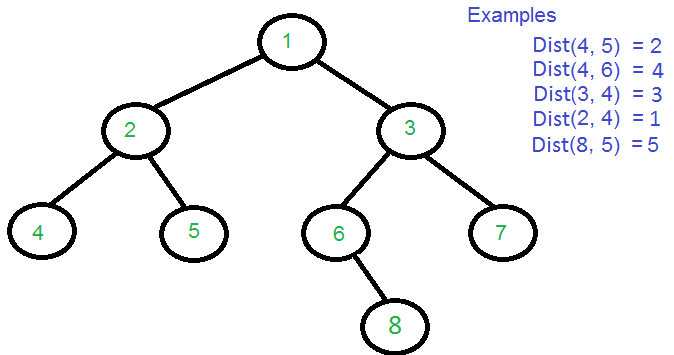
给定一棵二叉树,任务是找到二叉树中两个键之间的距离,没有给出父指针。两个节点之间的距离是从另一个节点到达一个节点所要遍历的最小边数。
我们已经讨论了一种使用段树将查询时间减少到 O(logn) 的方法,这里的任务是通过将空间复杂度降低到 O(nlogn) 来将查询时间减少到 O(1)。在这篇文章中,我们将使用稀疏表而不是段树来查找给定范围内的最小值,它使用动态规划和位操作来实现 O(1) 查询时间。
稀疏表将预处理 Nlogn 空间中 L 数组的给定范围的最小值,即每个节点将包含 log(i) 长度的值链,其中 i 是 L 数组中第 i 个节点的索引。稀疏表中的每个条目表示 M[i][j] 将表示子数组中最小值的索引,从 i 开始,长度为 2^j。
可以根据最低共同祖先获得两个节点之间的距离。
Dist(n1, n2) = Level[n1] + Level[n2] - 2*Level[lca] 这个问题可以分解为:
- 查找每个节点的级别
- 寻找二叉树的欧拉之旅
- 为 LCA 构建稀疏表。
这些步骤解释如下:
- Find the levels of each node by applying level order traversal.
- Find the LCA of two nodes in binary tree in O(logn) by Storing Euler tour of Binary tree in array and computing two other arrays with the help of levels of each node and Euler tour.
These steps are shown below:
(I) First, find Euler Tour of binary tree.
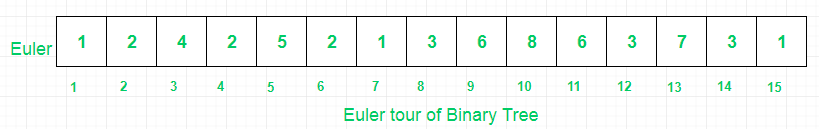
- (II) Then, store levels of each node in Euler array.
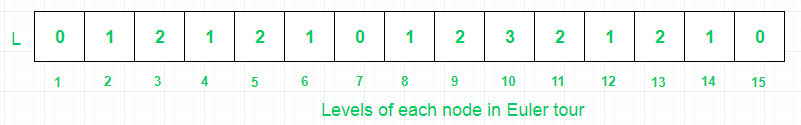
- (III) Then, store First occurrences of all nodes of binary tree in Euler array. H stores the indices of nodes from Euler array, so that range of query for finding minimum can be minimized and their by further optimizing the query time.
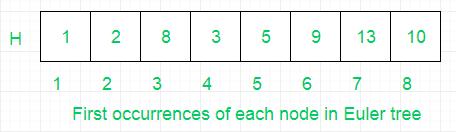
- Then build sparse table on L array and find the minimum value say X in range (H[A] to H[B]). Then, we use the index of value X as an index to Euler array to get LCA, i.e. Euler[index(X)].
Let, A=8 and B=5.
(I) H[8]= 1 and H[5]=2
(II) we get min value in L array between 1 and 2 as X=0, index=7
(III) Then, LCA= Euler[7], i.e LCA=1. - Finally, apply distance formula discussed above to get the distance between two nodes.
