先决条件 – 硬连线 v/s 微程序控制单元
基本上,控制单元 (CU)是在正确顺序的控制信号的帮助下运行计算机全部功能的引擎。在微程序控制单元方法中,与操作相关的控制信号存储在特殊的存储单元中。可以方便地将导致特定微操作发生的控制信号集视为“微指令”。微指令序列可以存储在内部“控制”存储器中。
根据控制存储器中存储的控制字的类型,微程序控制单元可分为两种类型,即水平微程序控制单元和垂直微程序控制单元。
- 在水平微程序控制单元中,控制信号以解码后的二进制格式表示,即1bit/CS。这里’n’个控制信号需要n位编码。另一方面。
- 在垂直微程序控制单元中,控制信号以编码的二进制格式表示。这里’n’个控制信号需要log 2 n 位编码。
卧式微程序控制单元与立式微程序控制单元的比较:
| Horizontal µ-programmed CU | Vertical µ-programmed CU |
|---|---|
| It supports longer control word. | It supports shorter control word. |
| It allows higher degree of parallelism. If degree is n, then n Control Signals are enabled at a time. | It allows low degree of parallelism i.e., degree of parallelism is either 0 or 1. |
| No additional hardware is required. | Additional hardware in the form of decoders are required to generate control signals. |
| It is faster than Vertical micro-programmed control unit. | it is slower than Horizontal micro-programmed control unit. |
| It is less flexible than Vertical micro-programmed control unit. | It is more flexible than Horizontal micro-programmed control unit. |
| Horizontal micro-programmed control unit uses horizontal microinstruction, where every bit in the control field attaches to a control line. | Vertical micro-programmed control unit uses vertical microinstruction, where a code is used for each action to be performedand thedecoder translates this code into individual control signals. |
| Horizontal micro-programmed control unit makes less use of ROM encoding than vertical micro-programmed control unit. | Vertical micro-programmed control unit makes more use of ROM encoding to reduce the length of the control word. |
示例:考虑一个支持 4k 字的假设控制单元。硬件包含 64 个控制信号和 16 个标志。使用的控制字的位大小和控制内存的字节大小是多少:
a) 水平编程
b) 垂直编程
解决方案:
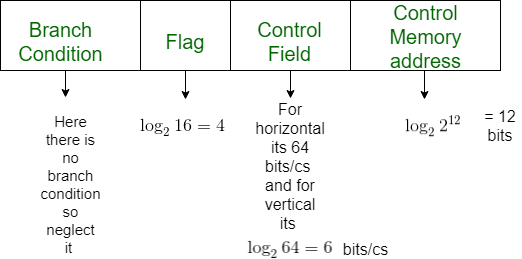
a)For Horizontal
64 bits for 64 signals
Control Word Size = 4 + 64 + 12 = 80 bits
Control Memory = 4 kW = ( (4* 80) / 8 ) = 40 kByte
a)For Vertical
6 bits for 64 signals i.e log264
Control Word Size = 4 + 6 + 12 = 22 bits
Control Memory = 4 kW = ( (4* 22) / 8 ) = 11 kByte