给定一个下三角矩阵Mat[][] ,任务是使用列主映射存储矩阵。
下三角矩阵:下三角矩阵是一个方阵,其中矩阵的下三角部分由非零元素组成,上三角部分由0组成。二维矩阵Mat[][]的下三角矩阵在数学上定义为:
- 如果i < j ,则设置Mat[i][j] = 0 。
- 如果i >= j ,则设置Mat[i][j] > 0 。
插图:
Below is a 5×5 lower triangular matrix. In general, such matrices can be stored in a 2D array, but when it comes to matrices of large size, it is not a good choice because of its high memory consumption due to the storage of unwanted 0s.
Such a matrix can be implemented in an optimized manner.
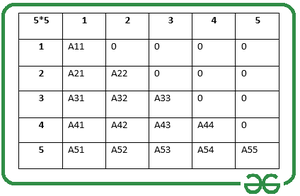
存储大小为N的下三角矩阵的有效方法:
- 非零元素的数量 = 1 + 2 + 3 + … + N = N * (N + 1) /2 。
- 0的计数= N 2 – (N * (N + 1) /2 = (N * (N – 1)/2 ) 。
现在让我们看看如何在程序中表示下三角矩阵。请注意,必须避免存储 0以减少内存消耗。根据计算,为了存储非零元素,需要N*(N + 1)/2空间。以上面的例子为例, N = 5 。需要大小为5 * (5 + 1)/2 = 15 的数组来存储非零元素。
现在,二维矩阵的元素可以逐列存储在一维数组中,如下所示:

用于存储下三角元素的数组
除了将元素存储在数组中之外,还需要提取与行和列号对应的元素的过程。使用Column-Major-Maping存储下三角矩阵,索引Mat[i][j]处的元素可以表示为:
Index of Mat[i][j] matrix in the array A[] = [n*(j-1)-(((j-2)*(j-1))/2)+ (i-j))]
下面是上面文章的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Dimensions of the matrix
const int N = 5;
// Structure of a memory
// efficient matrix
struct Matrix {
int* A;
int size;
};
// Function to set the
// values in the Matrix
void Set(struct Matrix* m, int i,
int j, int x)
{
if (i >= j)
m->A[((m->size)*(j-1)-(((j-2)
*(j-1))/2)+(i-j))] = x;
}
// Function to store the
// values in the Matrix
int Get(struct Matrix m, int i, int j)
{
if (i >= j)
return m.A[((m.size)*(j-1)-(((j-2)
*(j-1))/2)+(i-j))];
else
return 0;
}
// Function to display the
// elements of the matrix
void Display(struct Matrix m)
{
// Traverse the matrix
for (int i = 1; i <= m.size; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m.size; j++)
{
if (i >= j)
cout<< m.A[((m.size)*(j-1)-(((j-2)
*(j-1))/2)+(i-j))] <<" ";
else
cout<<"0 ";
}
cout< C
// C program for the above approach
#include
#include
// Dimensions of the matrix
const int N = 5;
// Structure of a memory
// efficient matrix
struct Matrix {
int* A;
int size;
};
// Function to set the
// values in the Matrix
void Set(struct Matrix* m, int i,
int j, int x)
{
if (i >= j)
m->A[((m->size)*(j-1)-(((j-2)
*(j-1))/2)+(i-j))] = x;
}
// Function to store the
// values in the Matrix
int Get(struct Matrix m, int i, int j)
{
if (i >= j)
return m.A[((m.size)*(j-1)-(((j-2)
*(j-1))/2)+(i-j))];
else
return 0;
}
// Function to display the
// elements of the matrix
void Display(struct Matrix m)
{
// Traverse the matrix
for (int i = 1; i <= m.size; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m.size; j++)
{
if (i >= j)
printf("%d ",
m.A[((m.size)*(j-1)-(((j-2)
*(j-1))/2)+(i-j))]);
else
printf("0 ");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// Function to generate an efficient matrix
struct Matrix createMat(int Mat[N][N])
{
// Declare efficient Matrix
struct Matrix mat;
// Initialize the Matrix
mat.size = N;
mat.A = (int*)malloc(
mat.size * (mat.size + 1) / 2
* sizeof(int));
// Set the values in matrix
for (int i = 1; i <= mat.size; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= mat.size; j++) {
Set(&mat, i, j, Mat[i - 1][j - 1]);
}
}
// Return the matrix
return mat;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int Mat[5][5] = { { 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 2, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 2, 3, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 0 },
{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 } };
// Function call to create a memory
// efficient matrix
struct Matrix mat = createMat(Mat);
// Function call to
// print the Matrix
Display(mat);
return 0;
} 1 0 0 0 0
1 2 0 0 0
1 2 3 0 0
1 2 3 4 0
1 2 3 4 5 时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
辅助空间: O(N 2 )
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。