给定具有N 个节点的树。两个玩家A和B分别从节点1和节点N开始。 A可以访问与A已经访问过的节点相邻的所有节点,但不能访问B已经访问过的任何节点,对于B也是如此。
访问更多城市的玩家获胜。如果他们都发挥最佳,找到获胜的玩家。
例子:
Input: 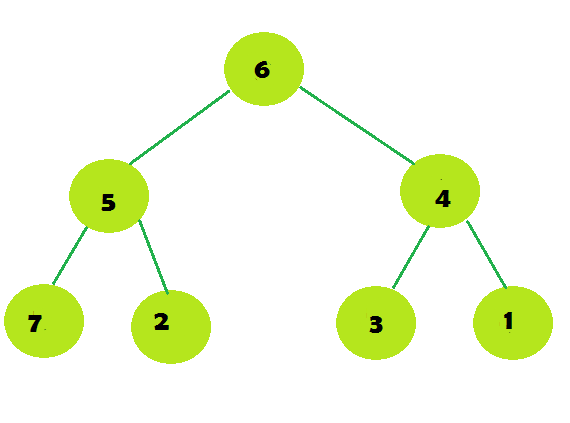
Output: A wins方法:最优的解决方案是两个播放器都开始访问位于连接节点1和节点N的路径上的节点。这是因为一个玩家不能访问另一个玩家已经访问过的节点,所以每个玩家都会尝试限制另一个玩家可以访问的节点数量。然后很容易计算每个玩家可以访问的节点数量并找出获胜者。
DFS 将用于找出两个节点之间的路径并将它们一一标记,如 1 或 2,A 为 1,B 为 2,然后用相应的值标记所有相邻的未访问节点,然后计算节点数A 和 B。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Vector to store Tree
vector > graph;
// To check if there
// is path or not
int found = 0, n;
// Path and temporary vector
vector path, temp;
// Count of A and B
int c_A = 0, c_B = 0;
// Function to find the path connecting 1 to n
void find(int i, int prev)
{
// Push the ith node
temp.push_back(i);
// If we reached our destination
if (i == n) {
path = (temp);
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < graph[i].size(); j++)
if (graph[i][j] != prev) {
// Dfs for its children
find(graph[i][j], i);
}
// Remove the node
temp.pop_back();
}
// Function to mark all the adjacent
// unvisited nodes
void mark(int i, int visited[], int c)
{
if (!visited[i]) {
// Increase the count
if (c == 1)
c_A++;
else
c_B++;
}
visited[i] = c;
// Increase the count
if (c == 1)
c_A++;
else
c_B++;
// Dfs for all its unvisited adjacent nodes
for (int j = 0; j < graph[i].size(); j++)
if (!visited[graph[i][j]])
mark(graph[i][j], visited, c);
}
// Function to find the winner among the players
void findWinner()
{
// Finds the path
find(1, -1);
int visited[n + 1] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) {
// Mark nodes visited by
// A as 1 and B as 2
if (i < ceil(path.size() / 2.0))
visited[path[i]] = 1, c_A++;
else
visited[path[i]] = 2, c_B++;
}
// Mark all the adjacent unvisited nodes
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++)
mark(path[i],
visited,
visited[path[i]]);
if (c_A > c_B)
cout << "A wins";
else if (c_A < c_B)
cout << "B wins";
else
cout << "Draw";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
n = 7;
graph.clear();
graph.resize(n + 1);
// Graph
graph[6].push_back(4);
graph[4].push_back(6);
graph[6].push_back(5);
graph[5].push_back(6);
graph[5].push_back(7);
graph[7].push_back(5);
graph[5].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(5);
graph[3].push_back(4);
graph[4].push_back(3);
graph[1].push_back(4);
graph[4].push_back(1);
findWinner();
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the
// above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Vector to store Tree
static Vector []graph;
// To check if there
// is path or not
static int found = 0, n;
// Path and temporary vector
static Vector path =
new Vector<>();
static Vector temp =
new Vector<>();
// Count of A and B
static int c_A = 0, c_B = 0;
// Function to find the path
// connecting 1 to n
static void find(int i,
int prev)
{
// Push the ith node
temp.add(i);
// If we reached our
// destination
if (i == n)
{
path = (temp);
return;
}
for (int j = 0;
j < graph[i].size(); j++)
if (graph[i].get(j) != prev)
{
// Dfs for its children
find(graph[i].get(j), i);
}
// Remove the node
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
// Function to mark all the
// adjacent unvisited nodes
static void mark(int i,
int visited[],
int c)
{
if (visited[i] > 0)
{
// Increase the count
if (c == 1)
c_A++;
else
c_B++;
}
visited[i] = c;
// Increase the count
if (c == 1)
c_A++;
else
c_B++;
// Dfs for all its unvisited
// adjacent nodes
for (int j = 0;
j < graph[i].size(); j++)
if (visited[graph[i].get(j)] > 0)
mark(graph[i].get(j),
visited, c);
}
// Function to find the winner
// among the players
static void findWinner()
{
// Finds the path
find(1, -1);
int visited[] = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0;
i < path.size(); i++)
{
// Mark nodes visited by
// A as 1 and B as 2
if (i < Math.ceil(path.size() / 2.0))
{
visited[path.get(i)] = 1;
c_A++;
}
else
{
visited[path.get(i)] = 2;
c_B++;
}
}
// Mark all the adjacent
// unvisited nodes
for (int i = 0;
i < path.size(); i++)
mark(path.get(i),
visited,
visited[path.get(i)]);
if (c_A > c_B)
System.out.print("A wins");
else if (c_A < c_B)
System.out.print("B wins");
else
System.out.print("Draw");
}
// Driver code
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(String[] args)
{
n = 7;