C++
#include
#define MAX 100001
using namespace std;
/* A tree node structure */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
/* Utility function to create a new Binary Tree node */
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* temp = new struct Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Array to store level of each node
int level[MAX];
// Utility Function to store level of all nodes
void FindLevels(struct Node* root)
{
if (!root)
return;
// queue to hold tree node with level
queue > q;
// let root node be at level 0
q.push({ root, 0 });
pair p;
// Do level Order Traversal of tree
while (!q.empty()) {
p = q.front();
q.pop();
// Node p.first is on level p.second
level[p.first->data] = p.second;
// If left child exits, put it in queue
// with current_level +1
if (p.first->left)
q.push({ p.first->left, p.second + 1 });
// If right child exists, put it in queue
// with current_level +1
if (p.first->right)
q.push({ p.first->right, p.second + 1 });
}
}
// Stores Euler Tour
int Euler[MAX];
// index in Euler array
int idx = 0;
// Find Euler Tour
void eulerTree(struct Node* root)
{
// store current node's data
Euler[++idx] = root->data;
// If left node exists
if (root->left) {
// traverse left subtree
eulerTree(root->left);
// store parent node's data
Euler[++idx] = root->data;
}
// If right node exists
if (root->right) {
// traverse right subtree
eulerTree(root->right);
// store parent node's data
Euler[++idx] = root->data;
}
}
// checks for visited nodes
int vis[MAX];
// Stores level of Euler Tour
int L[MAX];
// Stores indices of the first occurrence
// of nodes in Euler tour
int H[MAX];
// Preprocessing Euler Tour for finding LCA
void preprocessEuler(int size)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
L[i] = level[Euler[i]];
// If node is not visited before
if (vis[Euler[i]] == 0) {
// Add to first occurrence
H[Euler[i]] = i;
// Mark it visited
vis[Euler[i]] = 1;
}
}
}
// Sparse table of size [MAX][LOGMAX]
// M[i][j] is the index of the minimum value in
// the sub array starting at i having length 2^j
int M[MAX][18];
// Utility function to preprocess Sparse table
void preprocessLCA(int N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
M[i][0] = i;
for (int j = 1; 1 << j <= N; j++)
for (int i = 0; i + (1 << j) - 1 < N; i++)
if (L[M[i][j - 1]] < L[M[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]])
M[i][j] = M[i][j - 1];
else
M[i][j] = M[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1];
}
// Utility function to find the index of the minimum
// value in range a to b
int LCA(int a, int b)
{
// Subarray of length 2^j
int j = log2(b - a + 1);
if (L[M[a][j]] <= L[M[b - (1 << j) + 1][j]])
return M[a][j];
else
return M[b - (1 << j) + 1][j];
}
// Function to return distance between
// two nodes n1 and n2
int findDistance(int n1, int n2)
{
// Maintain original Values
int prevn1 = n1, prevn2 = n2;
// Get First Occurrence of n1
n1 = H[n1];
// Get First Occurrence of n2
n2 = H[n2];
// Swap if low>high
if (n2 < n1)
swap(n1, n2);
// Get position of minimum value
int lca = LCA(n1, n2);
// Extract value out of Euler tour
lca = Euler[lca];
// return calculated distance
return level[prevn1] + level[prevn2] - 2 * level[lca];
}
void preProcessing(Node* root, int N)
{
// Build Tree
eulerTree(root);
// Store Levels
FindLevels(root);
// Find L and H array
preprocessEuler(2 * N - 1);
// Build sparse table
preprocessLCA(2 * N - 1);
}
/* Driver function to test above functions */
int main()
{
// Number of nodes
int N = 8;
/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->right = newNode(8);
// Function to do all preprocessing
preProcessing(root, N);
cout << "Dist(4, 5) = " << findDistance(4, 5) << "\n";
cout << "Dist(4, 6) = " << findDistance(4, 6) << "\n";
cout << "Dist(3, 4) = " << findDistance(3, 4) << "\n";
cout << "Dist(2, 4) = " << findDistance(2, 4) << "\n";
cout << "Dist(8, 5) = " << findDistance(8, 5) << "\n";
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static class Pair {
T first;
V second;
Pair() {
}
Pair(T first, V second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
