % 2 != 0)) {
return count;
}
// Increment count when encounter leaf
// node with all node value even
if (!node->left && !node->right) {
count++;
}
// Left recursive call, and save the
// value of count
count = evenPaths(node->left, count);
// Right reursive call, and return
// value of count
return evenPaths(node->right, count);
}
// Function to count the even paths in a
// given Binary tree
int countEvenPaths(struct Node* node)
{
// Function call with count = 0
return evenPaths(node, 0);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Tree
Node* root = newNode(12);
root->left = newNode(13);
root->right = newNode(12);
root->right->left = newNode(14);
root->right->right = newNode(16);
root->right->left->left = newNode(21);
root->right->left->right = newNode(22);
root->right->right->left = newNode(22);
root->right->right->right = newNode(24);
root->right->right->right->left = newNode(8);
// Function call
cout << countEvenPaths(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// A Tree node
static class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
};
// Utility function to create a new node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return (temp);
}
// Utility function to count the even path
// in a given Binary tree
static int evenPaths(Node node, int count)
{
// Base Condition, when node pointer
// becomes null or node value is odd
if (node == null || (node.key % 2 != 0)) {
return count;
}
// Increment count when encounter leaf
// node with all node value even
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
count++;
}
// Left recursive call, and save the
// value of count
count = evenPaths(node.left, count);
// Right reursive call, and return
// value of count
return evenPaths(node.right, count);
}
// Function to count the even paths in a
// given Binary tree
static int countEvenPaths(Node node)
{
// Function call with count = 0
return evenPaths(node, 0);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Tree
Node root = newNode(12);
root.left = newNode(13);
root.right = newNode(12);
root.right.left = newNode(14);
root.right.right = newNode(16);
root.right.left.left = newNode(21);
root.right.left.right = newNode(22);
root.right.right.left = newNode(22);
root.right.right.right = newNode(24);
root.right.right.right.left = newNode(8);
// Function call
System.out.println(countEvenPaths(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by AbhiThakurPython3
# Python3 program for the
# above approach
# A Tree node
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.key = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Utility function to count
# the even path in a given
# Binary tree
def evenPaths(node, count):
# Base Condition, when node
# pointer becomes null or
# node value is odd
if (node == None or
(node.key % 2 != 0)):
return count
# Increment count when
# encounter leaf node
# with all node value even
if (not node.left and
not node.right):
count+=1
# Left recursive call, and
# save the value of count
count = evenPaths(node.left,
count)
# Right reursive call, and
# return value of count
return evenPaths(node.right,
count)
# Function to count the even
# paths in a given Binary tree
def countEvenPaths(node):
# Function call with count = 0
return evenPaths(node, 0)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
#Tree
root = Node(12)
root.left = Node(13)
root.right = Node(12)
root.right.left = Node(14)
root.right.right = Node(16)
root.right.left.left = Node(21)
root.right.left.right = Node(22)
root.right.right.left = Node(22)
root.right.right.right = Node(24)
root.right.right.right.left = Node(8)
#Function call
print(countEvenPaths(root))
# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar 29C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// A Tree node
class Node {
public int key;
public Node left, right;
};
// Utility function to create a new node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return (temp);
}
// Utility function to count the even path
// in a given Binary tree
static int evenPaths(Node node, int count)
{
// Base Condition, when node pointer
// becomes null or node value is odd
if (node == null || (node.key % 2 != 0)) {
return count;
}
// Increment count when encounter leaf
// node with all node value even
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
count++;
}
// Left recursive call, and save the
// value of count
count = evenPaths(node.left, count);
// Right reursive call, and return
// value of count
return evenPaths(node.right, count);
}
// Function to count the even paths in a
// given Binary tree
static int countEvenPaths(Node node)
{
// Function call with count = 0
return evenPaths(node, 0);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Tree
Node root = newNode(12);
root.left = newNode(13);
root.right = newNode(12);
root.right.left = newNode(14);
root.right.right = newNode(16);
root.right.left.left = newNode(21);
root.right.left.right = newNode(22);
root.right.right.left = newNode(22);
root.right.right.right = newNode(24);
root.right.right.right.left = newNode(8);
// Function call
Console.WriteLine(countEvenPaths(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992输出:
3
时间复杂度: O(N),其中 N 是给定二叉树中的节点数。
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live