给定四个包含 3 个数字的数组,每个数组代表两个三角形的边和角。任务是检查两个三角形是否全等。还打印出它们全等的定理。
注意:作为输入给出的所有边和角均适用于有效三角形。
例子:
Input : side1 = [3, 4, 5] angle1 = [90, 60, 30]
side2 = [4, 3, 5] angle2 = [60, 30, 90]
Output: Triangles are congruent by SSS SAS ASA AAS HL.
Input : side1 = [3, 5, 6] angle1 = [80, 50, 50]
side2 = [1, 1, 1] angle2 = [60, 60, 60]
Output: Triangles are not congruent
全等三角形是两个或更多的三角形,它们的所有对应边相等或一对边和夹角相等或一对角和边相等或一对角和另一边相等或斜边和一个边是平等的。
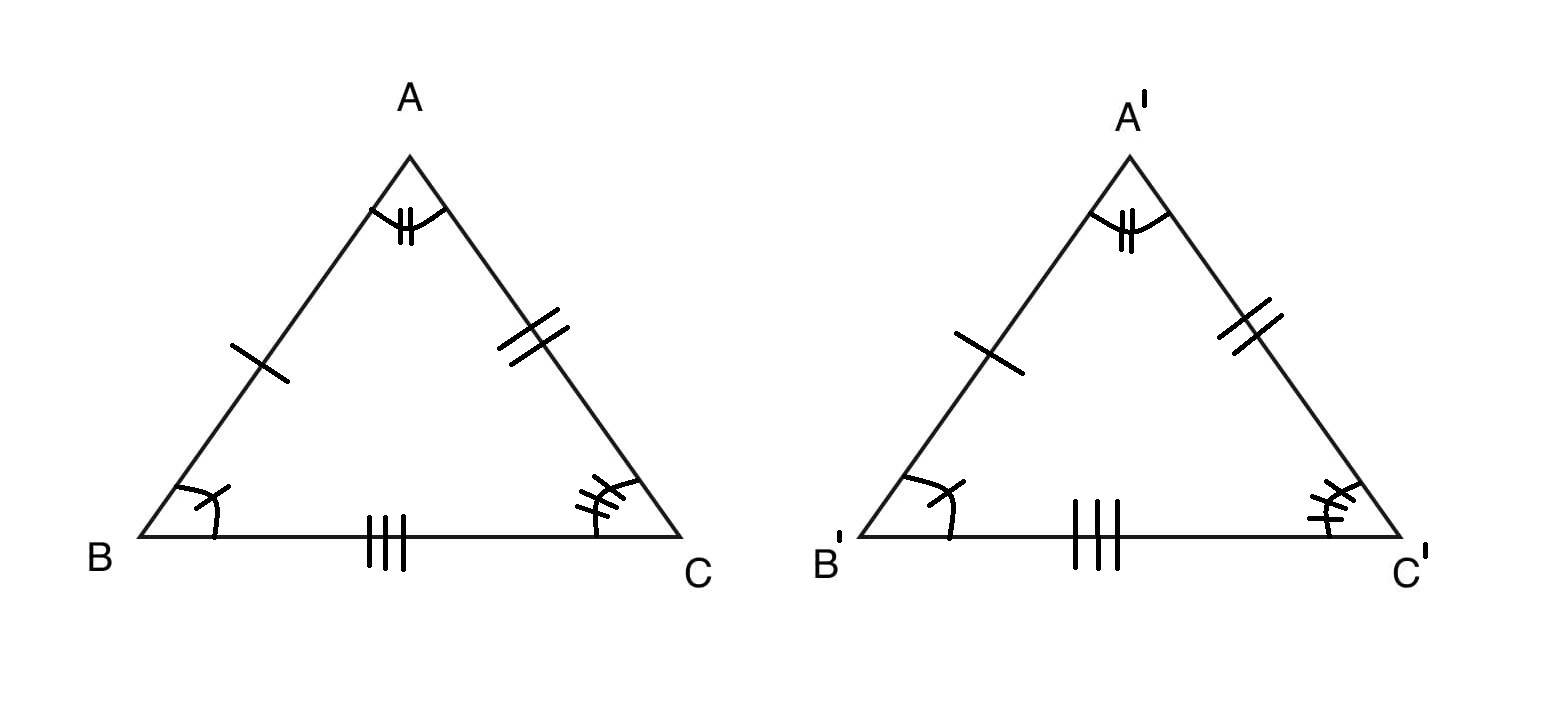
三角形的同余性可以由以下定理证明:
- Side-Side-Side (SSS) Congruency 标准:如果一个三角形的所有边都等于另一个三角形的边,那么根据Side-Side-Side (SSS) 的属性,三角形被称为是全等的。
在上面的三角形 ABC 和 A’B’C’ 中,如果 AB=A’B’ 和 BC=B’C’ 并且 CA=C’A’ 那么三角形是全等的。 - Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Congruent 标准:如果两个三角形的两条边相等并且它们之间的夹角在两个三角形中相同,那么根据Side-Angle-Side (SAS) 的属性,三角形被称为全等.在上面的三角形 ABC 和 A’B’C’ 中,如果 AB=A’B’ 和 BC=B’C’ 并且
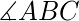 =
= 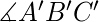 三角形是全等的。
三角形是全等的。 - Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) Congruent 标准:如果两个三角形的两个角相等并且它们之间的边长在两个三角形中相同,那么根据Angle-Side-Angle ( ASA). 在上面的三角形 ABC 和 A’B’C’ 中,如果,
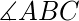 =
= 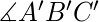 和
和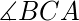 =
= 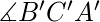 并且 BC=B’C’ 那么,三角形是全等的。
并且 BC=B’C’ 那么,三角形是全等的。 - Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) Congruent 标准:如果两个三角形的两个角相等,并且两个三角形的另一边的长度相同,那么根据Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) 的性质,我们称这两个三角形是全等的)。在上面的三角形 ABC 和 A’B’C’ 中,如果,
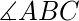 =
= 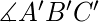 和
和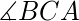 =
= 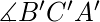 并且 CA=C’A’ 那么,三角形是全等的。
并且 CA=C’A’ 那么,三角形是全等的。 - 斜边腿 (HL) 一致标准:
如果这两个三角形的斜边相等并且任何其他一个边的长度是在两个三角形相同,则三角形被说成是由斜边-腿(HL)的特性一致。
下面是上述定理的实现。
# Python program to check
# similarity between two triangles.
# Function for SAS congruency
def cong_sas(s1, s2, a1, a2):
s1 = [float(i) for i in s1]
s2 = [float(i) for i in s2]
a1 = [float(i) for i in a1]
a2 = [float(i) for i in a2]
s1.sort()
s2.sort()
a1.sort()
a2.sort()
# Check for SAS
# angle b / w two smallest sides is largest.
if s1[0] == s2[0] and s1[1] == s2[1]:
# since we take angle b / w the sides.
if a1[2] == a2[2]:
return 1
if s1[1] == s2[1] and s1[2] == s2[2]:
if a1[0] == a2[0]:
return 1
if s1[2] == s2[2] and s1[0] == s2[0]:
if a1[1] == a2[1]:
return 1
return 0
# Function for ASA congruency
def cong_asa(s1, s2, a1, a2):
s1 = [float(i) for i in s1]
s2 = [float(i) for i in s2]
a1 = [float(i) for i in a1]
a2 = [float(i) for i in a2]
s1.sort()
s2.sort()
a1.sort()
a2.sort()
# Check for ASA
# side b / w two smallest angle is largest.
if a1[0] == a2[0] and a1[1] == a2[1]:
# since we take side b / w the angle.
if s1[2] == s2[2]:
return 1
if a1[1] == a2[1] and a1[2] == a2[2]:
if s1[0] == s2[0]:
return 1
if a1[2] == a2[2] and a1[0] == a2[0]:
if s1[1] == s2[1]:
return 1
return 0
# Function for AAS congruency
def cong_aas(s1, s2, a1, a2):
s1 = [float(i) for i in s1]
s2 = [float(i) for i in s2]
a1 = [float(i) for i in a1]
a2 = [float(i) for i in a2]
s1.sort()
s2.sort()
a1.sort()
a2.sort()
# Check for AAS
# side other two smallest angle is smallest or 2nd smallest.
if a1[0] == a2[0] and a1[1] == a2[1]:
# since we take side other than angles.
if s1[0] == s2[0] or s1[1] == s2[1]:
return 1
if a1[1] == a2[1] and a1[2] == a2[2]:
if s1[1] == s2[1] or s1[2] == s2[2]:
return 1
if a1[2] == a2[2] and a1[0] == a2[0]:
if s1[0] == s2[0] or s1[2] == s2[2]:
return 1
return 0
# Function for HL congruency
def cong_hl(s1, s2):
s1 = [float(i) for i in s1]
s2 = [float(i) for i in s2]
s1.sort()
s2.sort()
# Check for HL
if s1[2] == s2[2]:
if s1[1] == s2[1] or s1[0] == s2[0]:
return 1
return 0
# Function for SSS congruency
def cong_sss(s1, s2):
s1 = [float(i) for i in s1]
s2 = [float(i) for i in s2]
s1.sort()
s2.sort()
# Check for SSS
if(s1[0] == s2[0] and s1[1] == s2[1] and s1[2] == s2[2]):
return 1
return 0
# Driver Code
s1 = [3, 4, 5]
s2 = [4, 3, 5]
a1 = [90, 60, 30]
a2 = [60, 30, 90]
# function call for SSS congruency
sss = cong_sss(s1, s2)
# function call for SAS congruency
sas = cong_sas(s1, s2, a1, a2)
# function call for ASA congruency
asa = cong_asa(s1, s2, a1, a2)
# function call for AAS congruency
aas = cong_aas(s1, s2, a1, a2)
# function call for HL congruency
hl = cong_hl(s1, s2, )
# Check if triangles are congruent or not
if sss or sas or asa or aas or hl :
print "Triangles are congruent by",
if sss: print "SSS",
if sas: print "SAS",
if asa: print "ASA",
if aas: print "AAS",
if hl: print "HL",
else: print "Triangles are not congruent"
输出:
Triangles are congruent by SSS SAS ASA AAS HL