给定一个具有N 个节点和E 个边以及一个值K的无向图,任务是打印形成K大小团的所有节点集。
团是图的完全子图。
例子:
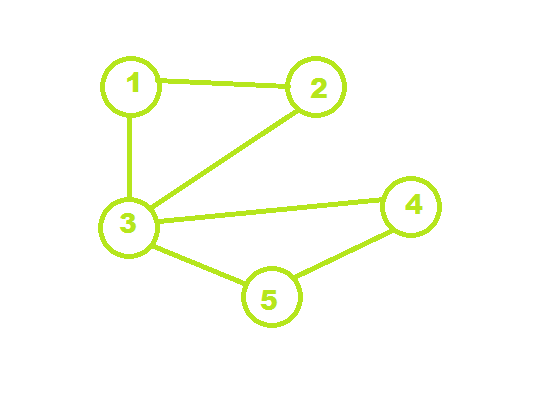
Input: N = 5, edges[] = { {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 1}, {4, 3}, {4, 5}, {5, 3} }, K = 3
Output: 1 2 3, 3 4 5
Explanation: Clearly from the image, 1->2->3 and 3->4->5 are the two complete subgraphs.
Input: N = 4, edges[] = { {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 1}, {4, 3} }, k = 3
Output: 1 2 3
Explanation: Subgraph 1-> 2->3 forms a complete subgraph from the given graph.
方法:思路是用递归来解决上述问题。找到所有度数大于或等于(K-1)的顶点,并检查 K 个顶点的哪个子集形成一个团。当另一个边被添加到当前列表时,检查通过添加该边,列表是否仍然形成一个集团。
可以按照以下步骤计算结果:
- 用三个参数起始节点、当前节点集的长度和期望的节点长度形成一个递归函数。
- 起始索引类似于没有节点可以添加到当前集合小于该索引。所以循环从该索引运行到 n。
- 如果发现在当前集合中加入一个节点后,该节点集合仍然是一个团。如果是,则添加该节点,并使用新添加节点的索引 +1、当前集合的长度 +1 和所需长度的参数调用递归函数。
- 如果达到所需长度,则打印节点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100;
// Stores the vertices
int store[MAX], n;
// Graph
int graph[MAX][MAX];
// Degree of the vertices
int d[MAX];
// Function to check if the given set of vertices
// in store array is a clique or not
bool is_clique(int b)
{
// Run a loop for all the set of edges
// for the select vertex
for (int i = 1; i < b; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < b; j++)
// If any edge is missing
if (graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to print the clique
void print(int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
cout << store[i] << " ";
cout << ", ";
}
// Function to find all the cliques of size s
void findCliques(int i, int l, int s)
{
// Check if any vertices from i+1 can be inserted
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n - (s - l); j++)
// If the degree of the graph is sufficient
if (d[j] >= s - 1) {
// Add the vertex to store
store[l] = j;
// If the graph is not a clique of size k
// then it cannot be a clique
// by adding another edge
if (is_clique(l + 1))
// If the length of the clique is
// still less than the desired size
if (l < s)
// Recursion to add vertices
findCliques(j, l + 1, s);
// Size is met
else
print(l + 1);
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int edges[][2] = { { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 3, 1 },
{ 4, 3 },
{ 4, 5 },
{ 5, 3 } },
k = 3;
int size = sizeof(edges) / sizeof(edges[0]);
n = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
graph[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i][1]][edges[i][0]] = 1;
d[edges[i][0]]++;
d[edges[i][1]]++;
}
findCliques(0, 1, k);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 100;
// Stores the vertices
static int []store = new int[MAX];
static int n;
// Graph
static int [][]graph = new int [MAX][MAX];
// Degree of the vertices
static int []d = new int[MAX];
// Function to check if the given set of vertices
// in store array is a clique or not
static boolean is_clique(int b)
{
// Run a loop for all the set of edges
// for the select vertex
for (int i = 1; i < b; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < b; j++)
// If any edge is missing
if (graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to print the clique
static void print(int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(store[i] + " ");
System.out.print(", ");
}
// Function to find all the cliques of size s
static void findCliques(int i, int l, int s)
{
// Check if any vertices from i+1 can be inserted
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n - (s - l); j++)
// If the degree of the graph is sufficient
if (d[j] >= s - 1)
{
// Add the vertex to store
store[l] = j;
// If the graph is not a clique of size k
// then it cannot be a clique
// by adding another edge
if (is_clique(l + 1))
// If the length of the clique is
// still less than the desired size
if (l < s)
// Recursion to add vertices
findCliques(j, l + 1, s);
// Size is met
else