graph = new Vector[n + 1];
for (int i = 0;
i < graph.length; i++)
graph[i] = new Vector();
// Graph
graph[6].add(4);
graph[4].add(6);
graph[6].add(5);
graph[5].add(6);
graph[5].add(7);
graph[7].add(5);
graph[5].add(2);
graph[2].add(5);
graph[3].add(4);
graph[4].add(3);
graph[1].add(4);
graph[4].add(1);
findWinner();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar Python3
# Python3 implementation of the above approach
from math import ceil, floor
# Vector to store Tree
graph = [[] for i in range(1000)]
# To check if there
# is path or not
found = 0
n = 0
# Path and temporary vector
path = []
temp = []
# Count of A and B
c_A = 0
c_B = 0
# Function to find the path connecting 1 to n
def find(i, prev):
global c_A, c_B, path
# Push the ith node
temp.append(i)
# If we reached our destination
if (i == n):
path = temp
return
for j in graph[i]:
if j != prev:
# Dfs for its children
find(j, i)
# Remove the node
del temp[-1]
# Function to mark all the adjacent
# unvisited nodes
def mark(i, visited, c):
global c_B, c_A
if visited[i] == 0:
# Increase the count
if (c == 1):
c_A += 1
else:
c_B += 1
visited[i] = c
# Increase the count
if (c == 1):
c_A += 1
else:
c_B += 1
# Dfs for all its unvisited adjacent nodes
for j in graph[i]:
if (visited[j] == 0):
mark(j, visited, c)
# Function to find the winner among the players
def findWinner():
global c_B, c_A, path
# Finds the path
find(1, -1)
visited = [0 for i in range(n + 1)]
for i in range(len(path)):
# Mark nodes visited by
# A as 1 and B as 2
if (i < ceil(len(path) / 2.0)):
visited[path[i]] = 1
c_A += 1
else:
visited[path[i]] = 2
c_B += 1
# Mark all the adjacent unvisited nodes
for i in path:
mark(i, visited, visited[i])
if (c_A > c_B):
print("A wins")
elif (c_A < c_B):
print("B wins")
else:
print("Draw")
# Driver code
n = 7
# Graph
graph[6].append(4)
graph[4].append(6)
graph[6].append(5)
graph[5].append(6)
graph[5].append(7)
graph[7].append(5)
graph[5].append(2)
graph[2].append(5)
graph[3].append(4)
graph[4].append(3)
graph[1].append(4)
graph[4].append(1)
findWinner()
# This code is contributed by Mohit KumarC#
// C# implementation of the
// above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// List to store Tree
static List []graph;
// To check if there
// is path or not
static int found = 0, n;
// Path and temporary vector
static List path =
new List();
static List temp =
new List();
// Count of A and B
static int c_A = 0, c_B = 0;
// Function to find the path
// connecting 1 to n
static void find(int i,
int prev)
{
// Push the ith node
temp.Add(i);
// If we reached our
// destination
if (i == n)
{
path = (temp);
return;
}
for (int j = 0;
j < graph[i].Count; j++)
if (graph[i][j] != prev)
{
// Dfs for its children
find(graph[i][j], i);
}
// Remove the node
temp.Remove(temp.Count - 1);
}
// Function to mark all the
// adjacent unvisited nodes
static void mark(int i,
int []visited,
int c)
{
if (visited[i] > 0)
{
// Increase the count
if (c == 1)
c_A++;
else
c_B++;
}
visited[i] = c;
// Increase the count
if (c == 1)
c_A++;
else
c_B++;
// Dfs for all its unvisited
// adjacent nodes
for (int j = 0;
j < graph[i].Count; j++)
if (visited[graph[i][j]] > 0)
mark(graph[i][j],
visited, c);
}
// Function to find the winner
// among the players
static void findWinner()
{
// Finds the path
find(1, -1);
int []visited = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0;
i < path.Count; i++)
{
// Mark nodes visited by
// A as 1 and B as 2
if (i < Math.Ceiling(path.Count / 2.0))
{
visited[path[i]] = 1;
c_A++;
}
else
{
visited[path[i]] = 2;
c_B++;
}
}
// Mark all the adjacent
// unvisited nodes
for (int i = 0;
i < path.Count; i++)
mark(path[i],
visited,
visited[path[i]]);
if (c_A > c_B)
Console.Write("A wins");
else if (c_A < c_B)
Console.Write("B wins");
else
Console.Write("Draw");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
n = 7;
graph = new List[n + 1];
for (int i = 0;
i < graph.Length; i++)
graph[i] = new List();
// Graph
graph[6].Add(4);
graph[4].Add(6);
graph[6].Add(5);
graph[5].Add(6);
graph[5].Add(7);
graph[7].Add(5);
graph[5].Add(2);
graph[2].Add(5);
graph[3].Add(4);
graph[4].Add(3);
graph[1].Add(4);
graph[4].Add(1);
findWinner();
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput Javascript
输出:
A wins