📌 相关文章
- 用C格式说明符
- C格式说明符(1)
- Java中的格式说明符(1)
- Java中的格式说明符
- PHP |格式说明符
- PHP |格式说明符(1)
- python 格式说明符 - Python (1)
- python 格式说明符 - Python 代码示例
- Julia 中的格式说明符
- Julia 中的格式说明符
- Julia 中的格式说明符(1)
- Julia 中的格式说明符(1)
- arduino 格式说明符 (1)
- 格式说明符后的空格 - C 编程语言(1)
- arduino 格式说明符 - 任何代码示例
- C语言中%d和%i格式说明符的区别(1)
- C语言中%d和%i格式说明符的区别
- 格式说明符后的空格 - C 编程语言代码示例
- bash 特殊格式说明符 (1)
- 在C中使用变量作为格式说明符
- 在C中使用变量作为格式说明符(1)
- C语言中的%d和%i格式说明符之间的区别
- C语言中的%d和%i格式说明符之间的区别(1)
- bash 特殊格式说明符 - 任何代码示例
- C程序使用%n格式说明符打印字符串的长度(1)
- C程序使用%n格式说明符打印字符串的长度
- C程序在不使用格式说明符的情况下打印字符(1)
- C程序在不使用格式说明符的情况下打印字符
- ValueError:无效的格式说明符 - Python 代码示例
📜 C格式说明符
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-21 08:01:34 🧑 作者: Mango
C格式说明符
格式说明符是在格式化的输入和输出函数中使用的字符串。格式字符串确定输入和输出的格式。格式字符串始终以’%’字符开头。
printf()函数中常用的格式说明符是:
| Format specifier | Description |
|---|---|
| %d or %i | It is used to print the signed integer value where signed integer means that the variable can hold both positive and negative values. |
| %u | It is used to print the unsigned integer value where the unsigned integer means that the variable can hold only positive value. |
| %o | It is used to print the octal unsigned integer where octal integer value always starts with a 0 value. |
| %x | It is used to print the hexadecimal unsigned integer where the hexadecimal integer value always starts with a 0x value. In this, alphabetical characters are printed in small letters such as a, b, c, etc. |
| %X | It is used to print the hexadecimal unsigned integer, but %X prints the alphabetical characters in uppercase such as A, B, C, etc. |
| %f | It is used for printing the decimal floating-point values. By default, it prints the 6 values after ‘.’. |
| %e/%E | It is used for scientific notation. It is also known as Mantissa or Exponent. |
| %g | It is used to print the decimal floating-point values, and it uses the fixed precision, i.e., the value after the decimal in input would be exactly the same as the value in the output. |
| %p | It is used to print the address in a hexadecimal form. |
| %c | It is used to print the unsigned character. |
| %s | It is used to print the strings. |
| %ld | It is used to print the long-signed integer value. |
让我们通过一个示例详细了解格式说明符。
- %d
int main()
{
