给出了一个凸多边形和一个凸裁剪区域。任务是使用 Sutherland-Hodgman 算法裁剪多边形边。输入是以顺时针顺序排列的多边形顶点的形式。
例子:
输入:多边形:(100,150), (200,250), (300,200) 裁剪区域:(150,150), (150,200), (200,200), (200,150) 即方形输出:(150, 50,202) (150,1020) , 200) (200, 174)  示例 2输入:多边形:(100,150)、(200,250)、(300,200) 剪切区域:(100,300)、(300,300)、(200,100) 输出:(242, 185) (166, 1626) (100,200) , 250) (260, 220)
示例 2输入:多边形:(100,150)、(200,250)、(300,200) 剪切区域:(100,300)、(300,300)、(200,100) 输出:(242, 185) (166, 1626) (100,200) , 250) (260, 220) 
算法概述:
Consider each edge e of clipping Area and do following:
a) Clip given polygon against e.
如何裁剪裁剪区域的边缘?
(剪切区域的)边缘无限延伸以创建边界,并且使用此边界剪切所有顶点。生成的新顶点列表以顺时针方式传递到裁剪多边形的下一条边,直到所有边都被使用。
对于给定多边形的任何给定边与当前剪裁边 e,有四种可能的情况。
- 两个顶点都在里面:只有第二个顶点被添加到输出列表中
- 第一个顶点在外面,第二个在里面:边与裁剪边界的交点和第二个顶点都被添加到输出列表中
- 第一个顶点在里面,第二个在外面:只有边与裁剪边界的交点被添加到输出列表中
- 两个顶点都在外面:没有顶点添加到输出列表中
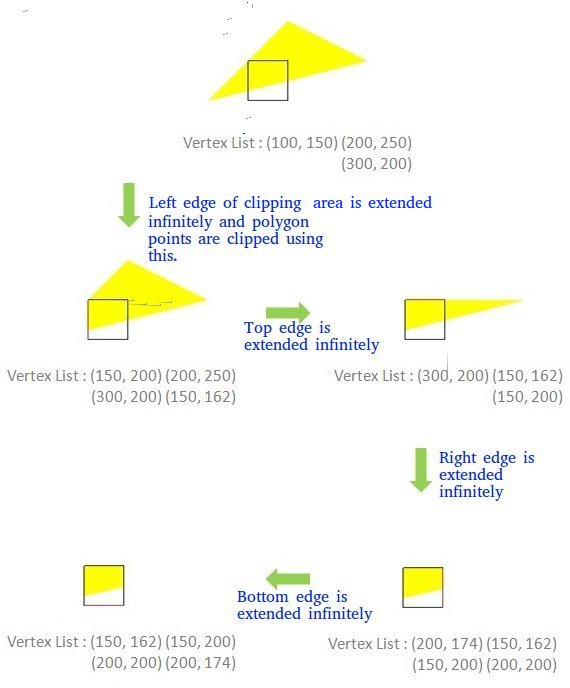
在实现算法之前需要讨论两个子问题:-
确定一个点是在裁剪多边形的内部还是外部
如果剪刀多边形的顶点按顺时针顺序给出,则剪刀边右侧的所有点都在该多边形内。这可以使用以下方法计算: 
查找边与剪辑边界的交点
如果已知每条线的两个点(1,2 & 3,4),则可以使用以下公式计算它们的交点:- 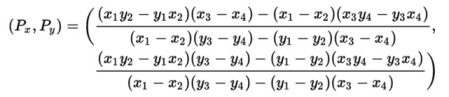
// C++ program for implementing Sutherland–Hodgman
// algorithm for polygon clipping
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX_POINTS = 20;
// Returns x-value of point of intersectipn of two
// lines
int x_intersect(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2,
int x3, int y3, int x4, int y4)
{
int num = (x1*y2 - y1*x2) * (x3-x4) -
(x1-x2) * (x3*y4 - y3*x4);
int den = (x1-x2) * (y3-y4) - (y1-y2) * (x3-x4);
return num/den;
}
// Returns y-value of point of intersectipn of
// two lines
int y_intersect(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2,
int x3, int y3, int x4, int y4)
{
int num = (x1*y2 - y1*x2) * (y3-y4) -
(y1-y2) * (x3*y4 - y3*x4);
int den = (x1-x2) * (y3-y4) - (y1-y2) * (x3-x4);
return num/den;
}
// This functions clips all the edges w.r.t one clip
// edge of clipping area
void clip(int poly_points[][2], int &poly_size,
int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
int new_points[MAX_POINTS][2], new_poly_size = 0;
// (ix,iy),(kx,ky) are the co-ordinate values of
// the points
for (int i = 0; i < poly_size; i++)
{
// i and k form a line in polygon
int k = (i+1) % poly_size;
int ix = poly_points[i][0], iy = poly_points[i][1];
int kx = poly_points[k][0], ky = poly_points[k][1];
// Calculating position of first point
// w.r.t. clipper line
int i_pos = (x2-x1) * (iy-y1) - (y2-y1) * (ix-x1);
// Calculating position of second point
// w.r.t. clipper line
int k_pos = (x2-x1) * (ky-y1) - (y2-y1) * (kx-x1);
// Case 1 : When both points are inside
if (i_pos < 0 && k_pos < 0)
{
//Only second point is added
new_points[new_poly_size][0] = kx;
new_points[new_poly_size][1] = ky;
new_poly_size++;
}
// Case 2: When only first point is outside
else if (i_pos >= 0 && k_pos < 0)
{
// Point of intersection with edge
// and the second point is added
new_points[new_poly_size][0] = x_intersect(x1,
y1, x2, y2, ix, iy, kx, ky);
new_points[new_poly_size][1] = y_intersect(x1,
y1, x2, y2, ix, iy, kx, ky);
new_poly_size++;
new_points[new_poly_size][0] = kx;
new_points[new_poly_size][1] = ky;
new_poly_size++;
}
// Case 3: When only second point is outside
else if (i_pos < 0 && k_pos >= 0)
{
//Only point of intersection with edge is added
new_points[new_poly_size][0] = x_intersect(x1,
y1, x2, y2, ix, iy, kx, ky);
new_points[new_poly_size][1] = y_intersect(x1,
y1, x2, y2, ix, iy, kx, ky);
new_poly_size++;
}
// Case 4: When both points are outside
else
{
//No points are added
}
}
// Copying new points into original array
// and changing the no. of vertices
poly_size = new_poly_size;
for (int i = 0; i < poly_size; i++)
{
poly_points[i][0] = new_points[i][0];
poly_points[i][1] = new_points[i][1];
}
}
// Implements Sutherland–Hodgman algorithm
void suthHodgClip(int poly_points[][2], int poly_size,
int clipper_points[][2], int clipper_size)
{
//i and k are two consecutive indexes
for (int i=0; i 输出:
(150, 162) (150, 200) (200, 200) (200, 174)
相关文章:
线剪裁 |第 1 组(Cohen-Sutherland 算法)
计算机图形学中的点裁剪算法
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。