static int MAX = 100001;
// Array to store level of each node
static int[] level = new int[MAX];
// Utility Function to store level of all nodes
static void FindLevels(Node root) {
if (root == null)
return;
// queue to hold tree node with level
Queue> q = new LinkedList<>();
// let root node be at level 0
q.add(new Pair<>(root, 0));
Pair p = new Pair<>();
// Do level Order Traversal of tree
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
p = q.poll();
// Node p.first is on level p.second
level[p.first.data] = p.second;
// If left child exits, put it in queue
// with current_level +1
if (p.first.left != null)
q.add(new Pair<>(p.first.left, p.second + 1));
// If right child exists, put it in queue
// with current_level +1
if (p.first.right != null)
q.add(new Pair<>(p.first.right, p.second + 1));
}
}
// Stores Euler Tour
static int[] Euler = new int[MAX];
// index in Euler array
static int idx = 0;
// Find Euler Tour
static void eulerTree(Node root) {
// store current node's data
Euler[++idx] = root.data;
// If left node exists
if (root.left != null) {
// traverse left subtree
eulerTree(root.left);
// store parent node's data
Euler[++idx] = root.data;
}
// If right node exists
if (root.right != null) {
// traverse right subtree
eulerTree(root.right);
// store parent node's data
Euler[++idx] = root.data;
}
}
// checks for visited nodes
static int[] vis = new int[MAX];
// Stores level of Euler Tour
static int[] L = new int[MAX];
// Stores indices of the first occurrence
// of nodes in Euler tour
static int[] H = new int[MAX];
// Preprocessing Euler Tour for finding LCA
static void preprocessEuler(int size) {
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
L[i] = level[Euler[i]];
// If node is not visited before
if (vis[Euler[i]] == 0) {
// Add to first occurrence
H[Euler[i]] = i;
// Mark it visited
vis[Euler[i]] = 1;
}
}
}
// Sparse table of size [MAX][LOGMAX]
// M[i][j] is the index of the minimum value in
// the sub array starting at i having length 2^j
static int[][] M = new int[MAX][18];
// Utility function to preprocess Sparse table
static void preprocessLCA(int N) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
M[i][0] = i;
for (int j = 1; 1 << j <= N; j++)
for (int i = 0; i + (1 << j) - 1 < N; i++)
if (L[M[i][j - 1]] < L[M[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]])
M[i][j] = M[i][j - 1];
else
M[i][j] = M[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1];
}
// Utility function to find the index of the minimum
// value in range a to b
static int LCA(int a, int b) {
// Subarray of length 2^j
int j = (int) (Math.log(b - a + 1) / Math.log(2));
if (L[M[a][j]] <= L[M[b - (1 << j) + 1][j]])
return M[a][j];
else
return M[b - (1 << j) + 1][j];
}
// Function to return distance between
// two nodes n1 and n2
static int findDistance(int n1, int n2) {
// Maintain original Values
int prevn1 = n1, prevn2 = n2;
// Get First Occurrence of n1
n1 = H[n1];
// Get First Occurrence of n2
n2 = H[n2];
// Swap if low>high
if (n2 < n1) {
int temp = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = temp;
}
// Get position of minimum value
int lca = LCA(n1, n2);
// Extract value out of Euler tour
lca = Euler[lca];
// return calculated distance
return level[prevn1] + level[prevn2] - 2 * level[lca];
}
static void preProcessing(Node root, int N) {
// Build Tree
eulerTree(root);
// Store Levels
FindLevels(root);
// Find L and H array
preprocessEuler(2 * N - 1);
// Build sparse table
preprocessLCA(2 * N - 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Number of nodes
int N = 8;
/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
// Function to do all preprocessing
preProcessing(root, N);
System.out.println("Dist(4, 5) = " + findDistance(4, 5));
System.out.println("Dist(4, 6) = " + findDistance(4, 6));
System.out.println("Dist(3, 4) = " + findDistance(3, 4));
System.out.println("Dist(2, 4) = " + findDistance(2, 4));
System.out.println("Dist(8, 5) = " + findDistance(8, 5));
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Python3
from collections import deque