int b=6;
int c=8;
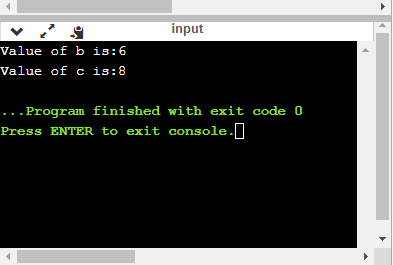
printf("Value of b is:%d", b);
printf("\nValue of c is:%d",c);
return 0;
}
在上面的代码中,我们使用%d说明符打印b和c的整数值。
输出量
- %u
int main()
{
int b=10;
int c= -10;
printf("Value of b is:%u", b);
printf("\nValue of c is:%u",c);
return 0;
}
在上述程序中,我们使用无符号格式说明符%u显示b和c的值。 b的值为正,因此%u说明符将打印b的确切值,但不会printc的值,因为c包含负值。
输出量

- %o
int main()
{
int a=0100;
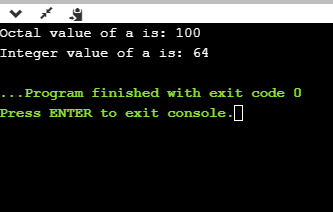
printf("Octal value of a is: %o", a);
printf("\nInteger value of a is: %d",a);
return 0;
}
在上面的代码中,我们显示a的八进制值和整数值。
输出量
- %x和%X
int main()
{
int y=0xA;
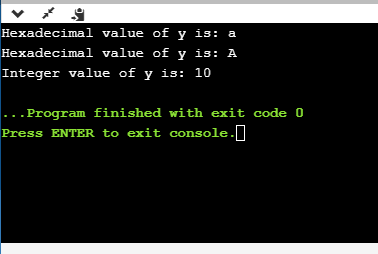
printf("Hexadecimal value of y is: %x", y);
printf("\nHexadecimal value of y is: %X",y);
printf("\nInteger value of y is: %d",y);
return 0;
}
在上面的代码中,y包含十六进制值“ A”。我们以两种格式显示y的十六进制值。我们使用%x和%X来print十六进制值,其中%x以小写字母显示值,即’a’,而%X以大写字母显示值,即’A’。
输出量
- %F
int main()
{
float y=3.4;
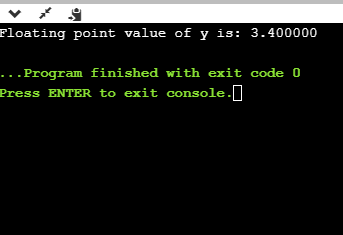
printf("Floating point value of y is: %f", y);
return 0;
}
上面的代码显示y的浮点值。
输出量
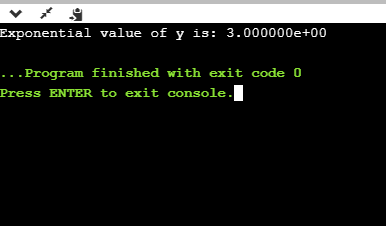
- %e
int main()
{
float y=3;
printf("Exponential value of y is: %e", y);
return 0;
}
输出量
- %E
int main()
{
float y=3;
printf("Exponential value of y is: %E", y);
return 0;
}
输出量

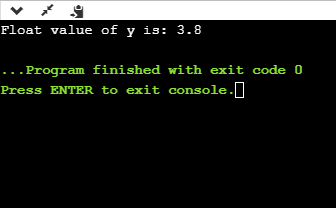
- %G
int main()
{
float y=3.8;
printf("Float value of y is: %g", y);
return 0;
}
在上面的代码中,我们使用%g说明符显示y的浮动值。 %g说明符以相同的精度显示与输入相同的输出。
输出量
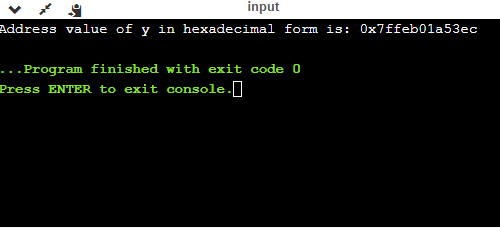
- %p
int main()
{
int y=5;
printf("Address value of y in hexadecimal form is: %p", &y);
return 0;
}
输出量
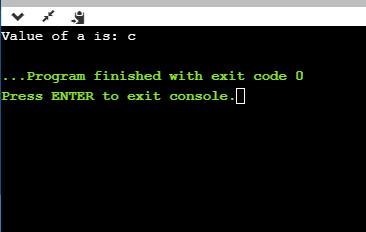
- %C
int main()
{
char a='c';
printf("Value of a is: %c", a);
return 0;
}
输出量
- %s
int main()
{
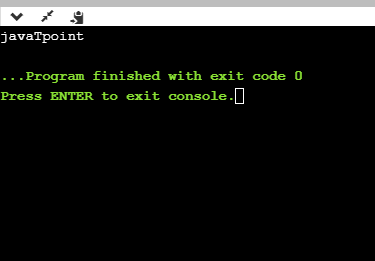
printf("%s", "javaTpoint");
return 0;
}
输出量
最小字段宽度说明符
假设我们要在屏幕上显示占用最少空间的输出。您可以通过在格式说明符的百分号后显示一个整数来实现此目的。
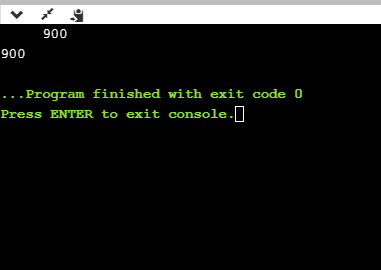
int main()
{
int x=900;
printf("%8d", x);
printf("\n%-8d",x);
return 0;
}
在上面的程序中,%8d说明符将在8个空格后显示该值,而%-8d说明符将使该值左对齐。
输出量
现在,我们将看到如何填充空白处。如以下代码所示:
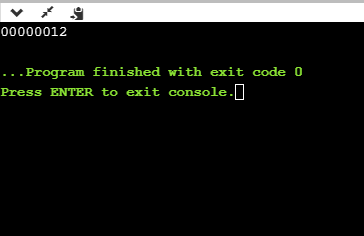
int main()
{
int x=12;
printf("%08d", x);
return 0;
}
在上面的程序中,%08d表示空白填充为零。
输出量
指定精度
我们可以使用’。’来指定精度。 (点)运算符,后跟整数和格式说明符。
int main()
{
float x=12.2;
printf("%.2f", x);
return 0;
}
输出量
