先决条件 – 载波侦听多路访问 (CSMA)
1. 1-持久CSMA:
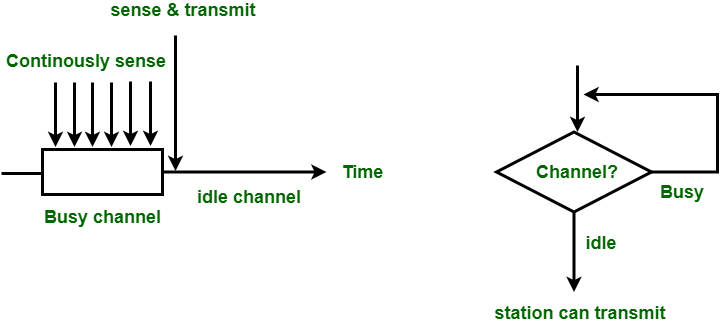
在 1-persistent CSMA 中,站点不断地侦听信道以检查其状态,即空闲或忙碌,以便它可以传输数据。在信道忙的情况下,站将等待信道变为空闲。当站点发现空闲信道时,它以概率1 无延迟地向信道传输帧。由于概率1,它被称为1-持久CSMA。这种方法的问题是碰撞的可能性很大,因为两个或多个站点可以在空闲状态下找到信道并同时传输帧。在发生冲突时,站必须等待随机时间让信道空闲并重新开始。
2. 非持久性 CSMA :
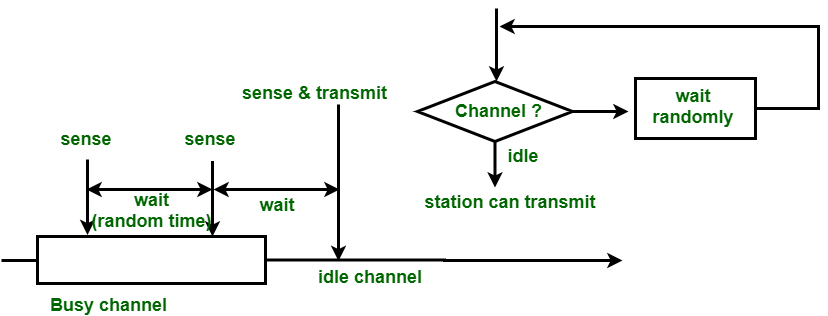
在非持久性 CSMA 中,具有要发送的帧的站仅感知信道。在空闲通道的情况下,它将立即向该通道发送帧。如果发现信道忙,它将等待固定的时间量并再次感知站的状态是空闲还是忙。在这种方法中,当站点检测到前一次传输结束时,它不会为了捕获信道而立即感知信道。这种方法减少了冲突的机会,但降低了网络的效率。
1-persistent 和 Non-persistent CSMA 的区别:
| Basis | 1-persistent CSMA | Non-persistent CSMA |
|---|---|---|
| Carrier Sense | When channel is idle it will send with probability 1. | When channel is idle it will send frame. |
| Waiting | It will continuously sense channel for transmission of frames. | It will wait for random amount of time to check carrier. |
| Chance of Collision | In this method, there are highest number of collisions observed. | In this method, chance of collision are less than in 1-persistent. |
| Utilization | It’s utilization is above ALOHA because frames are sent only when channel is found in idle state. | It’s utilization is above 1-persistent because in this all stations constantly check for channel at same time. |
| Delay Low Load | It is small because frames are sent only in idle state. | It is longer than 1-persistent as it only checks randomly when channel is busy. |
| Delay High Load | It is high due to collision. | It is longer than 1-persistent because stations check randomly when channel is busy. |