from math import log2
MAX = 100001
# A tree node structure
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Array to store level of each node
level = [0] * MAX
# Utility Function to store level of all nodes
def findLevels(root: Node):
global level
if root is None:
return
# queue to hold tree node with level
q = deque()
# let root node be at level 0
q.append((root, 0))
# Do level Order Traversal of tree
while q:
p = q[0]
q.popleft()
# Node p.first is on level p.second
level[p[0].data] = p[1]
# If left child exits, put it in queue
# with current_level +1
if p[0].left:
q.append((p[0].left, p[1] + 1))
# If right child exists, put it in queue
# with current_level +1
if p[0].right:
q.append((p[0].right, p[1] + 1))
# Stores Euler Tour
Euler = [0] * MAX
# index in Euler array
idx = 0
# Find Euler Tour
def eulerTree(root: Node):
global Euler, idx
idx += 1
# store current node's data
Euler[idx] = root.data
# If left node exists
if root.left:
# traverse left subtree
eulerTree(root.left)
idx += 1
# store parent node's data
Euler[idx] = root.data
# If right node exists
if root.right:
# traverse right subtree
eulerTree(root.right)
idx += 1
# store parent node's data
Euler[idx] = root.data
# checks for visited nodes
vis = [0] * MAX
# Stores level of Euler Tour
L = [0] * MAX
# Stores indices of the first occurrence
# of nodes in Euler tour
H = [0] * MAX
# Preprocessing Euler Tour for finding LCA
def preprocessEuler(size: int):
global L, H, vis
for i in range(1, size + 1):
L[i] = level[Euler[i]]
# If node is not visited before
if vis[Euler[i]] == 0:
# Add to first occurrence
H[Euler[i]] = i
# Mark it visited
vis[Euler[i]] = 1
# Sparse table of size [MAX][LOGMAX]
# M[i][j] is the index of the minimum value in
# the sub array starting at i having length 2^j
M = [[0 for i in range(18)] for j in range(MAX)]
# Utility function to preprocess Sparse table
def preprocessLCA(N: int):
global M
for i in range(N):
M[i][0] = i
j = 1
while 1 << j <= N:
i = 0
while i + (1 << j) - 1 < N:
if L[M[i][j - 1]] < L[M[i +
(1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]]:
M[i][j] = M[i][j - 1]
else:
M[i][j] = M[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]
i += 1
j += 1
# Utility function to find the index of the minimum
# value in range a to b
def LCA(a: int, b: int) -> int:
# Subarray of length 2^j
j = int(log2(b - a + 1))
if L[M[a][j]] <= L[M[b - (1 << j) + 1][j]]:
return M[a][j]
else:
return M[b - (1 << j) + 1][j]
# Function to return distance between
# two nodes n1 and n2
def findDistance(n1: int, n2: int) -> int:
# Maintain original Values
prevn1 = n1
prevn2 = n2
# Get First Occurrence of n1
n1 = H[n1]
# Get First Occurrence of n2
n2 = H[n2]
# Swap if low>high
if n2 < n1:
n1, n2 = n2, n1
# Get position of minimum value
lca = LCA(n1, n2)
# Extract value out of Euler tour
lca = Euler[lca]
# return calculated distance
return level[prevn1] + level[prevn2] - 2 * level[lca]
def preProcessing(root: Node, N: int):
# Build Tree
eulerTree(root)
# Store Levels
findLevels(root)
# Find L and H array
preprocessEuler(2 * N - 1)
# Build sparse table
preprocessLCA(2 * N - 1)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Number of nodes
N = 8
# Constructing tree given in the above figure
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
root.right.left.right = Node(8)
# Function to do all preprocessing
preProcessing(root, N)
print("Dist(4, 5) =", findDistance(4, 5))
print("Dist(4, 6) =", findDistance(4, 6))
print("Dist(3, 4) =", findDistance(3, 4))
print("Dist(2, 4) =", findDistance(2, 4))
print("Dist(8, 5) =", findDistance(8, 5))
# This code is contributed by
# sanjeev2552C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
public
class Pair
{
public
T first;
public
V second;
public
Pair() {
}
public
Pair(T first, V second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
public
class Node
{
public
int data;
public
Node left, right;
public
Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
static int MAX = 100001;
// Array to store level of each node
static int[] level = new int[MAX];