print(l + 1);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int edges[][] = { { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 3, 1 },
{ 4, 3 },
{ 4, 5 },
{ 5, 3 } },
k = 3;
int size = edges.length;
n = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
graph[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i][1]][edges[i][0]] = 1;
d[edges[i][0]]++;
d[edges[i][1]]++;
}
findCliques(0, 1, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
import numpy as np
MAX = 100;
# Stores the vertices
store = [0]* MAX;
# Graph
graph = np.zeros((MAX, MAX));
# Degree of the vertices
d = [0] * MAX;
# Function to check if the given set of vertices
# in store array is a clique or not
def is_clique(b) :
# Run a loop for all the set of edges
# for the select vertex
for i in range(1, b) :
for j in range(i + 1, b) :
# If any edge is missing
if (graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0) :
return False;
return True;
# Function to print the clique
def print_cli(n) :
for i in range(1, n) :
print(store[i], end = " ");
print(",", end=" ");
# Function to find all the cliques of size s
def findCliques(i, l, s) :
# Check if any vertices from i+1 can be inserted
for j in range( i + 1, n -(s - l) + 1) :
# If the degree of the graph is sufficient
if (d[j] >= s - 1) :
# Add the vertex to store
store[l] = j;
# If the graph is not a clique of size k
# then it cannot be a clique
# by adding another edge
if (is_clique(l + 1)) :
# If the length of the clique is
# still less than the desired size
if (l < s) :
# Recursion to add vertices
findCliques(j, l + 1, s);
# Size is met
else :
print_cli(l + 1);
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
edges = [ [ 1, 2 ],
[ 2, 3 ],
[ 3, 1 ],
[ 4, 3 ],
[ 4, 5 ],
[ 5, 3 ] ];
k = 3;
size = len(edges);
n = 5;
for i in range(size) :
graph[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i][1]][edges[i][0]] = 1;
d[edges[i][0]] += 1;
d[edges[i][1]] += 1;
findCliques(0, 1, k);
# This code is contributed by AnkitRai01C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 100;
// Stores the vertices
static int []store = new int[MAX];
static int n;
// Graph
static int [,]graph = new int [MAX, MAX];
// Degree of the vertices
static int []d = new int[MAX];
// Function to check if the given set of vertices
// in store array is a clique or not
static bool is_clique(int b)
{
// Run a loop for all the set of edges
// for the select vertex
for (int i = 1; i < b; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < b; j++)
// If any edge is missing
if (graph[store[i], store[j]] == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to print the clique
static void print(int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(store[i] + " ");
Console.Write(", ");
}
// Function to find all the cliques of size s
static void findCliques(int i, int l, int s)
{
// Check if any vertices from i+1 can be inserted
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n - (s - l); j++)
// If the degree of the graph is sufficient
if (d[j] >= s - 1)
{
// Add the vertex to store
store[l] = j;
// If the graph is not a clique of size k
// then it cannot be a clique
// by adding another edge
if (is_clique(l + 1))
// If the length of the clique is
// still less than the desired size
if (l < s)
// Recursion to add vertices
findCliques(j, l + 1, s);
// Size is met
else
print(l + 1);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int [,]edges = { { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 3, 1 },
{ 4, 3 },
{ 4, 5 },
{ 5, 3 } };
int k = 3;
int size = edges.GetLength(0);
n = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
graph[edges[i, 0], edges[i, 1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i, 1], edges[i, 0]] = 1;
d[edges[i, 0]]++;
d[edges[i, 1]]++;
}
findCliques(0, 1, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01输出:
1 2 3 , 3 4 5 ,
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。