// Utility Function to store level of all nodes
static void FindLevels(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// queue to hold tree node with level
Queue> q = new Queue>();
// let root node be at level 0
q.Enqueue(new Pair(root, 0));
Pair p = new Pair();
// Do level Order Traversal of tree
while (q.Count != 0)
{
p = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
// Node p.first is on level p.second
level[p.first.data] = p.second;
// If left child exits, put it in queue
// with current_level +1
if (p.first.left != null)
q.Enqueue(new Pair(p.first.left, p.second + 1));
// If right child exists, put it in queue
// with current_level +1
if (p.first.right != null)
q.Enqueue(new Pair(p.first.right, p.second + 1));
}
}
// Stores Euler Tour
static int[] Euler = new int[MAX];
// index in Euler array
static int idx = 0;
// Find Euler Tour
static void eulerTree(Node root)
{
// store current node's data
Euler[++idx] = root.data;
// If left node exists
if (root.left != null)
{
// traverse left subtree
eulerTree(root.left);
// store parent node's data
Euler[++idx] = root.data;
}
// If right node exists
if (root.right != null)
{
// traverse right subtree
eulerTree(root.right);
// store parent node's data
Euler[++idx] = root.data;
}
}
// checks for visited nodes
static int[] vis = new int[MAX];
// Stores level of Euler Tour
static int[] L = new int[MAX];
// Stores indices of the first occurrence
// of nodes in Euler tour
static int[] H = new int[MAX];
// Preprocessing Euler Tour for finding LCA
static void preprocessEuler(int size) {
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
L[i] = level[Euler[i]];
// If node is not visited before
if (vis[Euler[i]] == 0)
{
// Add to first occurrence
H[Euler[i]] = i;
// Mark it visited
vis[Euler[i]] = 1;
}
}
}
// Sparse table of size [MAX,LOGMAX]
// M[i,j] is the index of the minimum value in
// the sub array starting at i having length 2^j
static int[,] M = new int[MAX, 18];
// Utility function to preprocess Sparse table
static void preprocessLCA(int N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
M[i, 0] = i;
for (int j = 1; 1 << j <= N; j++)
for (int i = 0; i + (1 << j) - 1 < N; i++)
if (L[M[i, j - 1]] < L[M[i + (1 << (j - 1)), j - 1]])
M[i, j] = M[i, j - 1];
else
M[i, j] = M[i + (1 << (j - 1)), j - 1];
}
// Utility function to find the index of the minimum
// value in range a to b
static int LCA(int a, int b)
{
// Subarray of length 2^j
int j = (int) (Math.Log(b - a + 1) / Math.Log(2));
if (L[M[a,j]] <= L[M[b - (1 << j) + 1,j]])
return M[a,j];
else
return M[b - (1 << j) + 1,j];
}
// Function to return distance between
// two nodes n1 and n2
static int findDistance(int n1, int n2) {
// Maintain original Values
int prevn1 = n1, prevn2 = n2;
// Get First Occurrence of n1
n1 = H[n1];
// Get First Occurrence of n2
n2 = H[n2];
// Swap if low>high
if (n2 < n1)
{
int temp = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = temp;
}
// Get position of minimum value
int lca = LCA(n1, n2);
// Extract value out of Euler tour
lca = Euler[lca];
// return calculated distance
return level[prevn1] + level[prevn2] - 2 * level[lca];
}
static void preProcessing(Node root, int N)
{
// Build Tree
eulerTree(root);
// Store Levels
FindLevels(root);
// Find L and H array
preprocessEuler(2 * N - 1);
// Build sparse table
preprocessLCA(2 * N - 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Number of nodes
int N = 8;
/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
// Function to do all preprocessing
preProcessing(root, N);
Console.WriteLine("Dist(4, 5) = " + findDistance(4, 5));
Console.WriteLine("Dist(4, 6) = " + findDistance(4, 6));
Console.WriteLine("Dist(3, 4) = " + findDistance(3, 4));
Console.WriteLine("Dist(2, 4) = " + findDistance(2, 4));
Console.WriteLine("Dist(8, 5) = " + findDistance(8, 5));
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995 Javascript
输出:
Dist(4, 5) = 2
Dist(4, 6) = 4
Dist(3, 4) = 3
Dist(2, 4) = 1
Dist(8, 5) = 5时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(N log N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。